Volume 43, Number 1, 2 & 3 (January, March & May) 2012
1. P. ARUNA, G. PRABHAKARA REDDY AND G. KARUNA SAGAR [Effect of integrated nitrogen management on growth, yield, quality and post-harvest nutrient status of soil in aerobic rice (Oryza sativa L.)]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 1-4 (2012). Department of Agronomy Acharya N. G. Ranga Agricultural University, Tirupati-517 502 (Andhra Pradesh), India An experiment was conducted at S. V. Agricultural College Farm, Tirupati in the Southern Agro-climatic Zone of Andhra Pradesh to study the effect of integrated nitrogen management practices in aerobic rice on growth, yield, quality and post-harvest nutrient status of soil. The experiment was conducted in randomized block design, replicated thrice with 10 treatments viz., control (No nitrogen), 100% N through fertilizer, 25% N through FYM+75% fertilizer N, 50% N through FYM+50% fertilizer N, 75% N through FYM+25% fertilizer N, 100% N through FYM, 25% N through neem leaf manure (NLM)+75% fertilizer N, 50% N through NLM+50% fertilizer N, 75% N through NLM+25% fertilizer N and 100% N through NLM. The study revealed that 100% N through fertilizer recorded higher values of growth, yield and quality, but it was on par with 25% N through FYM+75% fertilizer N and 25% N through NLM+75% fertilizer N. Post-harvest soil fertility status was found to be significantly improved with 100% N through NLM, 100% N through FYM, 75% N through NLM+25% fertilizer N and 75% N through FYM+25% fertilizer N. 2. G. A. RAJANNA, K. MURALI, PRADEEP GOPAKKALI, PRADEEP NAYAK, T. M. SUDAKARA AND R. N. LAKSHMIPATHY [Effect of different sources and time of application of organic manures on residual fertility and nutrient balance in aerobic rice (Oryza sativa L.)*]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 5-9 (2012). Department of Agronomy University of Agricultural Sciences, GKVK, Bengaluru-560 065 (Karnataka), India A field experiment was conducted during kharif 2009 at Zonal Agricultural Research Station, V. C. Farm, Mandya, University of Agricultural Sciences, Bengaluru. The initial status of available N, P2O5 and K2O of the experimental site was 248.5, 26.8 and 202.8 kg/ha, respectively. The variety used was Thanu (KMP-101). The results of the field experiment showed that different organic sources did not significantly influence the organic carbon content, pH and EC of soil after harvest of aerobic rice. Significantly higher amount of nitrogen (272.7 kg/ha), phosphorus (37.2 kg/ha) and potassium (211.6 kg/ha) found in soil after harvest of the crop was observed with FYM 10 t/ha as a basal dose+cattle urine at 100% N equivalent basis. Significantly lower amount of nitrogen (255.2 kg/ha) and phosphorus (29.8 kg/ha) in soil after harvest of the crop was observed with recommended dose of fertilizers (100 : 50 : 50 kg N : P : K/ha) alongwith 10 t of FYM/ha. The study revealed that balance of nitrogen was negative in all the treatments. The least balance of nitrogen was in the treatment (T2 : -44.2 kg/ha) followed by T8 : -42.7 kg/ha and T4 : -42.4 kg/ha. Available phosphorus balance was negative in all the treatments except in the vermicompost alongwith cattle urine applied treatment (2.41 kg/ha). The cattle urine applied treatments resulted in greater negative balance of potassium. The lower nutrient content of organic manures resulted in greater negative balance of phosphorus and potassium as compared to other treatments. 3. PRADEEP GOPAKKALI*, D. CHANNANAIK, G. A. RAJANNA, H. G. SANNATHIMMAPPA, Y. M. RAMESHA AND VEERESHA [Economics and nutrient uptake of rice (Oryza sativa L.) as influenced by various levels of FYM and cattle urine application in Bhadra command area of Karnataka]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 10-14 (2012). Department of Agronomy University of Agricultural Sciences, GKVK, Bangalore-560 065 (Karnataka), India *(g.pradeep76@gmail.com) An experiment was conducted during kharif 2009 in sandy clay loam soil at Agricultural Research Station, Kathalagere, Davanagere District, Karnataka to study the growth and yield of rice as influenced by various levels of FYM and cattle urine application under Bhadra command area. The investigation consisting of 10 treatments was replicated thrice. Among different treatments, application of recommended dose of fertilizer+FYM at 10 t/ha recorded significantly higher nitrogen (122.9 kg/ha), phosphorus (31.3 kg/ha) and potassium uptake (94.0 kg/ha) as compared to other treatments. Whereas significantly lower uptake of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium was recorded with the application of FYM at 7.5 t/ha+cattle urine equivalent to 75 kg N/ha. Similarly, significantly higher grain yield (45.4 q/ha), straw yield (57.8 q/ha), net returns (Rs. 34732/ha) and B : C ratio (2.57) were recorded with the application of FYM at 12.5 t/ha+cattle urine equivalent to 125 kg N/ha as compared to other treatments. Whereas significantly lower grain yield (33.7 q/ha), straw yield (46.3 q/ha), net returns (Rs. 24024/ha) and B : C ratio (2.0) were recorded in the treatment with the application of FYM at 7.5 t/ha+cattle urine equivalent to 75 kg N/ha. 4. MOHINDER SINGH, R. K. PANNU*, S. S. DAHIYA AND A. K. DHAKA [Effect of agronomical practices on yield and quality of wheat under different cropping systems in Haryana]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 15-19 (2012). Department of Agronomy CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar-125 004 (Haryana), India *(e-mail : pannurk@hau.ernet.in) The survey was conducted in Haryana state during rabi season of 2005-06 on 972 farmers in 54 villages of 16 districts with respective cropping system i. e. pearl millet-wheat, cotton-wheat and rice-wheat. The 18 farmers from each village were selected randomly covering small (<2.0 ha), medium (2-4 ha) and large (>4.0 ha) group of land holders. Only those farmers were selected, who had grown PBW 343 variety of wheat. The sample sizes for pearl millet-wheat, cotton-wheat and rice-wheat of all three small, medium and large farm size groups were 90, 108 and 126, respectively. Yield reported in rice-wheat system was higher than cotton-wheat and pearl millet-wheat system. Maximum yield was observed with the use of more than five bags urea/ha. Numbers of irrigations above 4 and seed rate above 100 kg/ha were also reported to increase in yield. Protein content of wheat in pearl millet-wheat system was the highest. Protein content in late sown wheat in pearl millet-wheat system was higher than cotton-wheat and rice-wheat systems. Seed rate of 100 kg/ha and nitrogen dose of five bags of urea/ha gave significantly higher protein content. Quantitative production of wheat in rice-wheat and cotton-wheat cropping systems was higher than pearl millet-wheat system but quality in terms of protein content was significantly superior to both the rice-wheat and cotton-wheat systems. Hence, export market should be developed in quality grain producing zone i. e. in pearl millet-wheat growing areas, where lower percentage of farmers use higher nitrogen doses and cultivation practices were numerically better than other cropping systems. 5. NARESH KUMAR, RAM NIWAS, M. L. KHICHAR, JUGAL K. MANI AND SUBASH CHANDER [Influence of direction of sowing on growth and yield of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.)]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 20-23 (2012). Department of Agricultural Meteorology CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar-125 004 (Haryana), India Field experiment was conducted at the research area of the Department of Agricultural Meteorology, CCS Haryana Agricultural University Hisar, situated at 75º46¢E longitude, 29º10¢N latitude and altitude of 215.2 m above mean sea level during rabi season of 2004-05. The four varieties of barley viz., BH 393, BH 75, BH 338 and DWR 28 were sown in east-west and north-south row directions with three replications to study the influence of direction of sowing on growth and yield of barley. There was no much effect of direction of sowing on plant height of barley genotypes. The maximum value of LAI was higher in north-south direction (3.6) as compared to east-west direction (3.1). Dry matter produced at maturity was 1104.7 and 977.6 g/m2 in north-south and east-west direction, respectively. Highest dry matter was produced by BH 393 among cultivars. Maximum grain yield was observed in BH 393, whereas north-south sown crop produced higher grain yield as compared to east-west sown crop. Harvest index was observed maximum in north-south sowing (39.7) as compared to east-west sowing (38.5). 