Volume 45, Number 1, 2 & 3 (May 2013)
1. B. S. SOWMYALATHA*, C. RAMACHANDRA, N. SIVAKUMAR AND N. KRISHNAMURTHY [Studies on nutrient uptake of rice hybrids as influenced by methods of cultivation and fertility levels in Cauvery command area]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 1-5 (2013). Zonal Agricultural Research Station V. C. Farm, Mandya-571 405 (Karnataka), India *(e-mail : sowmyalatha.vinu@gmail.com) A field experiment was conducted during kharif and summer seasons of 2010-11 at ZARS, V. C. Farm, Mandya, Karnataka to study the effect of methods of cultivation and fertility levels on nutrient uptake of rice hybrids. The experiment involving methods of cultivation (SRI and conventional method of planting), rice hybrids (KRH-2, KRH-4 and Arize (6444) and fertility levels (100% RDF, 125% RDF and 150% RDF) was laid out in double split-plot design with three replications. The results revealed that SRI method of planting recorded significantly higher NPK uptake by grain (77.42, 21.77 and 61.46 kg/ha, respectively) with rice hybrid Arize (81.41, 25.46 and 61.84 kg/ha) at 150% RDF (76.91, 22.68 and 61.46 kg/ha, respectively). Significantly higher grain yield was obtained under SRI method of planting (7717 kg/ha) with rice hybrid Arize (7808 kg/ha) at 150% RDF (7821 kg/ha). 2. V. S. Meena*, B. R. Maurya, J. S. Bohra, R. Verma and M. D. Meena [Effect of concentrate manure and nutrient levels on enzymatic activities and microbial population under submerged rice in alluvium soil of Varanasi]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 6-12 (2013). Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221 005 (U. P.), India *(e-mail : vijayssac.bhu@gmail.com) A field experiment was conducted inkharif season of 2009 at Agricultural Research Farm, BHU, Varanasi. The aim of this study was to focus the effect of concentrated manure (wellgrow grain and wellgrow soil) and nutrient levels on microbial population of bacteria, fungi, actinomycetes and enzymatic activities in submerged rice soil of Varanasi. The experiment consisting nine treatments was laid out in randomised block design with three replications. Maximum dehydrogenase activity (188 µgTPF/g soil/day), urease (445 µg urea hydrolyzed/g soil/h) and phosphatase (114 µg PNP/g soil/h) at panicle initiation stage of rice were recorded with 100% RDF+200 kg wellgrow grain/ha. Enzymatic activities were positively and significantly correlated with content of organic carbon. Judicious use of 75% RDF along with 200 kg wellgrow/ha was the best combination in the applied treatments. 3. S. K. RAY and D. MUKHOPADHYAY [Effects of inorganic and organic inputs on yield of kharif rice (Oryza sativa) in West Bengal, India]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 13-19 (2013). Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry Uttar Banga Krishi Viswavidyalaya, Pundibari, Cooch Behar-736 165 (West Bengal), India A field experiment was carried out for two consecutive years (2006-08) during the kharif season to determine the effect of single or combined application of organic amendments (farm yard manure and green manure) and inorganic fertilizer (N-P-K-Zn) on yield, yield components, nutrient uptake and residual nutrient status of hybrid (var. NK-3325) and high-yielding (var. Swarna; HYV) rice varieties in North Bengal (26052¢11.20¢¢ N latitude and 88054¢36.7¢¢ E longitude). The combinedapplication of inorganic and organic inputs had a significant positive influence on yield components for both the HYV and hybrid rice as compared to the plants that received only inorganic fertilizer. The highest yield for both the rice varieties was obtained following application of 75% recommended N from NPK, 25% N from FYM and supplemental Zn. 4. KALYAN JANA* [Evaluation of aerobic rice system during boro season under red and laterite zone of West Bengal]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 20-23 (2013). Rice Research Station (Govt. of West Bengal), Bankura-722 101 (West Bengal), India *(e-mail : kjanarrs@gmail.com) To evaluate the feasibility of aerobic rice system during boro season, an observational field experiment was conducted at Rice Research Station, Bankura, West Bengal, India. Highest grain yield (4.15 and 4.36 t/ha) was recorded from Puspa (IET-17509) and satisfactory grain yield (2.98 and 3.23 t/ha) from Annada variety in aerobic rice system under unpuddled situation during boro season. Lowest grain yield (2.01 and 2.18 t/ha) was observed with Lalat. 10th February was the optimum time for direct sowing in aerobic situation for obtaining good crop stand with higher grain yield during boro season. It needs further study in depth. There is no need for raising nursery and dry direct sowing is done in non-puddled, non-flooded fields. It is the most promising approach for saving water and labour. This aerobic rice system will be sustainable rice production and productivity for the farmers under red and laterite zone of West Bengal and for the whole state in future. 5. A. V. Bulbule and P. N. Gajbhiye [Response of upland rice (Oryza sativa) to briquettes containing NPK]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 24-28 (2013). Zonal Agricultural Research Station, Shenda Park, Kolhapur-416 012 (Maharashtra), India Field experiments were conducted at Zonal Agricultural Research Station, Shenda Park, Farm Kolhapur on Entisol, Sub-Montane Zone of Maharashtra during the kharif seasons of 2007-08, 2008-09 and 2009-10 to study the response of kharif upland rice crop to fertilizer briquettes containing NPK. The response of conventional method of fertilizer application through fertilizers like urea, di-ammonium phosphate and muriate of potash was studied in comparison to application of the same fertilizers through briquettes at the different levels of NPK. The upland rice crop was sown in paired rows having alternate spacing of 15-25 cm and fertilized through briquettes placed in the 15 cm alternate bands of the paired rows to accommodate the different fertilizer levels. The recommended dose (RD) of fertilizers was applied at the rate of 100-50-50 (kg NPK/ha). The fertilizer treatments consisted of 100, 75 and 50% RD applied through conventional fertilizers to the crop and through briquettes. Nitrogen was applied in two splits for the conventional fertilizers, while phosphorus and potash were applied as basal. The briquettes containing the entire dose of fertilizers were applied as basal at the time of sowing. It was also compared to nitrogen application in two splits wherein half the dose of nitrogen was applied through briquettes along with P and K, while the rest half dose of nitrogen was applied after one month. Findings of study revealed that the basal application of fertilizers through briquettes significantly increased the grain yield of rice crop as compared to the conventional method of fertilizer application and nitrogen applied in splits. Application of fertilizer briquettes @ 100% RD to rice crop increased the grain yield of rice by 24% (37.0 q/ha) over the RD (29.9 q/ha) applied through conventional fertilizers. Application of nitrogen as basal through briquettes to rice was more effective and recorded higher yield of rice when compared to the split application of nitrogen. Basal application of nitrogen @ 75 and 100% RD through briquettes produced 15 and 6% higher grain yields of rice (34.5 and 37.0 q/ha), respectively, as compared to application of nitrogen in two splits (25.6, 29.9 and 34.9 q/ha) through briquettes. The straw yield and nutrient uptake by the crop also revealed similar trend. Fertilization of rice crop through the briquettes recorded relatively higher values of nutrient uptake which were reflected in higher grain, straw yields and yield contributing parameters. The soil nutrient contents after harvest of the rice crop revealed slightly higher soil test values when the crop was fertilized through briquettes. 6. T. MUBARAK, Z. A. BHAT, M. A. ZARGAR AND AKHLAQ A. WANI [Impact of improved technology on yield and economics of rice (Oryza sativa L.) at farmers’ field in temperate zone]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 29-32 (2013). Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Khanpora, Yaripora, Anantnag-192 232 (J & K), India Frontline demonstrations on rice variety Shalimar Rice-1 were conducted at farmers’ field in the plains of south Kashmir during the kharif2006 to 2008. The average seed yield ranged from 55.9 to 76.3 and 35.6 to 60.5 q/ha under improved technology and farmers’ practice, respectively. Increase in yield over farmers’ practice was 25 to 57% with improved rice technology. Highest net returns (Rs. 26780 to 47500/ha) were also realized from the improved practice. An additional net income of Rs.11950-152270/ha was obtained by improved technology against additional cost of Rs. 2850-4540/ha over farmers’ practice. Benefit : cost ratio was also higher with the improved technology. 7. M. Bhanu Prakash, M. Srinivasa Reddy, E. Aruna and P. Kavitha [Effect of N and P levels on growth parameters, yield parameters, yield, nutrient uptake and economics of rice (Oryza sativa)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 33-38 (2013). Department of Agronomy Agricultural College, Mahanandi-518 502, Kurnool District (Andhra Pradesh), India An experiment was conducted during kharif 2011 at Agricultural College Farm, Mahanandi, to study the growth parameters, yield parameters, yield and nutrient uptake of rice in grain and straw. The results indicated that highest values of growth parameters viz., plant height, leaf area index, dry matter production and number of total tillers were recorded with application of highest level of nitrogen viz., 240 kg N/ha but it was on par with application of 200 kg N/ha and significantly superior to 160 kg N/ha. Higher number of effective tillers/m2, grain and straw yield were recorded with application of 240 kg N/ha and it was on par with application of 200 kg N/ha and significantly superior to 160 kg N/ha. Highest nitrogen uptake in grain and straw was noticed with application of 240 kg N/ha and lowest was with application of 160 kg N/ha. Also the highest gross returns were with application of 240 kg N/ha and lowest was with application of 160 kg N/ha. Among phosphorus levels, highest values of growth parameters viz., plant height, leaf area index and total tillers/m2 were with application of 80 kg P2O5/ha and lowest were with control. Highest number of effective tillers/m2, grain and straw yield were recorded with application of 80 kg P2O5/ha and it was on par with application of 60 kg P2O5/ha. Highest phosphorus uptake in grain and straw was noticed with application of 80 kg P2O5/ha and lowest was with application of control. Highest gross returns were with application of 80 kg P2O5/ha and lowest were with application of control. Application of 200 kg N/ha and 60 kg P2O5/ha was found most suitable for low land rice. 8. Priyanka Singh, Dharm Prakash, Y. V. Singh and Shobhit Singh [Effect of zinc application on yield and benefit/cost (B/C) ratio of wheat in western Uttar Pradesh]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 39-41 (2013). Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry Raja Balwant Singh College, Bichpuri, Agra-283 105 (U. P.), India A field experiment was conducted for rabi season of 2009-10 at the cultivator field in order to find out the effect of zinc on wheat crop. A field experiment was undertaken to evaluate the effect of graded levels of zinc sulphate (0, 7.5, 15.0, 22.5 and 30.0 kg/ha) on the flag leaf, yield content and uptake of nutrient in wheat. The experimental soil was sandy loam in texture. Application of 22.5 kg Zn/ha gave significantly higher flag leaf, yield, Zn content and Zn uptake. The benefit/cost ratio was highest in T4 (12.91) that in the 22.5 kg Zn application is the adequate dose for wheat cultivation. 9. N. Krishnamurthy, Pradeep Nayak, K. P. Suresh Naik and H. M. Jayadeva [Influence of different establishment methods on energy balance and economics of rice (Oryza sativa L.) crop]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 42-44 (2013). Department of Agronomy University of Agricultural Sciences, Bengaluru (Karnataka), India A experiment was conducted in the farmers’ field at Mottedoddi village, Ramanagara district during kharif 2009 with a view to study the effect of establishment methods and cultivars on energy balance and economics of the rice (Oryza sativa L.) crop. The results of the experiment revealed that among the different methods of establishment, system of rice intensification (SRI) method recorded lower input energy (12292 MJ/ha), higher net energy returns (123657 MJ/ha) and energy use efficiency (11.06) and conventional method recorded higher energy output (137246 MJ/ha), respectively, than other establishment methods. Regarding economics, aerobic method showed least cost of production (Rs. 16562/ha), SRI method recorded higher gross returns (Rs. 56620/ha), net returns (Rs. 38629/ha) and B : C ratio (2.15). 10. MAHESH CHAND SINGH*, ANCHAL KUMAR JAIN AND SUNIL GARG [Simulation of soil moisture movement under rice field using Hydrus-2D]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 45-53 (2013). Department of Soil and Water Engineering Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana-141 004 (Punjab), India *(e-mail : mahesh25pau@yahoo.co.in) Soil moisture is a key variable in controlling the exchange of water between land surface and atmosphere through evaporation and plant transpiration. A field study was conducted at Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana (India), in the year 2009, to simulate the soil moisture movement under rice field using numerical model Hydrus-2D. The treatments included two dates of transplanting viz., June 5 (D1) and June 20 (D2), two varieties inbred PAU-201 (V1) and hybrid RH-257 (V2) of 120 and 90 days durations (from transplanting to harvest) and two irrigation regimes viz., intermittent irrigation at 2-days drainage period (I1) and irrigation based on soil water suction (SWS) of 16 k Pa (I2). A total of eight treatments were replicated thrice in 24 plots of each having size 10 x 4 m. The saturated hydraulic conductivity (Ks varied from 0.36 to 1.48 cm/day with an average value of 0.92 cm/day) and the fitting parameter (n varied from 1.58 to 2.76 with an average value of 2.17) were found to be very sensitive during calibration. The results from the experiment revealed that the soil moisture content was more in upper layer of the soil profile as compared to the lower layers due to effect of puddling. The application of Hydrus-2D confirmed that the simulated depth wise soil moisture content values were in good agreement with observed data. The model performance was evaluated by using parameters, namely, root mean square error, absolute percentage error, correlation coefficient and model efficiency. During validation, the average absolute error varied from 2.19 to 13.21%, root mean square error varied from 0.006 to 0.032 cm, correlation coefficient varied from 0.773 to 0.996 and the average model efficiency was 98.6%. The use of Hydrus-2D model can be successfully adopted for simulating soil moisture profiles under rice crop. 11. E. Sumathi* and G. Manickam [Field screening of rice accessions against rice gall midge (Orseolia oryzae Wood-Mason)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 54-58 (2013). Rice Research Station, Tirur-602 025, Thiruvallur (Tamil Nadu), India *(e-mail : sumathicicr@yahoo.com) Field trials on screening of rice accessions for resistance/susceptible to rice gall midge were carried out at Rice Research Station, Tirur, Thiruvallur district during samba, 2009. The rice cultures for all midge biotype monitoring trial (GMBT), gall midge screening (GMS) trial and multiple resistance screening trial (MRST) received from DRR, Hyderabad were raised in two rows of 20 hills per entry with a spacing of 15 x 15 cm in the main field. Gall midge incidence as silver shoot was recorded on 30 and 50 days after transplanting and scoring was done. Among the 17 entries screened in GMBT, the entries viz., ARC 6605 and INRC 3021 were recorded nil gall midge damage and found resistant to gall midge. The entries viz., INRC 202 and INRC 1997 were found to be moderately susceptible. The entries viz., Phalguna, Madhuri L 9, RP 2068-18-3-5, Abhaya and Aganni were found highly susceptible and the remaining seven entries were found susceptible to gall midge damage. The check variety TN 1 recorded the gall midge damage of 14.7% and found to be susceptible. Based on the reaction of the differentials (Resistant-Susceptible-Susceptible) the presence of biotype 3 was identified. Among 45 cultures screened in GMS, the cultures viz., RP 4683-29-2-645, RP 4683-30-1-648, RP 4686-49-1-943, RP 4687-52-2-1197, RP 4688-53-2-1258, RP 4688-53-2-1259, JGL 17025, JGL 17183, JGL 17187, JGL 17189, KAVYA, JGL 17190, JGL 17196, JGL 17198, JGL 17211 and JGL 17221 were recorded nil gall midge damage and found to be resistant in field screening. Check variety TN 1 was found to be highly susceptible. 12. Praveen Singh, Anil Pandey and Rajesh Kumar [Stability study in aromatic rice (Oryza sativa L.)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 59-65 (2013). Department of Plant Breeding & Genetics Rajendra Agricultural University, Pusa, Samastipur (Bihar), India The present study was undertaken with 30 aromatic rice genotypes grown in four environments (24 June and 14 July sown for two years; kharif 2008 and 2009) in randomized block design following standard package of practices for aromatic rice at Rice research Field, RAU, Pusa, Bihar. Observations were recorded on quantitative and quality traits. It was observed that among the different dates of sowing, E3 (24 June, kharif 2009) gave the highest grain yield followed by E1 (24 June, kharif 2008). Genotype × environment interaction was observed to be significant for most of the characters except for panicle length, effective tillers per plant, spikelets per panicle, filled grain per panicle, leaf area index, specific leaf weight and gelatinization temperature under study. For grain yield, Sanwal Basmati was observed as above average stable, whereas Pusa Sugandh-3 was the average stable and Jasmine and NDR 9542 were below average stable genotypes. These stable genotypes, namely, Sanwal Basmati, Pusa Sugandh-3, Jasmine and NDR 9542 have reflected stability for component traits. 13. VIJAYATA SINGH, G. S. PANWAR AND JOGENDRA SINGH [Validation of SSR markers for fertility restorer gene in drought tolerant advanced breeding lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 66-73 (2013). Barwale Foundation, Research and Tranining Centre, Hyderabad (A. P.), India A study was conducted during rabi 2008-09 to validate eight simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers for fertility restoration ability of 97 drought tolerant advanced breeding lines of rice (Oryza sativa L.) with one wild abortive (WA) based cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) line in their 97 F1s. The spikelet fertility percentage (SF%) was taken as criteria for restoration ability of lines, based on this IR 83641-518-B, IR 79915-B-83-4-4 and IR 80508-B-57-2-B were considered as the best restorer lines for WA based CMS line and used further for validation of SSR markers. Out of eight, only four markers, namely, RM 7446, RM 6100, RM 25661 and RM 25662 produced significant polymorphism between restorer and male sterile parents, were validated as they linked tightly with fertility restore (Rf) genes. These markers may facilitate marker assisted selection (MAS) of restorer lines in CMS-WA system from large source nurseries to avoid routine testcrosses in hybrid rice breeding programmes. 14. M. Girija Rani*, D. Adilakshmi, P. V. Satyanarayana and Y. Suryanarayana [Genetic diversity of rice genotypes for submergence tolerance]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 74-78 (2013). Andhra Pradesh Rice Research Institute and Regional Agricultural Research Station Maruteru-534 122, West Godavari District (Andhra Pradesh), India *(e-mail : girija_aprri@yahoo.co.in) Sixty-four rice genotypes were screened under submergence conditions to study the diversity pattern among the genotypes for identification and development of varieties suitable for flood prone areas. The genotypes were grouped into eight clusters. Maximum of 22 genotypes were grouped into cluster I followed by cluster II consisting of 14 genotypes. Clusters IV and VI were with single genotype indicating highest heterogeneity among the genotypes. Maximum inter-cluster distances were observed between clusters IV and VIII (3269.73) and V and VIII (3248.71). Maximum contribution to total divergence was observed from traits viz., test weight, relative shoot elongation, grain yield per plant and days to 50% flowering indicating importance of these characteristics for submergence tolerance. Hybridization between clusters IV and VIII may result in desirable segregants with high yield, minimal shoot elongation, fast recovery after de-submergence as these groups are extreme for traits associated with submergence tolerance. 