6. S. R. GADAKH, M. S. SHINDE, A. R. GAIKWAD AND V. R. PATIL [Phule Revati : A new rabi sorghum variety for irrigated condition]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 24-27 (2012). All India Co-ordinated Sorghum Improvement Project Mahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth, Rahuri-413 722, District Ahmednagar (M. S.), India Phule Revati (RSV 1006), a new rabi sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] variety developed from the cross CSV 216 x SPV 1502 through multi-environment testing was found superior in grain and fodder yield over the six checks viz., CSV 18, Phule Yashoda, Phule Vasudha, M 35-1, PKV Kranti and Parbhani Moti. On an average of 19 tests under irrigated condition, it gave 4585 kg/ha grain yield as against 3233 kg/ha of CSV 18, 3775 kg/ha of Phule Yashoda, 3947 kg/ha of Phule Vasudha,3392 kg/ha of M 35-1, 3825 kg/ha of PKV Kranti and 3387 kg/ha of Parbhani Moti, thus amounting to 41.8, 21.4, 16.1, 35.2, 19.8 and 35.3% increase over CSV 18, Phule Yashoda, Phule Vasudha, M 35-1, PKV Kranti and Parbhani Moti, respectively. As regards fodder yield, it had recorded higher mean of 11527 kg/ha over CSV 18 (9927 kg/ha), Phule Yashoda (9944 kg/ha), Phule Vasudha (9921 kg/ha), M 35-1 (9555 kg/ha), PKV Kranti (9893 kg/ha) and Parbhani Moti (9638 kg/ha), thus amounting to 16.1, 15.9, 16.2, 20.6, 16.5 and 19.6% increase over CSV 18, Phule Yashoda, Phule Vasudha, M 35-1, PKV Kranti and Parbhani Moti, respectively. Phule Revati gave 20.9 and 16.3% more grain yield over CSV 18 and Phule Vasudha, respectively, in 65 adaptive trials under irrigated conditions. As regards fodder yield, Phule Revati recorded 18.3 and 15.3% high fodder yield over CSV 18 and Phule Vasudha, respectively. Besides being the high yielder RSV 1006 (SPV 1830) was classified as medium maturity group (118-120 days), mid-tall (220-240 cm), medium bold grain (32-35 g/1000 seeds), pearly white round grain with high degree of tolerance to shootfly (DH 28.9%), stem borer (DH 4.68%) and charcoal rot (26.4 %). The roti and fodder qualities of Phule Revati are excellent to that of M 35-1. The variety RSV 1006 was, therefore, released under the name, Phule Revati for irrigated condition with medium to deep soils of western Maharashtra. 7. B. R. MUTKULE, M. S. SHINDE, V. R. PATIL, A. R. GAIKWAD AND S. R. GADAKH [Heat unit efficiency in sweet sorghum]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 28-30 (2012). All India Coordinated Sorghum Improvement Project Mahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth, Rahuri-413 722, District Ahmednagar (M. S.), India The experiment was conducted with 18 sweet sorghum genotypes during kharif and rabi 2009. The heat unit efficiency studies revealed that the heat unit efficiency (HUE) for cane yield and dry matter production was higher during kharif season, while lower during rabi season. The HUE for grain yield was higher during rabi season than kharif season. The genotypes RSSV-260, RSSV-138, CSV-19SS, RSSV-106 and RSSV-167 in kharif and RSSV-138, RSSV-106, RSSV-192 and RSSV-167 in rabi season were observed to be the most efficient in conversion of absorbed heat into green cane yield. The genotypes RSSV-167, RSSV-138, RSSV-82, RSSV-192, RSSV-104, CSV-19SS and RSSV-106 during kharif season and the genotypes RSSV-138, RSSV-167, RSSV-106, RSSV-192 and CSV-19SS during rabi season were observed to be the most efficient in conversion of absorbed heat into dry matter production. As regards grain yield, the genotypes RSSV-82, RSSV-191, RSSV-104, RSSV-120, RSSV-166, RSSV-138, RSSV-106, RSSV-167, SSV-84 and CSV-19SS in kharif and the genotypes RSSV-82, CSV-19SS and RSSV-99 in rabi season were observed to be the most efficient in conversion of absorbed heat into grain yield. 8. J. V. PATIL, S. R. GADAKH, M. S. SHINDE, A. R. GAIKWAD AND V. R. PATIL [CSV 22 (SPV 1626) : A new high yielding sorghum variety for post-rainy season]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 31-34 (2012). Sorghum Improvement Project Mahatma Phule Krishi Vidyapeeth, Rahuri-413 722 ( M. S.), India CSV 22 (SPV 1626), a new rabi sorghum variety developed from the cross SPV 1359 x RSP-2 at Rahuri was found superior in grain and fodder yield over two checks viz., M 35-1 and CSV 216. Overall mean of 35 tests, it gave the grain yield of 23.4 q/ha against 19.4 q/ha, of M 35-1 and 20.8 q/ha of CSV 216, thus amounting to an increase of 20.6 and 12.5% over checks, respectively. As regards fodder yields, it had recorded higher mean of 71.4 q/ha over M 35-1 (62.5 q/ha) and CSV 216 (70.8 q/ha), thus amounting to 14.2 and 0.85% increase over the checks, respectively. Besides being the higher yielder, CSV 22 was classified as medium maturity group (118 to 122 days), mid tall (180 to 210 cm), medium round grain (30 to 32 g/1000 seeds), pearly white grain with moderate tolerance to shootfly pest (39.7% dead heart) and tolerance to charcoal rot (22.7 %). Due to distinct superiority in yield was found over the M 35-1 and CSV 216, good grain and fodder quality on par with M 35-1 the variety SPV 1626 was, therefore, released under the name, CSV 22 for the cultivation in the rabi growing states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Gujarat for deep soils. 9. P. R. KHOSEPATIL, D. A. THAKKER, A. A. KHULE, A. H. RATHOD, P. O. VAGHELA AND B. S. RATHORE [Gene effects for yield, yield attributes and quality parameters in Indian mustard [Brassica juncea (L.) Czern and Coss] by generation mean analysis]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 35-38 (2012). Department of Genetics & Plant Breeding S. D. Agricultural University, Sardarkrushinagar-385 506 (Gujarat), India The components of generation means were partitioned for seed yield, yield attributes and quality parameters in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea (L.) Czern and Coss) with three sets of crosses viz., Cross I : GM 1 x NUDH YJ 3, Cross II : JM 2 x EC 287711 and Cross III : BIO772 R x NUDH YJ 3 using six basic generations (P1, P2, F1, F2, BC1 and BC2). The experimental material was grown in compact family block design (CFBD) with three replications during rabi 2010-11. Significant scaling tests for all the characters in all the crosses revealed that inter-allelic interactions were involved in the inheritance of all the characters except for length of main branch and lenoleic acid in cross III (BIO772 R x NUDH YJ 3), where only allelic interaction was involved for the inheritance of this trait. Estimates of gene effects revealed significant role of all the gene actions i. e. additive, dominance and epistasis in governing almost all the characters studied except 1000-seed weight, number of branches per plant and protein content. 10. RAJBEER SINGH TOMAR [Response of linseed (Linum usitatissimum) to sources and doses of sulphur in alluvial soils of Madhya Pradesh]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 39-41 (2012). Department of Soil Science R. V. S. Krishi Vishwa Vidyalaya, Gwalior-474 002 (Madhya Pradesh), India Field experiment was conducted on linseed crop with four sulphur sources viz., gypsum, single super phosphate, ammonium sulphate and elemental sulphur and four doses of sulphur i. e. 0, 10, 20 and 30 kg S/ha on Vertic Ustochrepts during rabi season of 2008-09. Results revealed that ammonium sulphate was the yielder and nutrient uptake significantly over elemental sulphur and single super phosphate. Highest N, P2O5 and S available status and balance sheet of nutrient recorded under ammonium sulphate and highest available and balance sheet of K2O was recorded with gypsum. Application of 20 kg S/ha recorded highest available and balance sheet of N, while 30 kg S/ha recorded highest available and balance sheet of P2O5, K2O and S. 11. RAJIB KUNDU* AND SUKANTA PAL [Arsenic accumulation in sesame (Sesamum indicum) cultivars under deltaic Bengal conditions]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 42-46 (2012). ICAR Niche Area of Excellence, Directorate of Research Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya, Kalyani-741 235, Nadia (West Bengal), India *(e-mail : rajibagro2007@gmail.com) Arsenic is a toxic metalloid, widely available in the natural ecosystem, and poses serious problem in Gangetic delta basin of India and Bangladesh through contamination of groundwater and drinking water. The widespread arsenic contamination in West Bengal, distributed over 111 blocks primarily within 12 districts of the state, adjoining the river Bhagirathi, as well as contiguous districts of Bangladesh is of great concern. Arsenic uptake by plants and its translocation to the edible parts were observed to vary with crops and even among the cultivars of the same crop. Keeping this in view, the present investigation has been undertaken to study the arsenic accumulation and the varietal tolerance with relative pattern of arsenic uptake vis-à-vis yield and yield attributes by selected cultivars of sesame at farmers’ fields of village Nonaghata in Nadia district of West Bengal during summer season of 2007-08. The experiment was laid out in randomized block design (RBD) replicated thrice having the six selected popular sesame cultivars. The arsenic accumulation of different plant parts was estimated by using AAS, PerkinElmer AAnalyst-200 coupled with FIAS-400. Results revealed that different cultivars of sesame accumulated different amount of arsenic in different plant parts and arsenic accumulation in different parts of sesame remained in an order to root >leaf >stem >seed irrespective of all the cultivars tested. Regarding varietal effect cv. SWB 32-10-1 showed maximum accumulation of As in its seeds, whereas the least accumulation was noted from the cv. Rama. The yield and different yield attributes of different cultivars of sesame were significantly different from each other. 12.C. Z. CAI*, J. B. SHAO AND Y. LIANG [Analyses on soybean yield in China based on prediction of yield potential]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 47-51 (2012). Institute of Economic Research Guizhou University of Finance and Economics, Guiyang-550 004, China *(e-mail : caichengzhi@263.net) The maximum yield growth range of per unit soybean yield in China is analyzed from three aspects including photosynthesis production potential of soybean, the changing trend of per unit soybean in the previous years and potential of distribution area of agricultural crops. In the paper, the potential of using light, the external potential of historical yield evolution trend and AEZ (agricultural ecological zone) are applied to calculate the per unit yield potential of Chinese soybean. The results show that the maximum growth range of per unit yield in different stages was different : before 1985, the growth range was 10%; before 1988, the growth range was 9%; before 1994, the growth range was 8%; before 1999, the growth range was 7% and before 2004, the growth range was 6%. Any variety of soybean and planting technology higher than above the growth range can only be promoted in restricted area or has the statistical error. The results are of reference significance to Chinese soybean production. 13. V. S. BAVISKAR, H. S. DAMAME, V. C. RAJ AND P. G. SHETE [Growth, yield and quality parameters of clusterbean [Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (L.) Taub.] as influenced by organic fertilizers and different levels of sulphur for vegetable purpose]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 52-54 (2012). Department of Agronomy Navsari Agricultural University, Navsari-396 450 (Gujarat), India *(e-mail : vijendra22kar@gmail.com) A field study was conducted during summer season of 2008 at College Farm, Navsari Agricultural University, Navsari to study the influence of organic fertilizer and different levels of sulphur on growth, yield and quality of clusterbean [Cyamopsis tetragonoloba (L.) Taub.] for vegetable purpose. Three levels of organic fertilizer and three levels of sulphur were tried. Among organic fertilizers, biocompost @ 5 t/ha registered significantly higher plant height (145.58 cm), dry matter production (65.95 g/plant), green pod (5325 kg/ha), straw (3137 kg/ha) yields, protein content (20.30%) and protein yield (188.68 kg/ha) over control. Similarly, sulphur levels also recorded significant effect in increasing all these growth, yield and quality parameters. Sulphur @ 50 kg/ha registered higher plant height (152.32 cm), dry matter production (67.17 g/plant), green pod (6071 kg/ha), straw yields (3344 kg/ha), protein content (21.23%) and protein yield (208.51 kg/ha) as compared to all other treatments. 14. SUDEEP SINGH AND G. S. BUTTAR [Integrated nutrient management in clusterbean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba) under irrigated conditions]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 55-56 (2012). PAU Regional Station, Bathinda-151 001 (Punjab), India The experiment was conducted at Research Farm of Punjab Agricultural University Regional Station, Bathinda during kharif seasons of 2008-09 and 2009-10. The results showed that application of fertilizer at the rate of 10 kg N+20 kg P2O5/ha and 20 kg N+40 kg P2O5/ha increased the mean seed yield to the tune of 10.7 and 19.6% over the control, respectively. The application of Rhizobium and PSB increased mean seed yield by 9.2 and 19.1% over control, respectively. However, the combination of both inoculants further failed to significantly increase the seed and straw yield of clusterbean further. 15. NEMJONG RONRANG, D. S. DABAS AND R. P. NARWAL [Effect of long-term application of farm yard manure and nitrogen on manganese fractions in soil]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 57-60 (2012). Department of Soil Science CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar-125 004 (Haryana), India A long-term field experiment on compensation of fertilizer nitrogen (N) through use of farm yard manure (FYM) on pearl millet (B)-wheat (W) sequence since October 1967 was undertaken at Research Farm of the Department of Soil Science, CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar. The present study was conducted to assess the effect of the experiment on the manganese (Mn) fractions in the soil after about 35 years of experimentation. The treatments of the experiment consisting of three doses of FYM (15, 30 and 45 mg/ha/year) indicated as F15, F30 and F45 applied in three different months i. e. in summer, in winter and in both the seasons (B+W). One control of FYM (F0) was also included. These 10 treatments (three FYM levels x three modes of FYM+1 control) were assigned in main plots and each main plot was divided into three sub-plots receiving nitrogen at the rate of 0, 60 and 120 kg/ha applied through urea. All the treatments were replicated four times. For the present study, soil samples were collected from only two out of three levels of nitrogen i. e. 0 and 120 kg N/ha and from two out of four replications. The FYM levels increased the readily soluble Mn in soil from 0.9 to 3.58 ppm. Similarly, the weakly and specifically adsorbed Mn increased from 6.42 to 12.74 ppm; carbonate bound Mn from 135.49 to 164.68 ppm; oxide Mn from 26.35 to 35.31 ppm and total Mn from 213 to 514 ppm from control of FYM to 45 mg FYM/ha year. 16. NEMJONG RONRANG, D. S. DABAS AND R. P. NARWAL [Dynamics of manganese adsorption and desorption in soil under long-term farm yard manure and nitrogen application]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 61-64 (2012). Department of Soil Science CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar-125 004 (Haryana), India A long-term field experiment on compensation of fertilizer nitrogen (N) through use of farm yard manure (FYM) on pearl millet (B)-wheat (W) sequence was undertaken since October 1967 at Research Farm of the Department of Soil Science, CCS Haryana agricultural university, Hisar. The treatments of the experiment consisted of three doses of FYM (15, 30 and 45 mg/ha/year) applied in three different months i. e. in summer bajra (B), in winter wheat (W) and in both the seasons (B+W). The control treatment of FYM (F0) was also included. These 10 treatments (three FYM levels x three modes of FYM+one control) were assigned in main plots and each main plot was divided into three sub-plots receiving nitrogen at the rate of 0, 60 and 120 kg/ha applied through urea. All the treatments were replicated four times. The present study was conducted to assess the sorption phenomena of Mn in the soil after about 35 years of start of the experiment. Soil samples were collected from only two out of three levels of nitrogen i. e. 0 and 120 kg N/ha and from two out of four replications. Sorption studies were made using Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption isotherms. The parameters of these equations were calculated to describe the adsorption phenomena. 17. PARTHA CHOUDHURI* AND J. C. JANA [Effect of intercropping on nutrient uptake and quality parameter estimation in potato based intercropping system]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 65-68 (2012). Department of Vegetable and Spice Crops Uttar Banga Krishi Viswavidyalaya, Pundibari, Cooch Behar-736 165 (West Bangal), India *(e-mail : partha2909@rediffmail.com) A field experiment was conducted at the Instructional Farm of UBKV during rabi seasons of 2008 and 2009 to assess the influence of intercropping on nutrient uptake and quality parameter estimation in potato. The treatments were : T1–Sole potato (control), T2–Sole mustard, T3–Potato +mustard at 1 : 1 row ratio, T4–Potato+mustard at 2 : 1 row ratio, T5–Potato+mustard at 3 : 1 row ratio, T6– Potato+mustard at 4 : 1 row ratio and T7–Potato+mustard at 5 : 1 row ratio and were laid out in randomized block design (RBD) with four replications. The results showed that significantly maximum residual nitrogen per hectare was obtained in sole mustard plots (178.32 kg). Experimental results also revealed that among different treatment combinations, maximum phosphorus content of soil after harvesting was obtained from sole potato plots (30.09 kg/ha) closely followed by sole mustard plots (29.34 kg). Lowest phosphorus content of soil after harvesting was obtained from potato and mustard grown in 2 : 1 ratio plots (24.87 kg/ha). Maximum potassium content (159.93 kg/ha) in soil after harvesting of potato and mustard was recorded in sole mustard plots. No significant differences were found for quality parameters due to intercropping. 18. A. W. GICHANGI, S. Y. C. ESSAH*, R. N. MBOGO, J. G. WAMUYU AND B. N. MACHARIA [Sweet potato marketing and estimation of post-harvest losses in Kenya]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 69-75 (2012). National Plant Breeding Research Center P. O. Private Bag, Kenya Agricultural Research Institute, Njoro, Kenya *(e-mail : sessah@lamar.colostate.edu) The evaluation of post-harvest losses at different stages of marketing and their impact on farmers’ net price, marketing costs, margins and efficiency are presented in this study. Studies have shown that the traditional methods that are used to estimate the economic impact of post-harvest losses tend to overestimate the farmers’ net price and margins of intermediaries. In this study, the margin of retailers after taking into account the physical loss during retailing has been found to be negative, which otherwise, was a profit in the traditional estimation method. The producers’ net share and wholesalers’ margins also decreased. The results of this study indicated that marketing efficiency was inversely proportional to marketing losses. Farmer group marketing was found to be a more efficient system in operation and price terms. Marketing cost was identified as the major constraint in the wholesale marketing channel, while commission charges demonstrated in the farmer group channel, were found to help in reducing the price-spread, and hence increased the producers’ margin. 