15. C. Rama Devi, D. M. Reddy, K. H. P. Reddy and P. Sudhakar [Selection strategy through genetic association studies for improvement of yield and quality under organic fertilizer management in rice (Oryza sativa L.)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 79-83 (2013). Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding S. V. Agricultural College, Tirupati-517 502 (A. P.), India The association among yield and quality components, their direct and indirect influence on grain yield in 32 genotypes of rice was carried out under organic fertilizer management. Grain yield per plant was significantly and positively correlated with its component characters like days to 50% flowering, days to maturity, number of effective tillers per plant, panicle length, number of grains per panicle and harvest index. Path coefficient analysis revealed that the direct effect of days to 50% flowering on grain yield was the highest, followed by number of grains per panicle and harvest index, suggesting that e. the improvement in grain yield could be efficient, if the selection is based on these component characters under organic fertilizer management in rice. 16. Priyanka Singh, Y. V. Singh, Shobhit Singh, P. K. Sharma and R. Meena [Zinc requirement of wheat and its influence on zinc fractions in an Inceptisol of Agra, Uttar Pradesh]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 84-87 (2013). Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry Raja Balwant Singh College, Bichpuri, Agra-283 105 (Uttar Pradesh), India Field experiment was conducted on Agricultural Research Farm, Agra (U. P.) on a zinc deficient Inceptisol soil to assess the effect of different rates, frequency and distribution of Zn in different fractions. Crop of wheat responded to applied Zn up to 22.5 kg/ha application of Zn at highest dose i. e. 30 kg ZnSO4/ha had effects up to wheat crop. For applied Zn on yield of wheat, a field experiment was undertaken to evaluate the effect of graded levels of zinc sulphate (0, 7.5, 15.0, 22.5 and 30.0 kg/ha) on the yield, content and uptake of nutrients in wheat. Different fractions of soil Zn were in dynamic equilibrium with each other. Depletion of water soluble, exchangeable and complexed forms of Zn occurred with a build-up organic, occluded and residual fractions of Zn. Depleted levels of readily available Zn in soil could be replenished by the other pools of soil Zn. 17. Dhram Prakash and Y. V. Singh* [Fertilizer requirement of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) for pre-set yield targets in an Inceptisol of Eastern Plain Zone of Uttar Pradesh]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 88-90 (2013). Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry Institute of Agricultural Sciences Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221 005 (U. P.), India *(e-mail : yvsingh59@rediffmail.co.in) An experiment on soil test crop response (STCR) correlation studies was conducted in Inceptisols of Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh during rabi 2010-11. Using the basic data, fertilizer adjustment equations have been developed for prescribing optimum fertilizer doses to attain different yield targets. The nutrient requirement of N, P2O5 and K2O was found to be 1.95, 0.42 and 2.47 kg/q, respectively, for producing one quintal of wheat. The per cent nutrient contributions from soil were 8.63, 8.03 and 12.48, and from fertilizers were 61.44, 58.74 and 188.17% for N, P2O5 and K2O, respectively. The targeted yield equations and the fertilizer ready reckoner developed for wheat will be useful for large scale recommendation by the soil testing laboratory of eastern Uttar Pradesh. 18. Om Vir and Sheikh M. Sultan [Genetic variability and character association in the germplasm of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) under rainfed conditions of Himalayas]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 91-95 (2013). Regional Centre, National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources Rangreth, Old Air Field, Srinagar-190 007 (J & K), India Genetic variability within available germplasm of barley is essential to initiate and sustain genetic improvement of barley using plant breeding methods. Field experiments were conducted during rabi2007-08, 2008-09 and 2009-10 with the aim of estimating variation in the germplasm and also to generate information on associations of yield components and their direct and indirect influence on the grain yield of barley. Thirty-four accessions were evaluated in randomized complete block design with three replicates. Results showed that there were significant genotypic differences for seed yield per plant, 100-seed weight, number of spikelets per spike, number of seeds per spike, spike length, plant height and days to 50% flowering in all the three years. Broad sense heritability estimates were high ranging from 0.55 for days to 50% flowering to 0.73 for 100-seed yield. Number of spikelets per spike, number of seeds per spike, spike length and days to 50% flowering exhibited positive and significant correlation with seed yield. Number of seeds per spike, number of spikelets per spike, 100-seed weight, number of days to 50% flowering and plant height and spike length had exerted positive and direct effects on seed yield. 19. GURPREET SINGH AULAKH, KRISHAN KUMAR VASHIST AND S. S. MAHAL [Effect of different irrigation regimes and nitrogen levels on growth parameters and yield of late kharif sown maize (Zea mays L.)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 96-105 (2013). Department of Agronomy Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana-141 004 (Punjab), India The field experiment was conducted at Students’ Research Farm, Department of Agronomy, Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana, during late kharif 2009-10 to study the effect of different irrigation regimes (IW/CPE ratio 0.50, 0.75, 1.00 and 1.25) and nitrogen levels (100, 125, 150 and 175 kg N/ha) on growth and yield of late kharif sown maize. The grain yield under irrigation regimes I1.25 (three irrigations) and I1.00 (three irrigations) was observed to the tune of 83.1 and 81.2 q/ha, respectively, which were statistically at par with each other but significantly higher than the grain yield observed under I0.75 (two irrigations) and I0.50 (one irrigation). Various growth parameters like plant height, number of leaves per plant, leaf area index (LAI), photosynthetically active radiation interception (PARI %), dry matter accumulation (DMA), crop growth rate (CGR), relative growth rate (RGR) and SPAD reading determining the chlorophyll content of leaves at tasselling stage were also higher under higher irrigation regimes. Among nitrogen levels, N150 and N175 being statistically at par with each other gave significantly higher grain yield over N125 and N100. Similar trend was observed for growth parameters viz., plant height, number of leaves per plant, LAI, PARI (%), DMA, CGR, RGR, leaf chlorophyll content, etc. 20. S. Lekshmi and V. R. Bhatt [Absorption and utilization of soluble organic nitrogen in the form of amino acids in maize plant]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 106-110 (2013). Department of Soil Science & Agricultural Chemistry Anand Agricultural University, Anand (Gujarat), India A sand culture study was conducted with 12 treatments. Sieved, acid washed and autoclaved sand was used to exclude microbial contamination. Five amino acids viz., glutamic acid, aspartic acid, glycine, cystine, tryptophan and their mixture as nitrogen source in Hoagland solution which served as the reference treatment and also as a source of all other nutrients. There were treatments where 50% nitrogen was supplied through Hoagland and remaining 50% was through glutamic acid, glycine and their mixture. Green and dry foliage yield, root biomass and photosynthetic rate were highest with Hoagland solution indicating that inorganic nitrogen was most suited. About 50 to 95% dry matter yield obtained by Hoagland solution could be produced by amino acids. An incubation study with the same sand used in the above pot study indicated that the nitrification rate of amino acids was 14 to 30% at 30 days, suggesting the direct absorption of amino acids by maize plant. Nutrient contents in the leaf and their uptake by the plant showed that their values were within the normal range irrespective of their nitrogen source. Maximum sulphur content was obtained when cystine was the sole source of nitrogen. Inclusion of 50% nitrogen as inorganic nitrogen or foliar spray of 1% amino acid did not have any distinct advantage in utilization of organic nitrogen. The results showed that the inorganic nitrogen was utilized better than that of organic nitrogen. At the same time, fairly good amount of organic nitrogen was absorbed and utilized. 21. P. LATHA, P. THANGAVEL, K. ARULMOZHISELVAN AND K. VELAYUDHAM [An investigation on distillery spentwash for maximizing production of maize crop]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 111-116 (2013). Department of Environmental Sciences Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore-641 003 (Tamil Nadu), India Distillery sentwash is effective organic liquid manure derived from molasses based distillery industries after biomethanation process. A field experiment was conducted during 2009 in Research and Development Farm of M/s. Bannari Amman Sugars Distillery Division Ltd., Erode to find out the concentration dosage of spentwash with inorganic fertilizers to obtain the maximum growth, quality and yield of maize (COH (M) 5). From the experiment, quality, physiological, biochemical and nutrient parameters were estimated. Growth, yield attributes and yield were recorded. The results revealed that application of spentwash @ 100 m3/ha+recommended dose of N, P and K recorded the higher grain and cob yield of 5815 and 6513 kg/ha, respectively, which was on par with spentwash @ 100 m3/ha+recommended dose of N and P over recommended dose of fertilizers. The utilization of spentwash increased the growth parameters thus enhancing the yield besides paving an ecofriendly approach for the disposal of the effluent. 