19. N. MONTESSORI DEVI, R. K. BHANISHANA DEVI AND RANJAN DAS [Enhancement of physiological efficiency of cabbage [Brassica oleracea (L.) var. capitata] using foliar nutrition of boron]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 76-80 (2012). Department of Botany and Plant Pathology Central Agricultural University, Imphal-795 001 (Manipur), India An experiment was conducted in two consecutive years (2009 and 2010) at Central Agricultural University, Imphal, Manipur to evaluate the effects of foliar application of borax @ 0.1% solution on cabbage [Bassica oleracea (L.) var. capitata]. The growth (plant height, leaf numbers, leaf length and fresh biomass production) was affected by the boron levels. The foliar spray was done twice at 25 and 50 days after transplanting (DAT). It showed significant increase in plant height, number of leaves, shoot fresh weight, dry weight, root fresh weight and dry weight and yield. The head size (diameter) was increased with application of borax. 20. M. PRAKASH, B. SUNIL KUMAR, S. PADMAVATHI AND G. SATHYANARAYANAN [Studies on combining ability and heterosis through full diallel analysis in bhendi [Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench]]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 81-84 (2012). Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding Annamalai University, Annamalainagar-608 002 (Karnataka), India A full diallel analysis involving six bhendi genotypes was used to study the combining ability and heterosis for fruit yield and its component characters. The study revealed that the Kamini, Bakra and P7 were good general combiners. The cross combinations of Kamini x Bakra exhibited highly significant and positive specific combining ability and standard heterosis for fruit yield and other yield contributing traits. 21. K. RADHA RANI [Genetic variability and character association in ridge gourd]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 85-88 (2012). Vegetable Breeding Station Agricultural Research Institute, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad (A. P.), India Fourteen genotypes of ridge gourd were evaluated during kharif 2006 and 2007 at Vegetable Breeding Station, Agricultural Research Institute, Rajendranagr, Hyderabad and showed that the phenotypic coefficient of variation was greater than genotypic coefficient of variation for most of the traits under study. Relatively high phenotypic and genotypic coefficients of variation were recorded for fruit length, number of fruits per vine and fruit yield. High heritability associated with high expected genetic advance as per cent of mean was observed for fruit length, number of fruits per vine and node number at first fruit harvested which could be improved by simple selection in early generations. The results revealed that the yield was significantly and positively correlated with number of fruits per vine both at genotypic and phenotypic levels. 22. TALWARE PRATAP, N. K. GUPTA AND SAKET DUBEY [Effect of organic, inorganic and biofertilizers on growth and productivity of garlic (Allium sativum) cv. G-323]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 89-97 (2012). Department of Horticulture College of Agriculture, Indore (M. P.), India The fertilizers are the substances which are used to improve the fertility of soil, thus improving the level of production, but still the rate of improvement of growth and production varies with types of fertilizers used i. e. organic, inorganic or biofertilizers, so the present investigation was designed to determine the efficacy of improvement in garlic (Allium sativum) cv. G-323 under different categories of fertilizer and in their various combination ratios. The present investigation was laid out during rabi season in randomized block design having seven treatments containing inorganic (RDF), organic (FYM) and biofertilizer (Azotobacter+PSB) in various proportions. The growth parameters of garlic viz., plant height, number of leaves per plant, length and width of leaf, fresh and dry weight of plant and leaf area index were recorded, while in case of productive parameters, weight per bulb, weight of cloves per bulb and number of cloves per bulb and maximum bulb yield were recorded. The growth parameters like plant height, number of leaves per plant, length and width of leaf, fresh and dry weight of plant and leaf area index were significantly superior under the treatment 75% RDF + 5 t FYM/ha + Azotobacter + PSB over rest of the treatments. Seed inoculation with PSB and Azotobacter under 75% RDF with incorporation of 5 t FYM/ha resulted in significantly longer and wider bulb diameter (3.52 and 3.54 cm, respectively), weight per bulb, weight of cloves per bulb and number of cloves per bulb and longer clove with maximum bulb yield (133.16 q/ha). Also, the maximum net return amount was also found to be with this treatment combination. Therefore, application of 75% RDF+5 t FYM/ha+Azotobacter+PSB annexed with highest benefit : cost ratio (5.54) and is the best recommended treatment combination. 23. H. CHOUDHURY, R. K. GOSWAMI, S. BORA, P. MAHANTA AND J. DAS [Effect of lead on germination and early seedling growth of French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.)]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 98-101 (2012). Department of Crop Physiology A. A. U. B. N. College of Agriculture, Biswanath Chariali, Sonitpur-784 176 (Assam), India The phytotoxicity effect of different concentrations of lead on germination and early seedling growth of French bean was studied in the year 2008-09. During the study, it was found that the seed germination per cent and early seedling growth of French bean in terms of root length, shoot length, fresh and dry weight of root and shoot, vigour index and tolerance index were maximum at control and a gradual reduction of the above mentioned indices was observed with the increase in lead concentration. The phytotoxicity percentage in the tested seeds, on the other hand, was in ascending order with the increase in lead concentration. However, at fairly high concentration of 100 ppm lead, 58.05% French bean seeds germinated with 25.75% tolerance index. 24. S. ANUJA [Genetic variability studies in vegetable amaranthus]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 102-105 (2012). Department of Horticulture Annamalai University, Annamalainagar-608 002 (Tamil Nadu), India Genetic variability, heritability and genetic advance for 14 characters in 100 genotypes of vegetable amaranth (Amaranthus sp.) were studied. Considerable amount of phenotypic and genotypic variability was observed for number of leaves, root weight and leaf weight in both summer and monsoon seasons. High heritability coupled with high genetic advance was observed for plant height, number of leaves, leaf length, leaf width and green yield per plant indicating that additive gene effects were operating for these characters and selection pressure could be applied on them for yield improvement. 25. S. ANUJA [Correlation and path coefficient analysis in amaranthus]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 106-111 (2012). Department of Horticulture Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar-608 002 (Tamil Nadu), India In the present study, correlation and path coefficient anlaysis with 13 quantitative characters was carried out in 100 genotypes of vegetable amaranth. Highly significant and positive correlation with green yield was observed with leaf weight, stem weight and plant height, whereas leaf/stem ratio showed negative association with green yield. Path coefficient analysis revealed that stem weight, leaf weight and root weight were the most important yield components. Selection programme based on these characters is suggested for further improvement. 26. KN. MONTESSORI DEVI, R. K. BHANISHANA DEVI, A. PREMILA DEVI AND RANJAN DAS [Changes of some nutrient contents in Pyrus indica fruits of Manipur under storage condition]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 112-115 (2012). Department of Botany and Plant Pathology Central Agricultural University, Imphal-795 001, India In the present study analysis of healthy and infected Heitup fruit, Pyrus indica of the same variety (during storage) was studied. Samples of both healthy and infected pyrus fruit were analyzed for the nutritional components except moisture content. The mineral contents (N and Fe) were determined by spectrophotometically Similarly, carbohydrate content was lower in diseased leaves than in healthy onion leaves. The both the minerals were significantly (P<0.05) lower in diseased fruit compared to the healthy (control) fruit indicating the deterioration of pyrus fruit which had a significant impact in reducing and total sugars in the nutritional value of the pyrus fruit. It is important to avoid such deterioration with a view to enhance nutrient bioavailability for human consumption. 27. PRITY DAS, L. PASWAN, H. CHOUDHURY, JYOTSHNA DAS AND PINKI SAIKIA [Effect of inorganic, organic and biofertilizers on flower yield and flower quality of tuberose (Polianthes tuberose L.)]