22. V. SOBHANA, ASHOK KUMAR AND ISHWAR SINGH [Plant population and nutrient needs of baby corn (Zea mays L.) hybrids]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 117-120 (2013). Division of Agronomy Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi-110 012, India HM 4 plant population level of 83,333 plants/ha and the nutrient level of N187.5P32.75K62.5 recorded more baby corn yields with and without husk and green fodder yield. HM 4 also noticed more brix value than PEHM 2. Reduction in cob protein was noticed with increase in plant population from 66,666 to 83,333 plants/ha. Increasing plant population from 66,666 to 83,333 plants/ha considerably reduced available N, P and K contents in soil. However, contents of all these nutrients improved with each increase in nutrient levels from control to the highest dose of NPK. N, P and K uptake in baby corn and fodder was found maximum with application of N187.5P32.75K62.5 kg/ha. The net returns remained more with HM 4 and 83,333 plants/ha. There was substantial improvement in net returns with each increase in nutrient levels. 23. MAHESH KUMAR* AND M. S. GREWAL [Identification of genotypes for their potential yield and yield attributes of baby corn]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 121-123 (2013). Department of Plant Breeding and Genetics Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana-141 004 (Punjab), India * (e-mail : maheshkumarvats@yahoo.co.in) A field experiment was conducted at Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana during kharif season of 2008. Six genotypes viz., FH-3438, VL Baby Corn, Vivek Hybrid-17, HIM-129, Parkash and HM-4 were evaluated for their yield and yield attributes of baby corn (Zea mays L.). Significantly higher baby corn yield without husk was recorded in Vivek Hybrid-17 (16.04 q/ha), which was at par with VL Baby Corn (15.26 q/ha). The highest green fodder yield (266.93 q/ha) was recorded in hybrid Parkash and it was higher than all other genotypes. The baby corn length was highest in HM-4 (8.50 cm). Genotypes VL Baby Corn, FH-3438 and Parkash exhibited less girth 3.92, 4.10 and 4.10 cm, respectively, in comparison to HM-4 (4.30 cm) and Vivek Hybrid-17 (4.27 cm). VL Baby Corn produced more babies per plant (2.65) as compared to other genotypes. However, it was at par with Parkash (2.52) and Vivek Hybrid-17 (2.40). 24. H. A. AVINASHE*, S. S. JAIWAR, S. M. KHANORKAR, V. K. GIRASE AND S. A. RAWOOL [Assessment of combining ability and heterosis for yield, yield contributing characters and oil content in maize (Zea mays L.)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 124-131 (2013). Department of Agricultural Botany Anand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110 (Gujarat), India *(e-mail : havinashe@gmail.com) The present investigation was conducted at Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Anand Agricultural University, Anand during 2010. The experimental material consisting of 45 F1s, their 18 parents and three standard checks (HQPM-1, HM-5 and Gujarat Makai-2) was grown in a randomized block design with three replications. The hybrids were evaluated to know the extent of heterosis and combining ability for grain yield per plant, yield contributing characters and oil content in maize. Considerable variability existed among the genotypes for all the characters studied as observed from the significant mean squares due to genotypes. Combining ability analysis showed the predominant role of non-additive gene action for all the characters studied. The lines I-07-10-1, I-07-56-4 and tester CLQ-30 were found to be good general combiners for grain yield per plant. Crosses I-07-7-4 × CLQ-30, I-07-8-6 × CLQ-30 and I-07-57-5 × HKI-163 revealed high specific combining ability effects for grain yield per plant. The hybrids I-07-10-1 × HKI-163, I-07-8-6 × CLQ-30 and I-07-7-4 × CLQ-30 were identified as superior hybrids as these recorded high percentage of relative heterosis, heterobeltiosis and standard heterosis for grain yield per plant along with other characters. These hybrids were identified as potential hybrids for widespread cultivation and commercial exploitation. 25. S. V. NIRMAL, U. S. DALVI and S. R. GADAKH [Effect of water stress conditions on root characteristics of sorghum plant under irrigated and rainfed conditions]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 132-135 (2013). Sorghum Improvement Project Mahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth, Rahuri-413 722 (Maharashtra), India Thirteen sorghum genotypes including seven rabi adopted and six stay green ones were characterized for key root parameters that help surviving under drought conditions. This experiment was conducted in wooden structure which was filled by medium type of soil. Various observations such as root length, root dry mass and number were recorded at physiological maturity, while aerial observations such as leaf area index, leaf area water content and chlorophyll stability index at 50% flowering. Root length at maturity varied from 44.6 to 62.8 cm in rabi adopted entries as a group recorded slightly more root length at maturity over stay green ones. RSV 423 (62.8 cm) in rabi adopted and E 36-1 (60.2 cm) in stay green were superior for root length. Similarly, rabi adopted ones under rainfed conditions recorded higher root numbers, root and shoot mass, root volume and also LAI, RLWC over stay green types under irrigated and rainfed conditions. 26. S. R. Gadakh, M. S. Shinde, A. R. Gaikwad, S. V. Nirmal and U. D. Chavan [Phule Suchitra : A new rabisorghum variety for medium soils]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 136-140 (2013). All India Co-ordinated Sorghum Improvement Project Mahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth, Rahuri-413 722, Ahmednagar (Maharashtra), India Phule Suchitra (RSV 1098/SPV 2048), a new rabisorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] variety identified and developed from the cross SPV 1359 x SPV 1502 through multi-environment testing at Rahuri was found to be superior in grain and fodder yield over checks viz., Phule Chitra, Phule Maulee and M 35-1 on medium soils. Average of 16 tests under rainfed situations on medium soils, it gave 2118 kg/ha grain yield as against 1742 kg/ha of Phule Chitra, 1309 kg/ha of Phule Maulee and 1723 kg/ha of M 35-1, thus amounting to 21.6, 61.8 and 22.9% increase over Phule Chitra, Phule Maulee and M 35-1, respectively. As regards fodder, it had recorded higher mean of 6710 kg/ha over Phule Chitra (5790 kg/ha), Phule Maulee (4920 kg/ha) and M 35-1 (5620 kg/ha) and was 15.9, 36.4 and 19.3% more than Phule Chitra, Phule Maulee and M 35-1, respectively. Considering average performance in 23 adaptive trials on cultivators’ fields, the variety Phule Suchitra (RSV 1098/SPV 2048) gave 21.6% more grain and 22.6% more fodder yield over Phule Chitra under rainfed condition on medium soils. Besides being the higher yield, Phule Suchitra is characterized as midlate (120-125 days), mid tall (230-240 cm), medium bold grain (30-32 g/1000 seeds), pearly white round grain with high degree of tolerance to shootfly (26.6%), stem borer (10%) and charcoal rot (20%). It was also characterized as drought tolerant because of its superior physiological traits under moisture stress. The roti and fodder quality of Phule Suchitra are excellent to that of Phule Chitra, Phule Maulee and M 35-1. The variety RSV 1098 (SPV 2048) was, therefore, released under the name Phule Suchitra for replacement of existing variety Phule Chitra for western Maharashtra on medium soil under rainfed conditions. 27. P. H. AHIWALE, L. S. CHAVAN, D. N. JAGTAP*, U. V. MAHADKAR and M. B. GAWADE [Effect of establishment methods and nutrient management on yield attributes and yield of finger millet (Eleusine coracana G.)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 141-145 (2013). Department of Agronomy Dr. Balasaheb Sawant Konkan Krishi Vidyapeeth, Dapoli-415 712, Ratnagiri (M. S.), India *(e-mail : jagtapmauli_296@rediffmail.com) The field experiment was conducted at the Central Farm, Central Experiment Station, Wakawali, Dr. Balasaheb Sawant Konkan Krishi Vidyapeeth, Dapoli, District Ratnagiri (M. S.) during kharif season of the year 2009 on terraced upland to study the effect of establishment methods and nutrient management on yield attributes and yield of finger millet (Eleusine coracana G.). The experiment was laid out in a split plot design. The main plot treatments comprised four methods of crop establishment and sub-plot treatments consisted of five nutrient management practices. Thus, there were 20 treatment combinations replicated three times. On the basis of results obtained from present investigation, it was concluded that kharif finger millet grown under south Konkan conditions be established by transplanting and supplied with FYM @ 5 t/ha plus 75% RDF (60 : 30 : 00 kg NPK/ha) plus biofertilizers (Azospirillum+PSB), so as to obtain higher yield of finger millet. 28. P. C. YADAV, U. S. SHARMA, O. P. AMETA, A. MORDIA AND G. C. JAT [Different management schedules against tobacco caterpillar (Spodoptera litura Fab.) in groundnut]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 146-148 (2013). Department of Entomology Maharana Pratap University of Agriculture & Technology, Udaipur-313 001 (Rajasthan), India Field experiment was conducted at CTAE farm, Maharana Pratap University of Agriculture & Technology, Udaipur, Rajasthan during kharif 2010 to study the effectiveness of different management schedules against tobacco caterpillar. The results revealed that among different schedules application of phorate 10 G @ 25 kg/ha at the time of sowing followed by two sprays of flubendiamide 240 SC @ 250 ml/ha at 15 days interval was found most effective. 29. V. Thirumala Rao, V. Venkanna, D. Bhadru, K. G. K. Murthy and S. H. Reddy [Studies on character association and path analysis under drought in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 149-151 (2013). Regional Agricultural Research Station Polasa, Jagtial-505 529, Karimnagar (A. P.), India Groundnut yield in rainfed areas has been limited by drought stress because pod yield and other growth parameters have been severely affected. The objective of this study is to evaluate the association between yield and yield components under drought, it will serve to make simultaneous selection of various characters. Dry pod yield exhibited significant positive association with pods per plant, 100-kernel weight and SPAD chlorophyll meter reading (SCMR). Partitioning of phenotypic correlation coefficients of various component characters with dry pod yield into direct and indirect contribution revealed that the direct effect was high and positive for pods per plant, SPAD chlorophyll meter reading (SCMR) and 100-kernel weight. It could be inferred the reliance on pods per plant, 100-kernel weight and SPAD chlorophyll meter reading (SCMR) resulted in improvement of pod yield in groundnut under drought. 30. S. PAVANI, K. BHANU REKHA, S. N. SUDHAKARA BABU AND MADHU MOGULOJU [Effect of nitrogen and sulphur on growth, yield and quality of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 152-154 (2013). Department of Agronomy Acharya N. G. Ranga Agricultural University, Hyderabad-500 030 (A. P.), India An experiment on response of sunflower to different levels of nitrogen and sulphur was conducted during kharif 2011. The increase in the plant height, number of leaves/plant, leaf area index, dry matter accumulation and stem girth were significant with each increment of nitrogen upto 120 kg/ha and sulphur upto 30 kg/ha. Application of 120 kg N/ha registered higher seed yield (2108 kg/ha) over 60 and 90 kg N/ha. Among the sulphur treatments, application of 30 kg S/ha recorded highest seed yield (2048 kg/ha) over 0 and 15 kg S/ha. Application of 120 kg N/ha recorded maximum stalk yield (4072 kg/ha) over 60 and 90 kg N/ha, while the lowest stalk yield (3638 kg/ha) was observed in plots fertilized with 60 kg N/ha. Application of 30 kg S/ha recorded more stalk yield (4028 kg/ha), whereas low stalk yield (3696 kg/ha) was observed in plots with no sulphur application. Quality parameters viz., oil content, oil yield and protein yield were significantly higher with higher levels of nitrogen (120 kg/ha) and sulphur (30 kg/ha). 31. G. S. Laharia, Darshana U. Patil and P. R. Damre [Effect of organic sources on soil fertility, nutrient uptake and yield of soybean]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 155-159 (2013). Department of Soil Science & Agricultural Chemistry Dr. Panjabrao Deshmukh Krishi Vidyapeeth, Akola-444 004 (M. S.), India A field experiment was conducted with soybean (var. JS-335) on clayey soil at experimental farm of Dr. PDKV, Akola to compare response of organic sources. Soil fertility after harvest of soybean, nutrient uptake and yield of soybean were found statistically significant under different organic treatments over control. Application of 100% RDN through vermicompost+jeevamrut was found beneficial. Beneficial effect of organic sources was in the order of vermicompost > FYM > compost > crop residues. 32. T. M. SUDHAKARA, S. SRIDHARA, K. P. SURESH NAIK AND G. A. RAJANNA [Bio-efficacy and phytotoxicity evaluation of clethodim in soybean (Glycine max L.) and succeeding greengram]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 160-164 (2013). Department of Agronomy University of Agricultural Sciences, GKVK, Bangalore-560 065 (Karnataka), India A field experiment was conducted at College of Agriculture, Navile, Shivamogga, University of Agricultural Sciences, Bengaluru during kharif 2010 to study the diversity and dynamics of weeds as influenced by clethodim in soybean (Glycine max L.) and its residual effect on succeeding crop. The experiment was laid out in randomized complete block design with three replications. Clethodim 24% EC @ 60 g a. i./ha along with NIS+AMS reported lower number of weeds as well as reduced the weed dry weight significantly as compared to all other treatments except application of clethodim 24% EC @ 48 g a. i./ha along non-ionic surfactant (NIS)+ammonium sulfate (AMS). The weed control treatments did not show any observable phytotoxicity symptoms on soybean as well as the succeeding greengram crop. 33. JAYALAKKSHMI MITANALA, S. G. WANKHADE, MOHAN RAO PULI AND D. G. M. SAROJA [Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus levels on oil quality of rainfed Palmarosa (Cymbopogan martini var. Motia)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 165-169 (2013). Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry Dr. Panjabrao Deshmukh Krishi Vidyapeeth, Akola-444 104 (M. S.), India A field experiment was conducted during 2007-08 to study the effect of different levels of nitrogen and phosphorus on oil quality of Palmarosa (both physical and chemical tests) under rainfed conditions on vertisols. The experiment was laid out in factorial randomized block design with 12 treatments and three replications. The treatments consisted of four levels of nitrogen viz., 0 kg (N0), 40 kg (N1), 60 kg (N2) and 80 kg (N3) and three levels of phosphorus 0 kg (P0), 20 kg (P1) and 40 kg (P2)/ha. The study revealed that highest significant difference was recorded in acid value (2.92) (2.23) and ester value (33.65) (28.39) when treated with the combinations of nitrogen @ 80 kg/ha (N3) and phosphorus @ 40 kg/ha (P2), respectively, followed by nitrogen @ 60 kg/ha (N2) and phosphorus @ 20 kg/ha (P2), while nitrogen @ 0 kg/ha (N0) and phosphorus @ 0 kg/ha (P0) showed lowest acid value (1.01) (1.94) and ester value (20.64) (23.67), respectively, whereas the physical properties of the essential oil showed neither deteriorated nor improved by nitrogen and phosphorus treatments. Both the values of acid and ester were found increased with each treatment combination of N and P levels. 34. K. CHANDRASHAKER, V. SAILAJA AND P. CHANDRASEKHAR RAO [Effect of integrated use of organic and inorganic sources of phosphorus on acid and alkaline phosphatase activity in soil and phosphorus nutrition of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.)]–Combining ability, heterosis and their inter-relationships]. Crop Res. 45 (1, 2 & 3) : 170-174 (2013). Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry Acharya N. G. Ranga Agricultural University, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad-500 030 (A. P.), India A field experiment was conducted during 2009-10 on sandy loam soil Alfisol at College Farm, College of Agriculture, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad, A. P., India to study the response of phosphorus levels in combination with FYM @ 10 t/ha and phosphate solubilizing bacteria (PSB) @ 2 kg/ha on the acid and alkaline phosphatase activity in the rhizosphere soil of chickpea at flowering. The acid and alkaline phosphatase activity decreased with increasing inorganic phosphorus levels and significantly lower activity of both the enzymes was observed in the treatment receiving 75 kg P2O5/ha alone. The highest alkaline phosphatase activity was 292.6 µg p-nitrophenol/g soil/h with 50 kg P2O5+PSB @ 2 kg/ha. Application of 75 kg P2O5/ha to chickpea resulted in a significantly lower acid phosphatase activity of 84.4 µg p-nitrophenol/g soil/h. Significantly higher removal of P by chickpea at flowering was 2.90 kg/ha when inorganic P at 50 kg P2O5/ha was applied in combination with FYM and PSB. The mean P uptake by seed also showed a significant influence of the integrated use of the organics and inorganics supplying P to chickpea. 35. GULAB SINGH MARKO, H. S. KUSHWAHA, SEEMA SINGH, K. N. NAMDEO AND R. D. SHARMA [Effect of sulphur and biofertilizers on growth, yield and quality of blackgram (Phaseolus mungo L.)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 175-178 (2013). Department of Crop Science M. G. Chitrakoot Gramodaya Vishwa Vidyalaya, Chitrakoot, Satna-485 780 (M. P.), India A field experiment was conducted during rainy seasons of 2010 and 2011 to study the effect of sulphur and biofertilizers on growth, yield and quality of blackgram. Application of sulphur up to 60 kg/ha to blackgram cv. Jawahar Urad-2 proved the most beneficial with respect to enhance all the growth and yield attributing characters, seed yield, seed quality and net income per hectare. The maximum seed yield was 11.97 q/ha, seed protein 23.88%, protein yield 286.4 kg/ha, seed carbohydrate 0.50%, net income Rs. 23908/ha and B : C ratio up to 2.20. Amongst the biofertilizer treatments, Rhizobium+PSB performed the best with respect to all these parameters. The treatment interactions were found to be non-significant in case of grain yield per hectare. The findings allude that 60 kg S/ha with dual biofertilizers may be applied to achieve maximum productivity and economical gain from blackgram cv. JU-2. 36. GULAB SINGH MARKO, H. S. KUSHWAHA, SEEMA SINGH, K. N. NAMDEO AND R. D. SHARMA [Effect of sulphur and biofertilizers on nutrient contents and uptake of blackgram (Phaseolus mungo L.)]. Crop Res. 45 (1, 2 & 3) : 179-182 (2013). Department of Crop Science M. G. Chitrakoot Gramodaya Vishwa Vidyalaya, Chitrakoot, Satna-485 780 (M. P.), India A field experiment was conducted during rainy seasons of 2010 and 2011 to study the effect of sulphur and biofertilizers on nutrient contents and uptake of blackgram. The nutrient contents in grain and straw viz., N, P, K and S deviated significantly due to sulphur levels and biofertilizers as well as their interactions. The highest sulphur level (60 kg/ha) and dual biofertilizers (Rhizobium+PSB) resulted in almost significantly higher N, P, K and S contents and their uptake of blackgram. The highest uptake of nutrients by blackgram producing a total biomass up to 31.36 q/ha with highest S level was 99.56 kg N, 11.70 kg P, 52.07 kg K and 5.41 kg S/ha. Similarly, under dual biofertilizers, the corresponding uptake values were 101.61 kg N, 10.62 kg P, 53.20 kg K and 5.57 kg S/ha. The findings suggest that due to heavy withdrawal of nutrients by blackgram cv. JU-2, the succeeding crop must be nourished properly based on nutrients status of the soil. . 37. NEETHA JAYARAM, S. RAMESH, M. BYREGOWDA, H. K. RAMAPPA, B. MANJUNATH AND G. A. MARY REENA [Nature and genetics of response to pigeonpea sterility mosaic virus disease infection in recombinant inbred lines]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 183-187 (2013). Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding University of Agricultural Sciences, G. K. V. K., Bengaluru-560 065 (Karnataka), India Sterility mosaic disease (SMD) of pigeonpea caused by pigeonpea sterility mosaic virus (PPSMV) and transmitted by eriophyid mite, Aceria cajani is one of the most important diseases which can cause yield loss up to 95% under favourable conditions. Development and deployment of SMD resistant cultivars is the most eco-friendly and economical method for mitigating losses due to SMD. In the present study, 120 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) derived from SMD resistant (ICP 7035) and susceptible parents (TTB 7) were screened for response to SMD following leaf stapling technique for use in locating genomic regions controlling SMD resistance. Positively skewed and leptokurtic distribution of RILs suggested that the responses to SMD infection were controlled by fewer genes with decreasing and unequal additive effects with complementary epistasis in desired direction. The implications of the results are discussed in relation to the effectiveness of selection for SMD resistance. 