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 116-119 (2012). Department of Horticulture Assam Agricultural University, Jorhat-785 013 (Assam), India During 2008-09, a field experiment was conducted to study the effect of inorganic, organic and biofertilizers on flower yield and flower quality of tuberose. The results of the investigation revealed that the flower yield and flower quality of tuberose in terms of spike length, floret number/spike, rachis length, self life of spike and vase life of floret were significantly affected by different treatments. The plants treated with enriched compost @ 10 t/ha produced the best results in respect of all the above mentioned parameters followed by plants treated with enriched compost (10 t/ha)+biofertilizer. The highest benefit : cost ratio (3.38 : 1) was calculated in tuberose treated with enriched compost @ 10 t/ha. 28. DEEPAK SINGH AND SANJAY PATHAK [Effect of IBA and NAA on propagation of Barbados cherry through layering]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 120-122 (2012). Department of Horticulture Narendra Deva University of Agriculture & Technology, Faizabad-224 229 (U. P.), India An experiment was carried out during 2008-09 at Main Experimental Station, Department of Horticulture, Narendra Deva University of Agriculture & Technology, Kumarganj, Faizabad (U. P.) with the objective to find out optimum concentration of IBA, NAA and their combinations on air layering of Barbados cherry. Amongst various concentrations of IBA, NAA and their combinations, IBA 1500 ppm treatment proved best treatment in respect of per cent rooted air layers, number of primary roots, number of secondary roots, root quality and per cent establishment. 29. B. MAMATHA AND T. N. SHIVANANDA [Nutrient uptake of Coleus vettiveroides as influenced by different quantities of organic manures]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 123-127 (2012). Indian Institute of Horticultural Research Hessarghatta Lake Post, Bangalore-560 089 (Karnataka), India Coleus vettiveroides, commonly known as Hrivera, is a perennial herb belonging to family Lamiaceae, grown on sandy loams along riverbanks in plains. Among various cultural practices conducive for enhancing root yield, nutrient management plays an important role in enhancing the yield per unit area. The rooted stem cuttings of C. vettiveroides were planted to main field with a spacing of 60 x 45 cm between plant to plant and row to row. There were 21 plots with size 4.0 m length and 3.5 m breadth accommodating 36 plants per plot, each treatment replicated three times. The growth observations and yield data were taken from selected plants excluding the border plants and plants were harvested after 140 days after planting and biomass was calculated and plant and soil samples were collected for further analysis. Total N uptake (50.13 kg/ha) and total K uptake (119.11 kg/ha) was found to be significantly higher with the application of recommended FYM 10 t/ha+recommended NPK and total P uptake (8.58kg/ha) and was found to be significantly higher with recommended FYM 10 t/ha+100% N. 30. B. MAMATHA AND T. N. SHIVANANDA [Influence of different growth media to promote plant and root growth of Coleus vettiveroides]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 128-130 (2012). Indian Institute of Horticultural Research Hessarghatta Lake Post, Bangalore-560 089 (Karnataka), India Coleus vettiveroides, commonly known as Hrivera, is a perennial herb belonging to family Lamiaceae. Plant is succulent, aromatic herb with quadrangular stems and branches and deep straw coloured roots, leaves glandular hairy, broadly ovate with dentate margins and prominent veins on the back. A pot experiment was conducted to standardize the growth media for optimum secondary root yield. The experiment was conducted at the Indian Institute of Horticultural Research (IIHR), Hesaraghatta, Bangalore. Plant height (83 cm) was significantly higher with 25% sand + 75% soil, which was on par with 50% sand+50% soil+FYM 10 t/ha (82.34 cm). Number of leaves per plant (108), number of branches per plant (14), leaf weight per plant (236 g), stem weight per plant (440 g) and primary root weight per plant (45 g) were significantly higher with the pot mixture of 50% sand+50% soil+FYM 10 t/ha. Secondary root weight per plant (67.67 g) was significantly higher in 100% soil. Total biomass per plant (782.34 g) was significantly higher with pot mixture of 50% sand+50% soil+FYM 10 t/ha. 31. S. R. PANCHOLI, S. N. SHARMA, YOGENDRA SHARMA AND S. R. MALOO [Combining ability computation from diallel crosses comprising ten bread wheat cultivars]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 131-141 (2012). All India Coordinated Wheat and Barley Improvement Project S. K. R. A. U., Agricultural Research Station, Durgapura, Jaipur-302 018 (Rajasthan), India Combination ability analysis in bread wheat [Triticum aestivum (L.) em. Thell.] involving 10 diverse parents and their 45 F1 and F2 progenies under normal sown condition indicated significant differences among the parents for gca and crosses for sca for all the characters studied. The gca and sca components of variance were significant for all the traits. The gca/sca ratio showed preponderance of non-additive gene actions for characters. Based on per se performance and gca effects, parents Raj 4058 and HP 1863 emerged as good general combiners for grain yield per plant and average to high combiners for other important traits. On the basis of per se performance and sca effects the crosses for grain yield HP 1863 x Raj 4058, WH 786 x UP 2611 and PBW 533 x PBW 509 emerged as good specific cross combinations. To ensure further increase in grain yield, combining desirable yield components are advocated. The exploitation of additive and non-additive gene actions through bi-parental mating and/or diallel selective mating systems is suggested for tangible advancement of grain yield in bread wheat. 32. G. RAMYA*, K. MADHUSUDAN, P. E. PRADEEP, I. K. KALAPPANAVAR AND V. SUJAY [Multivariate analysis through D2 statistic among free threshable mutants of tetraploid wheat (Triticum sp.)]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 142-146 (2012). Dr. Sanjaya Rajaram Wheat Laboratory All India Coordinated Wheat Improvement Project University of Agricultural Sciences, Dharwad-580 005 (Karnataa), India *(e-mail : ramyag108@gmail.com) Assessment of genetic diversity using quantitative traits has been of prime importance in many contexts particularly in differentiating well defined populations and hence present study was undertaken to estimate genetic diversity among the free threshable lines of tetraploid wheat (Triticum sp.) derived through induced mutagenesis. During rabi 2009-10, 101 free threshable mutants which are in M4 generation with checks DWR 1006, DDK 1001 and DDK 1025 were evaluated in RCBD with two replications at Dharwad. Mahalanobis’s (1936) D2 statistic analysis was used for assessing the genetic divergence among the test entries. It was observed that days to maturity was the single largest contributor (64.34%) towards divergence followed by plant height (9.80%). Cluster pattern revealed that cluster I consisting of 82 genotypes (81 mutants and check DWR 1006) was the largest followed by clusters II, III and IV with 11, 7 and 2 mutants and 1 each in clusters V and VI with checks DDK 1001 and DDK 1025, respectively. Many free threshable mutants grouped in cluster I with check DWR 1006 may be due to durrumization of free threshable mutants. Considerable amount of genetic diversity in the material representing different mutagenic treatments revealed no relation between mutagenic treatment and genetic diversity. Maximum differences among the genotypes within the same cluster were shown by cluster IV (D2 =5.47) and clusters V and VI had no intra-cluster distance (D2=0.00) as they were represented by single genotype. When diversity among the clusters was studied, it showed a range of 5.90 to 12.84. Clusters II and III showed maximum inter-cluster distance (D2=12.84) and lowest inter-cluster distance was noticed between clusters I and V (D2=5.90). 33. ANITA R. SEHRAWAT, S. UPPAL, KRISHAN SEHRAWAT AND SUBHASH KAJLA [Efficient callus induction, plant regeneration and their selection at different NaCl levels in wheat crosses]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 147-152 (2012). Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar-125 004 (Haryana), India The experiment encompasses the in vitro culture of immature embryo of nine F1 hybrids including two salt tolerant cultivars Kharchia 375 and Kharchia 65, which were used as female parents. Initially all embryos were cultured on MS medium supplemented with 2, 4-D (5.0 mg/l) for callus formation. Proliferation of the callus on MS medium was fortified with 2, 4-D (3.0 mg/l). The callusing percentage among different crosses varied from 86.85-97.20%. These calli were placed on callus selection medium with graded concentrations of NaCl (4, 12, 20, 28 and 36 dS/m) and a gradual decrease in relative growth of calli under NaCl salinity (1068.80- 29.39) was observed. The different crosses reflected significant difference in the terms of their relative growth and dry weight of calli. The best cross among the various crosses for determination of relative growth (631.98) was between Kh 375 x HD 2009 and for dry weight (21.8 mg/g) between Kh 375 x WH 147. The regeneration potential of non-selected and selected cell lines was assessed on MS medium fortified with 1.0 mg/l BAP and 0.2 mg/l IAA. The shoot regeneration of cell lines selected on various concentrations of NaCl (4, 8, 12, 20 and 28 dS/m) was obtained. The per cent calli forming shoots were decreased with increasing NaCl concentrations of all the tested crosses. However, whole plant regeneration was recorded from untreated calli of all the hybrids. Total 147 spikes obtained from various crosses provided a wide genetic base showing variations for spike length, spikelet number and grain number per spike. Hence, the investigation seems to be relevant for production of somaclones and will prove a beneficial research for development of salt tolerant genotypes in wheat in future. 