38. POOJA DHUPPAR, SUBHASH C. BIYAN, BASANTI CHINTAPALLI AND D. SARVESHWARA RAO [Studies on the response of lentil crop to integrated nutrient management practices at Agra (Western U. P.)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 188-191 (2013). Department of Botany Dayalbagh Educational Institute (Deemed University), Agra-282 110 (U. P.), India A field experiment was carried out to find the response of farm yard manure (FYM), chemical fertilizer and biofertilizer on lentil crop at experimental farm of Dayalbagh Educational Institute, Agra during rabi seasons of 2010 and 2011. Five treatments were applied and the impacts of the treatments were observed on yield and yield attributes of lentil crop. The application of FYM+chemical fertilizer increased the grain yield of lentil by 48.8 and 69.0% during 2010 and 2011, respectively. Seed inoculation with biofertilizer along with FYM influenced grain yield and yield attributes of lentil. However, combination of FYM+biofertilizer+chemical fertilizer showed maximum increase in grain yield (50.5 and 80.5%) and biological yield (34.9 and 40.2%), respectively, over the control in both the years. Suitability of the above integrated nutrient management practice for the sandy loam soils of Agra is ascertained for lentil crop production system. 39. B. R. DHAKA, A. R. K. PATHAN* AND R. S. DHAYAL [Response of cowpea to organic manures and soil salinity]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 192-195 (2013). Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry Agricultural Research Station, Durgapura-302 018, Jaipur (Rajasthan), India *(e-mail : arkpathan@gmail.com) A pot experiment was conducted at S. K. N. College of Agriculture, Jobner during rabi using cowpea as a test crop to study the response of cowpea to organic manures and soil salinity. The seed yield of cowpea increased to the extent of 13.5 and 27.3, and 24.9 and 32.3 and stover yield to the extent of 8.6 and 13.2, and 12.4 and 19.9% with the application of 5 and 10 t FYM/ha and 2.5 and 5 t vermicompost/ha, respectively, over control. The increasing level of organic manures increased the N, P, K Ca and Mg content of seed and stover and OC of soil, while decreased Na content of seed and stover, bulk density, ECe, pH and ESP of the soil. The P, K, Ca and Mg content of seed and straw and OC pH and ESP decreased with increasing level of EC, while N and Na content of seed and stover, bulk density and ECe of soil increased with increasing level of EC of soil. 40. Y. R. Kadam, A. I. Patel, P. P. Chaudhari, J. M. Patel and S. J. More [Combining ability study in vegetable cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.]]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 196-201 (2013). Department of Vegetable Science Navsari Agricultural University, Navsari (Gujarat), India The present investigation on diallel analysis was conducted in cowpea to study the combining ability in vegetable cowpea for 14 plant characters including green pod yield and its component characters. Combining ability analysis revealed that both additive as well as non-additive effects were important in the inheritance of all the traits studied. However, magnitude of general combining ability (gca) variances was smaller than the specific combining ability (sca) variances for all the traits indicating the preponderance of non-additive gene effects for all the characters. General combining ability effects revealed that the five parents viz., GC-0203, GC-0502, Subhra, GC-4 and Anand Cowpea-1 were the good general combiners for green pod yield per plant which had also the good general combining ability effects for the yield attributes like pods per plant, seeds per pod and 100-seed weight. Specific combining ability revealed that three top yielding hybrids viz., GC-0203 x Anand Cowpea-1, Subhra x GC-4 and GC-0203 x Pusa Komal expressed significant sca effects for green pod yield and its attributing characters involving good x good, good x good and good x average parental interaction, respectively. Cross GC-0203 x Anand Cowpea-1 had good mean performance for green pod yield involving parents with good x good gca effects and also having high sca effects for green pod yield, days to first picking and pods per plant. 41. Y. R. Kadam, A. I. Patel, J. M. Patel, P. P. Chaudhari and S. J. More [Heterosis study in vegetable cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.]]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 202-205 (2013). Department of Vegetable Science Navsari Agricultural University, Navsari (Gujarat), India The present investigation on diallel analysis was conducted in cowpea to study the magnitude of heterosis in cowpea for 14 plant characters including green pod yield and its component characters. The experimental material comprised eight genetically diverse parental lines and their 28 hybrids (excluding reciprocals). Significant standard heterosis and high per se performance with regards to green pod yield and its components were recorded by GC-0203 x Anand Cowpea-1 (21.72% and 111.17 g), Subhra x GC-4 (8.83% and 99.40 g), GC-0203 x GC-0502 (5.26% and 96.13 g) and GC-0502 x Pusa Komal (5.04% and 95.93 g) in positive direction. 42. K. Kalyani, V. Sailaja and P. Chandrasekhar Rao [Critical limits of available potassium for cauliflower (Brassica oleracea var. Botrytis) in light textured soils of Rangareddy district]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 206-209 (2013). Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry Acharya N. G. Ranga Agricultural University, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad-500 030, (A. P.), India The critical limits of available K in soil with two different extractants were determined through a pot culture experiment with 30 soils of Rangareddy district. NH4OAc (NN) and NaBPh4 (0.2 M) extractable K were found to be positively and significantly correlated with plant K content and curd yield of cauliflower. The critical limits of available K for cauliflower growing soils of Rangareddy district were found to be 120.8 and 334.2 ppm, respectively, for NH4OAc (NN) and NaBPh4 (0.2 M). The critical plant of K content of cauliflower was found to be 2.6%. The curd yield of the cauliflower increased with increased levels of potassium. 43. T. CHAITANYA*, G. PADMAJA AND P. CHANDRASEKHAR RAO [Activity of soil urease, phosphatase and dehydrogenase as influenced by integrated nutrient management in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) grown on alfisol]. Crop Res. 45 (1, 2 & 3) : 210-214 (2013). Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry Acharya N. G. Ranga Agricultural Univesity, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad-500 030 (A. P.), India *(e-mail : tukkanichaitanya@gmail.com) A field experiment was conducted during kharif2010 on sandy loam soil at Students’ Farm, College of Agriculture, Rajendranagar to study the different nitrogen sources (inorganic nitrogen, vermicompost and poultry manure) and their integration effect on soil dehydrogenase, phoaphatase (acid and alkaline) and urease activities in tomato at vegetative, flowering and harvest stages. Significantly highest urease activity of 234.0, 288.8 and 126.7 µg of NH4+ -N released/5 g soil/2 h with the combined application of 75% RDNF+25% VC, significantly highest dehydrogenase activity of 161.0, 177.1 and 133.4 µg of TPF produced/g soil/d, the highest acid phosphatase activity of 35.23, 48.55, 25.55 µg of PNP released/g soil/h and the highest alkaline phosphatase activity of 65.07, 88.64, 71.27 µg of PNP released/g soil/h were obtained at vegetative, flowering and harvest stages, respectively, with the combined application of 50% VC and 50% PM. All three enzyme activities were increased from the vegetative to flowering stage and later showed decrease from flowering to harvest stage. 44. M. Sunil Kumar, M. Madhavi, K. Chandrasekhar Reddy and A. Manohar Rao [Influence of integrated weed management on growth and yield of tomato].Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 215-217 (2013). College of Horticulture, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad-500 030 (Andhra Pradesh), India An experiment was conducted at the Model Orchard, College of Horticulture, Hyderabad, APHU to study the influence of integrated weed management on growth and yield of tomato. The results indicated that pre-emergence application of pendimethalin, metribuzin, oxadiargyl and post-emergence application of quizalofop ethyl did not show any phytotoxic effect on the tomato crop. An integrated treatment of pre-emergence application of metribuzin @ 0.5 kg/ha followed by one hand weeding at 30 DAT recorded the highest yield of tomato (30.33 t/ha). All the herbicides in combination with one hand weeding produced significantly the higher yield of tomato than the treatments of these herbicides applied alone. 45. M. HANUMAN NAIK*, G. SRIHARI AND B. GOPALA RAO [Organic production of onion]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 218-220 (2013). J. V. R. Horticulture Research Station Dr. Y. S. R. Horticultural University, Malyal (P. O.), Warangal-506 101 (A. P.), India *(e-mail : naik.hort@gmail.com) An experiment was carried out for three years to produce onion organically using farm yard manure, vermicompost, neem cake and sheep manure in comparison with chemical fertilizer at RDF. Plant height, bulb weight and yield per ha were significantly influenced by different treatments. RDF produced tallest plants, while neem cake produced shortest plants. Diameter of bulb was maximum with vermicompost, while it was least with sheep manure. Vermicompost application resulted in highest bulb weight and bulb yield. The yield was least with sheep manure. RDF was at third in position in yield. However, the cost : benefit ratio was highest with RDF and least with sheep manure indicating organic farming in onion was not cheaper than farming with RDF. 46. Savita Kumari, Anil Kumar Singh and Ashok Kumar Verma [Role of lead on growth and root morphology of leafy vegetable crops]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 221-224 (2013). Department of Botany MMH College, Ghaziabad (Uttar Pradesh), India The focus of the present study was to explore lead (Pb) induced root growth alterations vis-à-vis root morphological changes in leafy vegetable crops, namely, spinach [Spinacia oleracea (L.) cv. Pusa Bharti] and cabbage [Brassica oleracea (L.) cv Golden Acre] to establish the correlation between Pb accumulation and various root parameters. Both the crops were as exposed to different Pb concentrations (0, 2.5, 5.0, 7.5 and 10.0 mg/l) in irrigation water and changes in various root characteristics, namely, root fresh weight, dry weight, length, surface area, volume, length density, tips, forks and root crossings in both the crops were studied. The majority of the root parameters were adversely affected in spinach more as compared to cabbage even at very low concentration of Pb (2.5 mg/l) in irrigation water. However, at highest level of Pb (10.0 mg/l) the root fresh weight, dry weight, length, surface area, volume, length density, tips, forks and root crossings in spinach were reduced by 68, 79, 81, 81, 76, 73, 84, 82 and 81%, respectively, while for cabbage, the above parameters were reduced by 59, 55, 81, 79, 95, 82, 84, 76 and 89% in the same order. It is suggested that spinach is more sensitive to Pb than cabbage. Both the crops being leafy vegetable should not be advocated to grow with Pb contaminated environment as it caused lead to food chain contamination. 47. P. P. Chaudhari, A. I. Patel, Y. R. Kadam and J. M. Patel [Genetic divergence study in vegetable Indian bean [Lablab purpureus (L.) Sweet]]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 225-228 (2013). Department of Vegetable Science Navsari Agricultural University, Navsari (Gujarat), India Mahalanobis’s D2 statistics was used to study the genetic diversity among 40 genotypes of vegetable Indian bean(Lablab purpureus L.) grown during kharif 2011-12. Observations recorded on 13 characters revealed the wide genetic diversity. By adopting Tocher’s technique, the 40 genotypes were grouped into nine clusters. The average intra-cluster distance revealed that the genetic diversity among the genotypes in cluster-I (6.36) was minimum followed by cluster-VIII (6.52). The maximum intra-cluster distance was observed in the cluster-VI (7.34). Selection within this cluster might be exercised with emphasis on high mean values for the desirable traits. The relative divergence of each cluster from other clusters (inter-cluster distance) indicated high order of divergence between clusters-VII and VIII (29.23) followed by clusters-V and VII (26.06) and clusters- IV and VIII (24.78). Selection of parents from these clusters would help to achieve novel recombinations in future breeding programmes. Per se performance had maximum contribution of 61.15% by number of pods per plant followed by green pod yield per plant (15.77%) towards the divergence. 48. P. P. CHAUDHARI, A. I. PATEL, Y. R. KADAM AND J. M. PATEL [Variability, correlation and path analysis study in vegetable Indian bean [Lablab purpureus (L.) Sweet]]. Crop Res. 45 (1, 2 & 3) : 229-236 (2013). Department of Vegetable Science Navsari Agricultural University, Navsari (Gujarat), India Forty vegetable Indian bean genotypes were studied to estimate the variability, correlation and path analysis. A wide range of variation was apparent for all the characters among which the number of pods per plant had highest. Green pod yield per plant varied highest from 68.74 to 452.07 g indicating the presence of high yielding genotypes. The genotypic coefficient of variation, heritability and genetic advance were observed higher for the characters viz., green pod yield per plant, number of pods per cluster, number of pods per plant and 100-fresh seed weight. Green pod yield was highly significantly and positively correlated with number of branches per plant, number of pods per cluster, number of pods per plant at both the genotypic and phenotypic levels. Path coefficient analysis indicated the high positive direct effect for number of pods per plant followed by number of seeds per pod and number of days to last picking. The character pod length exhibited high negative direct effect on green pod yield per plant followed by days to 50% flowering, plant height and days to first picking. 49. C. N. BYANNA, I. N. DOREYAPPA GOWDA AND V. K. RAO [Standardization of sweet orange and pomegranate blended RTS beverage using sugar substitutes].Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 237-243 (2013). Department of Horticulture University of Agricultural Sciences, G. K. V. K., Bengaluru-560 065 (Karnataka), India The investigation on standardization of sweet orange and pomegranate blended RTS beverage using sugar substitutes was carried out at the Processing Laboratory in the Division of Post Harvest Technology, Indian Institute of Horticulture Research, Bengaluru from November 2009 to June 2010. The RTS beverage prepared from sweet orange and pomegranate juices at the ratio of 50 : 50 with sugar and sugar substitutes and their combinations revealed that the treatments 50% sucrose+50% fructose and 50% sucrose+50% sucralose were on par with sucrose in respect of overall acceptability scores and these were rated the better recipes in sensory evaluation. Among the treatments, highest TSS of 14.600 Brix, pH 3.31, acidity of 0.28%, ascorbic acid of 6.53 mg/100 g, reducing sugars of 12.48%, non-reducing sugars of 3.58% and total sugars of 14.12% were recorded in 50% sucrose+50% fructose, sucralose and 50% sucrose+50% fructose, sucralose, 50% sucrose+50% fructose, 50% sucrose+50% fructose, 50% sucrose+50% aspartame and 50% sucrose+50% fructose, respectively. The TSS, titratable acidity and reducing sugars were increased, while pH, total sugars, non-reducing sugars and ascorbic acid were decreased during storage in all the treatments. The sweet orange and kokum blended RTS beverage with sugar substitutes had storage stability up to six months. 50. K. SWATHI AND TEJASWINI [Effect of pollen source on maximising hybrid seed production : Case study in petunia]. Crop Res. 45 (1, 2 & 3) : 244-247 (2013). Division of Ornamental Crops Indian Institute of Horticultural Research, Hessaraghatta, Bangalore-560 089 (Karnataka), India Hybrids are gaining importance because of their advantages in uniformity and vigour. The present study was taken up to maximise the hybrid seed production by identifying the right source of pollen grains. Individual anther and flowers were considered as independent source of pollen grains. Pollen sourced from single flower, from multiple flowers of single plant and from multiple flowers of different plants from single line was compared. The study was taken up in two different cross combinations involving four different inbred lines, to identify the interaction effect of pollen source and genetic background. The results indicated that seed qualities like pod weight and number of seeds/mg were highest when pollen was collected from multiple flowers of different plants. Hybrid seed production can be maximised by taking care to source pollen from multiple flowers of different plants. 51. R. D. Jat and R. K. Nanwal [Growth, nutrient uptake and profitability of Bt cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) influenced by spacing and nutrient levels]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 248-252 (2013). Department of Agronomy CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar-125 004 (Haryana), India A study was conducted at Research Farm, Department of Agronomy, CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar during kharif 2010. The soil of experimental field was sandy loam in texture and slightly high in pH. Soil was tested low in organic carbon and available nitrogen and medium in available phosphorus and high in potassium. The experiment was conducted in split plot design with three replications. The combination of three spacings (100 x 40 cm, 100 x 50 cm and 100 x 60 cm), two times of N fertilizer applicationviz., T1 : 50% at flowering and 50% at square formation and T2 : 25% as basal, 37.5% at flowering and 37.5% at square formation, were kept in main plots, while three nutrient levels viz., F1–131.2 : 45 : 45 NPK (kg/ha) F2–175.0 : 60 : 60 NPK (kg/ha) and F3–218.7 : 75 : 75 NPK (kg/ha) were kept in sub-plots. Maximum plant height was recorded at closer spacing of 100 x 40 cm. Maximum sympods/plant were recorded in wider spacing (100 x 60 cm) which were significantly higher than closer spacing (100 x 40 and 100 x 50 cm). Weight/boll (g) was recorded non-significant in spacing manure. Time of N fertilizer application had a significant effect on plant height and sympods/plant. Maximum plant height and sympods/plant were recorded with three split applications of N fertilizer. Maximum plant height was recorded at a NPK fertilizer dose of 218.75 : 75 : 75 (125% RDF) kg/ha followed by 175 : 60 : 60 (100% RDF) kg/ha. Spacing (100 x 60 cm) exhibited significantly higher available N, P and K in soil than closer spacing. The maximum available N, P and K in soil was observed with two split doses of N application as compared to three split doses of N application. Significantly higher available N, P and K in soil after harvest of crop was found with 125% RDF, which is significantly superior over 75 and 100% RDF. Total cost of cultivation, gross returns, net returns and benefit : cost ratio were significantly higher with spacing of 100 x 40 cm followed by spacing of 100 x 50 cm with three split applications of N fertilizer and 100% of recommended dose of fertilizers. Cost of cultivation was significantly better in fertilizer levels with 125% of recommended dose of fertilizers. 52. SANGH RAVIKIRAN* and A. S. HALEPYATI [Yield and yield components, quality parameters, uptake of nutrients and economics of Bt cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) as influenced by macro and soluble micronutrients under irrigation1]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 253-258 (2013). Department of Agronomy University of Agricultural Sciences, Raichur-584 102, India *(e-mail : rksangh28@gmail.com) A field experiment was conducted during kharif 2010 at Agricultural College Farm, Raichur to study the effect of macro and soluble micronutrients on growth and yield of Bt cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) under irrigation. The results revealed that application of 125% RDF in combination with 0.5% tracel micronutrient recorded the highest seed cotton yield, lint index, uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus and gross returns (19.88 q/ha, 96.99 g/plant, 5.20 and 32.34 kg/ha and Rs. 79,533/ha, respectively), whereas in absence of foliar nutrition with 100% RDF recorded the lowest seed cotton yield, lint index, uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus and gross returns (12.12 q/ha, 59.09 g/plant, 4.69, 88.13 and 18.51 kg/ha and Rs. 48,462/ha, respectively), but application of 125% RDF with the foliar spray of 1% mangala MgSO4 recorded the highest ginning percentage (34.70) and application of 100% RDF without foliar spray recorded the lowest ginning percentage (32.67), whereas application of 125% RDF with the foliar spray of 0.5% tracel micronutrient recorded the highest uptake of potassium (115.52 kg/ha) and lowest uptake (89.58 kg/ha) in absence of water soluble micronutrients when compared to RDF levels and foliar spray of water soluble micronutrients alone. 