34. B. SUNIL KUMAR*, M. PRAKASH, G. SATHYANARAYANAN AND S. PADMAVATHI [Studies on combining ability and heterosis through line x tester analysis in maize (Zea mays L.)]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 153-157 (2012). Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar-608 002 (Tamil Nadu), India *(e-mail : sunil62@gmail.com) The present investigation was carried out in maize to identify the best combining parents, nature of gene action and heterosis. Combining ability studies revealed non-additive gene action for plant height, days to 50% tasseling, days to 50% silking, cob length, cob girth, number of grain rows per cob, number of grains per row, 100-grain weight and grain yield per plant. Based on per se performance, the lines FC 2, G 507 and the tester Lakshmi 2277 were adjudged as the best for most of the traits. Among the hybrids, FC 2/Lakshmi 4950 and G 507/Lakshmi 2277 exhibited high sca for all the economic traits. The hybrid G 507/Lakshmi 2277 was adjudged as the best, as it possessed significant and positive heterosis for all the characters except days to 50% silking. The hybrids FC 2/Lakshmi 4950 and G 507/Lakshmi 2277 showed desirable performance based on per se performance, sca and standard heterosis for most of the economic traits and could be exploited for further crop improvement. 35. S. VIJAYA BHASKAR REDDY, FARZANA JABEEN, M. R. SUDARSHAN, R. RANGA REDDY AND V. RAM REDDY [Combining ability studies for grain yield and its components and post-flowering stalk rot resistance in maize (Zea mays L.)]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 158-163 (2012). Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding College of Agriculture, Rajendranagar-500 030, Hyderabad (A. P.), India Line x tester analysis was conducted to study combining ability for yield, its components and post-flowering stalk rot disease resistance (PFSR) in maize. The mean sum of squares due to gca and sca were significant for all the characters indicating the presence of variability in combining ability of parents involved. Variances due to sca were larger than gca for all the characters indicating the predominance of non-additive gene action in expression of various traits studied. Among the lines CM-211 and BPPTI-38 were found to be the best general combiners for grain yield and PFSR disease resistance and likewise among hybrids, CM-120 x BPPTI-29, CM-207 x BPPTI-34, CM-120 x BPPTI-43 and CM-210 x BPPTI-34 were the best specific combiners for grain yield and PFSR disease resistance. 36. VISHAL PATEL, H. R. KHER, H. P. PARMAR AND R. M. PATEL [Combining ability analysis for qualitative characters in forage sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 164-166 (2012). Main Forage Research Station Anand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110 (Gujarat), India Combining ability for various qualitative traits viz., crude protein content, hydrocyanic acid content, neutral detergent fibre content and crude fibre content was studied through 3 x 15 line x tester mating design. Highly significant mean squares for gca and sca for majority of the traits indicated that sufficient variability existed for gca effects in the parents and that for the sca effects in the crosses. Higher and significant sca variance suggested a higher non-additive gene action for these traits. Parents S 1049, MP CHARI and GFS-3 among males and SURAT-1 and SURAT-2 among females were found to be the best general combiners. The hybrids viz., SURAT-1 x GFS-3 for crude protein content, SURAT-1 x GUNDRI for hydrocyanic acid content, SURAT-3 x GFS-3 for neutral detergent fibre content and SURAT-3 x AFS-30 for crude fibre content were best specific crosses and, therefore, these can be further exploited for selection of transgressive segregants. 37. VISHAL PATEL, H. R. KHER, H. P. PARMAR AND R. M. PATEL [Combining ability analysis for quantitative characters in forage sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 167-170 (2012). Main Forage Research Station Anand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110 (Gujarat), India Combining ability for various quantitative traits viz., days to 50% flowering, plant height at flowering, number of tillers per plant, number of leaves per plant, green fodder yield per plant and dry matter yield per plant were studied through 3 x 15 line x tester mating design. Highly significant mean squares for gca and sca for majority of the traits indicated that sufficient variability existed for gca effects in the parents and that for the sca effects in the crosses. Higher and significant sca variance suggested a higher non-additive gene action for these traits. Parents S 1049, GUNDRI and SSG-59-3 among males and SURAT-3 followed by SURAT-1 among females were found to be the best general combiners. The hybrids viz., SURAT-2 x PHULE AMRUTA, SURAT-1 x GUNDRI and SURAT-1 x SRF-286 were found to be the best specific crosses for green fodder yield per plant and, therefore, these can be further exploited for selection of transgressive segregants. 38. RAVI S. SINGH, B. C. SOOD AND NARESH KUMAR [Identification of yield attributes for selection through correlation and path analysis of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.)]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 171-177 (2012). Department of Crop Improvement CSK Himachal Pradesh Krishi Vishvavidyalaya, Palampur-176 062 (H. P.), India The importance of obtaining genetic diversity in support of plant breeding programme can hardly be overemphasized. Hence, the information on the relative magnitude of genotypic and phenotypic variability and correlation is of immense value in starting a scientific breeding programme. Further, knowledge of relative contribution of characters to yield, directly as well as indirectly, is also important in formulating suitable selection procedure. Early maturity coupled with high number of pods per plant, pod clusters per plant, biological yield per plant and harvest index appeared to be important constituents of an ideal high yielding lentil plant ideotype. The study further revealed that days to 50% flowering, days to 75% maturity, pod clusters per plant, pods per plant, 100-seed weight, biological yield per plant, seeds per plant and harvest index were important for selection. Therefore, for improvement in seed yield per plant in lentil, early selection can be practised effectively on the basis of days to 50% flowering, days to 75% maturity, pod clusters per plant and pods per plant. 39. A. I. PATEL, S. C. MALI, C. G. INTWALA AND J. R. NIZAMA [Genetic variability, correlation, path analysis and genetic divergence in greengram [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek]]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 178-184 (2012). Department of Tree Biology and Improvement Navsari Agricultural University, Navsari (Gujarat), India Variability, correlation, path coefficient and genetic divergence were studied in a set of 86 genotypes of greengram [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] grown at different locations in a randomized block design with three replications at Navsari Agricultural University, Navsari (Gujarat). Analysis of variance revealed that differences due to various genotypes were highly significant for all the characters, indicating considerable amount of variability among the genotypes tested. Correlation analysis revealed that seed yield per plant was found to be highly significant and positively correlated with plant height, number of clusters per plant, number of pods per cluster, number of pods per plant and number of seeds per pod at genotypic level. Path analysis indicated the highest positive direct effect for number of clusters per plant followed by plant height, 100-seed weight, number of pods per plant, number of seeds per pod and days to 50% flowering. The characters viz., number of pods per plant, seed yield per plant, number of clusters per plant, number of pods per cluster and plant height contributed maximum to the divergence. 40. T. KALAIMAGAL, A. R. MUTHIAH AND D. KUMARESAN [Inheritance of fertility restoration for A2 cytoplasm of pigeonpea [Cajanus scarabaeoides (L.) Thouars]]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 185-188 (2012). Department of Pulses Centre for Plant Breeding and Genetics Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore-641 003 (Tamil Nadu), India Information on the genetics of fertility restoration in a cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS) system facilitates breeding and or selection of restorer lines in hybrid breeding programmes involving CMS system. Inheritance of fertility restoration of A2 cytoplasm [Cajanus scarabaeoides (L.) Thouars] in pigeonpea was studied utilizing two CMS lines, CORG 990052A and CORG 990047A in combination with three restorers viz., Co 1R, Co 2R and Co 3R. Each cross was used to develop a set of materials consisting of the following generations viz., parental lines A, B and R; A x R- F1; A x F1–BC1F1 and F1 x F1–F2. The study of F2 generation indicated that the fertility restoration in Co 1R for CORG 990052A was governed by two independent dominant genes, while fertility restoration in Co 2R and Co 3R for CORG 990047A was governed by single dominant gene. The results were confirmed by studying the BC1F1 generation of the three crosses’ combinations. 