53. V. M. Choudki, S. G. Savita, Prashanth Sangannavar, H. M. Vamadevaiah, B. M. Khadi, Rajesh S. Patil and I. S. Katageri [Genetic improvement of fibre strength in diploid cotton (G. herbaceum L.) through interspecific hybridization using G. anomalum wild species]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 259-267 (2013). UAS Agricultural Research Station, Dharwad Farm-580 007 (Karnataka), India The inherent breaking strength of individual fibers is considered to be the most important factor in determining the strength of yarn spun from the cotton fibers. The mismatch between required fiber qualities and available fiber properties in commercial varieties and hybrids impels research to improve fiber properties of Indian germplasm. Diploid cotton, G. herbaceum is having wide adaptability and high degree of resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. Development of diploid cotton suitable for 40 count yarn will make them more remunerative to diploid cotton growers. We started genetic introgression studies through inter-specific cross using G. anomalum to improve fiber strength of G. herbaceum cotton. Pedigree selection from F2 to F11 was practised. These F11 lines were evaluated at ARS, Dharwad Farm, during 2009-10 in augmented design-II. Observations on fiber traits, seed cotton yield and ginning turnout were recorded and analysed using Windostat version 8.5. Seed cotton yield ranged from 75-2557 kg/ha with 832.99% GCV, 80% heritability and 67.93% genetic advance as per cent of mean. Range for ginning outturn was 28.22-39.77% with 65% heritability, 24.59% GCV and 16.98% genetic advance as per cent of mean. Recorded fibre strength was in the range of 16.35-24.65 g/tex with variability parameters like 2.58% GCV, 93% heritability and 1.35% genetic advance as per cent of mean. The value for 2.5% span length ranged from 21.97 to 30.92 mm with 18.19% GCV, 73% heritability and 11.51% genetic advance as per cent of mean. Recorded micronaire value ranged from 3.29 to 6.64 µg/in with GCV of 14.38%, heritability of 74% and genetic advance as per cent of mean of 22.37%. The seven selections PSCANOI-5, 42, 62, 160, 166, 170 and 173 recorded significantly higher in both fibre strength (18.05-21.85 g/tex) and seed cotton yield (1680.49-1896.69 kg/ha) than diploid cotton commercial variety DLSa-17 (Seed cotton yield 1236.97 kg/ha, GOT 36.42%, 2.5% span length 26.47 mm, fibre strength 18.0-19.5 g/tex and micronaire 5.03 µg/in). These selections recorded 36 to 53% yield increase over DLSa-17. It indicates the possibility of improvement in both seed cotton yield and fibre quality traits of G. herbaceum cotton through interspecific hybridization using wild species G. anomalum as a donor parent. 54. K. Nalini, P. Muthukrishan, C. Chinnusamy and P. Janaki [Response of soil microflora in herbicide residue of winter irrigated cotton]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 268-271 (2013). Department of Agronomy Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore-641 003 (Tamil Nadu), India Field experiments were conducted during winter seasons of 2008-09 and 2009-10 at Eastern Block Farm, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore to study the efficiency of new formulation pre-emergence herbicide pendimethalin 38.7% on growth and development of cotton to ensure the better weed management in a cost effective manner. Pendimethalin 38.7% was tried in four different doses viz., 1.5, 2.0, 2.5 and 4.0 kg/ha and it was compared with pendimethalin 30% @ 1.0 kg/ha, early post-emergence herbicide trifloxysulfuron, power weeders and hand weeding. The experimental results revealed that the herbicides exerted a significant detrimental effect on soil bacteria, fungi and actinomycetes. The counts of bacteria, fungus and actinomycetes recorded at 3 DAHS revealed that soil microbes were more sensitive to pendimethalin (38.7%) 1.5, 2.0, 2.5 and 4.0 kg/ha and pendimethalin (30%) 1.0 kg/ha as evident from significant reduction in their population on 15 and 30 DAHS, eventually microbial density started to recover slowly. 55. Intikhab Aalum Jehangir, FAISUL-UR-RASOOL, H. U. Khan, T. MUBARAK, Tahir ali AND s. a. bANGROO [Response of fodder oats (avena sativa L.) to sowing dates, fertility levels and cutting management]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 272-275 (2013). Division of Soil Science Sher-e kashmir university of agricultural sciences and technology, shalimar-191 121 (J & K), India The result of two-year experiment conducted to find out the influence of sowing dates, fertility levels and cutting management on the yield and quality of oats revealed that September 30 sowing recorded an increase in green fodder yield by 41.97 and 43.56% and dry matter yield by 23.15 and 22.51% over October 10 sowing during 2009-10 and 2010-11, respectively. crude protein was highest in October 10 sown crop, whereas crude fibre was highest in September 20 sown crop. The fertility level 150 : 70 : 40 N : P2O5 : K2O kg/ha increased the green fodder yield by 5.63 and 16.91% during 2009-10 and 6.25 and 22.48% in 2010-11 and dry matter yield by 5.63 and 13.70% in 2009-10 and 5.51 and 18.60% in 2010-11 over 125 : 60 : 30 and 100 : 50 : 20 N : P2O5 : K2O kg/ha, respectively. crude protein content increased, while crude fibre content decreased with increase in fertility level. Double cut crop recorded 14.75 and 16.24% increase in green fodder yield and 3.70 and 1.36% in dry matter yield over single cut crop during 2009-10 and 2010-11, respectively. crude protein content was higher and crude fibre content was lower in double cut compared to single cut crop. 56. MEHARBAN SINGH YADAV, BRIJESH YADAV AND SOMRAJ SINGH [Response of ashwagandha [Withania somnifera (L.)Dunal) to integrated nutrient management system (INMS)]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 276-279 (2013). Department of Soil Science J. N. Krishi Vishwa Vidyalaya, Jabalpur-482 004 (M. P.), India A field experiment was conducted during the (rainy) kharif season of 2008-09 at Jabalpur to study the effect of INMS on biochemical parameters, alkaloids, yield, nutrient uptake and status of nutrients of ashwagandha. INMS resulted in highest biochemical parameters (chlorophyll ‘a’, chlorophyll ‘b’ and carotenoids), alkaloids (withaferin A, withanoloide A and withanoloide B), yield (seed and root), nutrient uptake (N, P, K, S and Zn) and status of nutrients (N, P, K, S and Zn) were recorded with the application of 50% NPK/ha+5 t FYM+PSB+Azotobacter+5 kg Zn/ha which was at par with 10 t FYM/ha +PSB+Azotobacter 3 kg/ha+5 kg Zn/ha followed by 50% NPK/ha+5 t FYM+PSB +Azotobacter. 57. SUSHANTA SAHA, BHOLANATH SAHA, R. S. ANTIL AND D. S. DAHIYA [Urea hydrolysis and N transformation in soils amended with different proportions of neem cake]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 280-283 (2013). Department of Soil Science CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar-125 004 (Haryana), India The effect of substituting N with neem cake at different levels on urea hydrolysis and N-transformation in soils at periodic intervals measuring urea-, NH4+– and NO3–-N in the medium was studied. The amount of unhydrolysed urea-N decreased from 99.86 to 5.42 mg N/kg in soil treated with 100% N through urea; the respective values were 83.87 to 11.88, 61.99 to 14.02 and 33.82 to 8.21 for soil amended with 25, 50 and 75% N substituted through neem cake. The content of NH4+-N increased up to 1st day of incubation in soils containing treatments from control to 50% N supplied through neem cake and decreased with progress of incubation. Similarly, soil with 75% N substituted through neem cake showed that NH4+-N increased up to seven days of incubation and decreased thereafter. On the other hand, the increase in NH4+-N content was found up to 28 days in soil with only neem cake and then decreased. The amount of NO3–-N increased with progress of incubation in all the soils. The NO3–-N content decreased significantly at each incubation period as the proportions of N through neem cake increased from 25 to 100% as compared to soil treated with 100% N through urea. 58. MAHESH KUMAR*, S. P. S. BRAR AND SUKHCHAIN [Effect of nutrient levels on growth and yield of winter maize genotypes]. Crop Res. 45(1, 2 & 3): 284-285 (2013). Department of Plant Breeding and Genetics Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana-141 004 (Punjab), India *(e-mail : maheshkumarvats@yahoo.co.in) A field experiment was conducted at Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana during kharif season of 2008 to study the effect of different nutrient levels on growth and yield of winter maize genotypes was studied during rabi season of 2008-09. Three nutrient levels (100 : 50 : 50, 150 : 65 : 65 and 200 : 80 : 80 kg N : P2O5 : K2O/ha) as main plots and four genotypes (Kaveri-50, Mon-27, Buland and Seed Tec-2324) in sub-plots were evaluated for their effect on growth and yield of maize. Application of 200 : 80 : 80 kg N : P2O5 : K2O/ha gave significantly higher grain yield than 100 : 50 : 50 kg N : P2O5 : K2O/ha. The genotype Mon-27 produced significantly higher grain yield than Buland and Seed Tec-2324. However, it was statistically on par with Kaveri-50 (9350 kg/ha). ********ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT



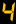

 Users Today : 21
Users Today : 21 Users Yesterday : 78
Users Yesterday : 78 Users Last 7 days : 638
Users Last 7 days : 638 Users Last 30 days : 2872
Users Last 30 days : 2872 Users This Month : 1985
Users This Month : 1985 Users This Year : 8400
Users This Year : 8400 Total Users : 8401
Total Users : 8401 Views Today : 37
Views Today : 37 Views Yesterday : 94
Views Yesterday : 94 Views Last 7 days : 786
Views Last 7 days : 786 Views Last 30 days : 3573
Views Last 30 days : 3573 Views This Month : 2408
Views This Month : 2408 Views This Year : 12367
Views This Year : 12367 Total views : 33713
Total views : 33713 Who's Online : 0
Who's Online : 0