41. MOHD. RAFIQ WANI, SAMIULLAH KHAN AND M. IMRAN KOZGAR* [Genetic enhancement of mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] through induced mutagenesis]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 189-193 (2012). Mutation Breeding Laboratory, Department of Botany Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh-202 002 (Uttar Pradesh), India *(e-mail : ) Mutagenesis has been widely used as a potent method of enhancing genetic variability for crop improvement. The variability induced by ethylmethane sulphonate (EMS) and hydrazine hydrate (HZ) for four quantitative traits viz., fertile branches per plant, pods per plant, 100-seed weight (g) and total plant yield (g) was evaluated to find out the selection response in M2 and M3 generations of mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek] var. NM-1. The mean values for yield and yield components increased significantly with all the treatments in both the generations. The genotypic coefficient of variation, heritability and genetic advance increased manifold in the treated population indicating that these traits are controlled by additive genetic variance and selection would be effective. Increase in mean values coupled with an increase in genetic variability for yield attributing traits suggests further possibilities of selecting more promising lines with high yield potential. 42. R. K. KHULBE, D. P. PANT AND D. V. SINGH [Genetic studies in horsegram from NW Himalayan regions of Uttarakhand, India]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 194-196 (2012). Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding G. B. Pant University of Agriculture & Technology, Pantnagar (Uttarakhand), India Evaluation of 26 horsegram accessions alongwith two checks, VLG-1 and VLG-10, revealed presence of moderate to high range of variation for all the characters. Coefficient of variation was high for pods/plant and yield/plant and low for days to maturity and seeds/pod. High broad sense heritability estimates were obtained for days to 50% flowering (73%), plant height (64%) and yield/plant (60%), and low for seeds/pod (14%). Genetic advance as per cent of mean was highest for pods/plant (19.32) and lowest for seeds/pod (0.14). Pods/plant exhibited highly significant and positive association with seed yield/plant (0.60). Pods/plant and 100-seed weight had positive direct effect, while plant height exhibited negative direct effect on seed yield/plant. The study suggested that emphasis may be placed on pods/plant and 100-seed weight in selecting superior genotypes. Three accessions IC 355888, PGR G-8 and PGR G-18 exhibited significantly higher yield than the best check VLG-10, suggesting scope for genetic enhancement of the crop by exploiting natural variation among the local cultivars and land races. 43. S. S. PRASAD* AND P. K. GUPTA [Compatibility of new insecticides and fungicides against stem borer and leaf blast on semi-deep water rice]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 197-200 (2012). N. D. U. A. & T. Crop Research Station, Ghaghraghat, Bahraich-271 901 (U. P.), India *(ssprasad24@gmail.com) Field experiments were conducted on semi-deep water rice variety Jalpriya during kharif seasons of 2007-08, 2008-09 and 2009-10 to study the compatibility of insecticides viz., flubendiamide and spinosad; and fungicides viz., isoprothiolane Fugi 1 and carpropamid Protega alone and tank mixed in all possible combinations against rice stem borer and leaf blast disease. The experiment failed during 2008-09 due to excess flooding of field at late stage of the crop. The infestation of stem borer and leaf blast varied from 2.12 to 7.27% and 2.29 to 15.35%, respectively, during the period. The results of two kharif seasons indicated that insecticidal and fungicidal treatments alone were effective against stem borer and leaf blast, respectively, whereas the combination treatments were effective against both stem borer and leaf blast. The combination of flubendiamide 20 WDG @ 0.25 g/l+isoprothiolane Fugi 1 @ 1.5 ml/l was most effective against both stem borer and leaf blast with 2.54 and 3.50% infestation, respectively, and fetched average grain yield of 23.53 q/ha. It was closely followed by flubendiamide 20 WDG @ 0.25 g/l + carpropamid Protega @ 1.0 ml/l with 2.35% stem borer infestation, 4.03% leaf blast disease severity and 22.51 q/ha grain yield. 44. DEVATA B. PATIL, S. M. THAKARE AND S. A. KONDE [Management modules for pod borers of pigeonpea, Cajanus cajan L.]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 201-206 (2012). Department of Entomology Post Graduate Institute Dr. Panjabrao Deshmukh Krishi Vidyapeeth, Akola-444 104 (M. S.), India Pigeonpea is found to be badly affected by pod borer complex since last four to five years and now it is a serious problem in all pigeonpea growing regions. This complex comprises Helicoverpa armigera, Exelastis atomosa and Melanagromyza obtusa, which is responsible to cause direct damage to pods and grains which result in the grain yield loss and fodder too. Because of this, India is facing deficit problems in pulses. This research made efforts to find out the suitable management modules, comprising the low cost and eco-safe technologies to manage this problem at the initiation point to avoid the damage and loss with keeping environmental harmony as synthetic pesticides have been found hazardous. The investigated results indicate that the ‘Biointensive module’ comprising seed treatment of Trichoderma @ 4 g/kg seed followed by spraying of Neem seed extract 5% at bud initiation stage followed by spraying of spinosad 45 SC @ 0.01% at 15 days after bud initiation stage, was found most effective in reducing larval population [Helicoverpa armigera, Exelastis atomosa (1.72; 2.54 l/plant, respectively)]; and pod damage at harvest by pod borer complex (13.2%) and recorded highest yield and ICBR alongwith higher population of natural enemies followed by IPM module i. e. collection and destruction of last year residues, ploughing of soil in April, selection of resistant variety, increased seed rate by 20%, seed treatment with Trichoderma @ 4 g/kg seed, spraying NSE 5% at bud initiation stage, spraying of NSE 5% at 5% fruiting bodies damage level and spraying of HaNPV 250 LE/ha for H. armigera if observed; and low cost technology module, consisting of deep ploughing in April, mechanical collection of larvae, use of moderately pest resistant variety i. e. Asha, increased seed rate by 20%, seed treatment with Trichoderma @ 4 g/kg seeds and spraying of NSE 5% at bud initiation stage and 15 days after bud initiation stage. All these three modules recorded lower larval population of pod borer complex, pod damage at harvest and recorded higher population of natural enemies and higher ICBR. 45. T. N. RAMESH, S. L. BASAVARAJU, K. PRASHANT, S. B. REVANAPPA, N. N. SRINIVAS AND RAJKUMAR [Studies on comparative biology of groundnut pod bug, Elasmolomus sordidus (Fabricius) (Hemiptera : Lygaeidae) reared on groundnut, sesamum, soybean and sunflower]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 207-210 (2012). Department of Entomology University of Agricultural Sciences (GKVK Campus), Bangalore-560 065 (Karnataka), India Studies were carried out at the Department of Entomology, University of Agricultural Sciences, Gandhi Krishi Vignana Kendra (GKVK), Bangalore to understand the biology of Elasmolomus sordidus on different crops such as groundnut, sesamum, soybean and sunflower. Groundnut pod bug, Elasmolomus sordidus (F.) is a serious post-harvest pest of groundnut. The pod bug due to its feeding, in addition to causing weight loss in affected pods, also affects the quality parameters of groundnut such as oil content, flavour and seed viability. Adult E. sordidus reared on groundnut, sunflower and sesamum laid on an average 194.76±55.39, 182.56±75.08 and 223±57.75 eggs, respectively. The total lifecycle of the bug on groundnut, sunflower and sesamum was 54.71±8.34, 54.47±5.98 and 53.20±6.92 days, respectively. From the above investigation, it is clear that the pod bug reared on sesamum showed the shortest post-embryonic development, highest fecundity and lowest longevity. 46. BHARTI MALHOTRA, NEHANJALI PARMAR, SUHASINI HUDDONE AND SATYA VRAT BHARDWAJ [Development of diagnostic tools for accurate and efficient detection of lily symptomless carlavirus by RT-PCR]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 211-215 (2012). Department of Biotechnology Dr. Y. S. Parmar University of Horticulture and Forestry, Nauni, Solan-173 230, (H. P.), India To facilitate efficient and accurate detection of lily symptomless carlavirus (LSV), specific primers were designed on the basis of nucleotide sequences of LSV coat protein (CP) gene. It has been found that amongst various viruses infecting Lilium in Himachal Pradesh, LSV is the most prevalent virus infecting lilies, with an incidence as high as 95% and it causes 30% reduction in flower yield per plant. After assuring the presence of virus by serological indexing, different softwares were used for primer designing specific for CP gene of LSV viz., ExomeTM1.4, Web-Primer and ClustalW. Out of all these tools, primers designed by Web-Primer software were found to be the best on the basis of important parameters like length, melting temperature (Tm), GC content and secondary structures, which are necessary for proper functioning of primers. For validating the authenticity of primers, BLAST search was performed with all the virus sequences present in NCBI database. The primers were validated under laboratory conditions for characterization of LSV coat protein gene using RT-PCR. The primer pair-1, designed by Web-primer software was found to be the best one for detection of LSV infecting local lily cultivars of Himachal Pradesh. 47. PRAMOD DASHORA AND SUDHIR GUPTA [Effect of integrated nutrient management on yield, nutrient uptake and changes in soil fertility under sugarcane-ratoon system in sub-humid agro eco-system of Rajasthan]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 216-221 (2012). All India Coordinated Research Project on Sugarcane Agricultural Research Station, Ummedganj, Kota-324 001 (Rajasthan), India A field experiment with integrated nutrient management by organic and inorganic fertilizers on sugarcane-ratoon system for two cycles was conducted at Agricultural Research Station, Kota. The experimental crop was planted on February 25, 2005, ratooning initiated on January 20, 2006 and ratooning of plant crop during 2006-07 was initiated on January 30, 2007 to study the influence of integrated use of organic sources with different levels of mineral nutrition, biofertilizer and biopesticides in plant and ratoon crop, respectively. It was comprised of five treatments. Results revealed that treatment consisting of organic and inorganic fertilizer (T5) significantly produced higher plant and ratoon cane yield over T2 and T3 treatments. There was a drastic decrease in cane growth when resulted to mineral nutrition (T1). The treatment T5 having combination of 75% recommended NPK through inorganic+25% through organic fertilizer (FYM)+biofertilizer and biopesticides) showed higher net monetary return, higher uptake of NPK and higher sugar yield compared to T1 treatment (recommended NPK+micronutrient through inorganics) in plant and ratoon crop. There was a slight reduction in soil pH and increase in electrical conductivity with the application of organic manure. At the end of plant and ratoon crop, the significant increase in available N and K was recorded with the application of T5 treatment over T1 and T4 treatments, whereas T5 treatment was significantly superior over T1 and T2 with respect to available 48. PRAMOD DASHORA [Effect of integrated weed management on weed dynamics and cane yield of sugarcane ratoon]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 222-226 (2012). All India Coordinated Research Project on Sugarcane Agricultural Research Station, Ummedganj, Kota-324 001 (Rajasthan), India A field experiment was conducted from 2005 to 2009 at Agricultural Research Station, Kota to assess the effect of cultural, mechanical and chemical weed control measures on weeds, sugarcane ratoon yield and weed population dynamics under three cycles of sugarcane–ratoon system. Treatments applied in the ratoon significantly increased yield and highest ratoon yield (77.15 t/ha) was recorded with three hoeings (1, 4 and 7th week after ratoon initiation) followed by application of T6 (T6–Metribuzin @ 1 kg a. i./ha (PE)+1 hoeing at 45 DARI) 73.45 t/ha and T9 (Trash mulching in alternate rows+hoeing at 1 and 6 weeks after ratoon initiation) 73.88 t/ha. Effect of treatment on weed population dynamics was evident from reduced abundance of grass (less then 5) in ratoon, under all treatments compared to weedy check. Adoption of weed control measures caused occupation of field by grasses, broad leaf weeds and sedges, whereas in weedy-check grasses were most abundant in ratoon. Significantly lower weed density (10.00 No./m2 and weed dry weight (44 g/m2) were recorded under three hoeings (1,4 and 7th week after ratoon initiation and highest weed control efficiency (74.9%) was also recorded in same treatment (1,4 and 7th week after ratoon initiation). The highest net returns of Rs. 49935/ha were recorded with the application of T6 (Metribuzin @ 1 kg a. i./ha (PE)+ 1 hoeing at 45 DARI) followed by three hoeings (1,4 and 7th week after ratoon initiation) and T9 (Trash mulching in alternate rows+hoeing at 1 and 6 weeks) after ratoon initiation). 49. A. I. PATEL, S. C. MALI, C. G. INTWALA AND J. R. NIZAMA [Effect of 2,4-D on callusing and morphogenesis of sugarcane (Saccharum spp. Hybrid)]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 227-229 (2012). Department of Tree Biology and Improvement Navsari Agricultural University, Navsari (Gujarat), India Tender leaf material of two prominent sugarcane cultivars viz., Co 99004 and CoN 05071 was cultured on MS medium augmented with various levels of 2,4-D (2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid) for callusing and 6-BAP ( 6-benzyl amino purine) and NAA (Naphthalene acetic acid) for morphogenesis. Among different levels and combinations the 3 to 5 mg/l 2,4-D included in MS medium produced maximum dry, soft, compact and whitish callus within 18-30 days in both the cultivars. Whereas the 3 and 4 mg/l BAP and NAA induced 81-100% morphogenesis or organogenesis within 27-35 days after culturing of both the varieties. The average number of shoots after organogenesis also varied with different levels of auxin like BAP and NAA. The combination 3 and 4 mg/l BAP and NAA produced maximum number of shoots upto 10.8 to 12.5 in Co 99004 and 11.9 to 13.5 in CoN 05071. Whereas maximum length of shoot ranged upto 4.8 to 7.5 and 4.8 to 6.8, respectively. 50. PRAMOD DASHORA AND P. ROKADIA [Transfer of technology to bridge the yield gap of sugarcane in south-east Rajasthan]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 230-233 (2012). All India Coordinated Research Project on Sugarcane Agricultural Research Station, Ummedganj, Kota-324 001 (Rajasthan), India The study on technology gap of sugarcane was conducted in Bundi district of Rajasthan. The production of sugarcane for the last 10-12 years is almost stagnating of about 60 t/ha. It was found that adoption gap of sugarcane technologies was more in weed control followed by plant protection measures, time of sowing, irrigation, methods of sowing, high yielding varieties and seed rate, respectively. The most important constraints faced by the farmers were irregular supply of electricity and canal water for irrigation in the cropping season, low price of produce in comparison to cost of cultivation and lack of confidence about purity of seeds. 51. A. ALIPATRA, C. K. KUNDU, P. BANDOPADHYAY, P. S. BERA AND H. BANERJEE* [Growth, yield and quality of fodder oat (Avena sativa L.) as affected by split application of fertilizer and cutting management]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 234-237 (2012). Department of Agronomy Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya, Mohanpur-741 252, Nadia (West Bengal), India *(e-mail : hirak.bckv@gmail.com) The effect of split application of fertilizer on the performance of forage oat crop (var. JHO-822) under single and double cut management practice was studied at Central Research Farm, Gayeshpur under Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya on sandy loam alluvial soil. The experiment was laid out in factorial randomized block design with 18 treatment combinations replicated thrice. The results revealed that split application of fertilizers had a significant influence on growth of oat with respect to plant height, LAI and leaf : stem ratio. Green forage yield, dry matter yield and also quality aspects of oat such as crude protein yield and crude fibre yield were significantly improved by split application of fertilizer under both single and double cut management. But under double cut management, total green and dry forage yield as well as total crude protein and crude fibre yield were significantly higher than single cut management practice. Application of nitrogen (90 kg/ha) in three splits (½ dose as basal+¼ dose at 20 DAS+¼ dose at 40 DAS) and potassium (60 kg/ha) in two splits (½ as basal+½ at 20 DAS) under double cutting management was the best proposition for obtaining highest green and dry fodder as well as crude protein yield and crude fibre yield of fodder oats in new alluvial soils of West Bengal. 52. T. N. PUSHPA, M. CHANDREGOWDA, D. SRIKANTAPRASAD AND A. P. MALLIKARJUNA GOWDA [Evaluation of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) genotypes for growth and seed yield]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 238-244 (2012). Department of Horticulture University of Agricultural Sciences, GKVK Campus, Bangalore-560 065 (Karnataka), India An effort was made to find out the promising genotypes suitable for Bengaluru with 25 genotypes of fenugreek with diverse geographical origins during kharif 2009 in randomized block design with two replications. The mean data were subjected to statistical analysis. All the genotypes varied significantly with respect to growth and yield parameters. The genotype CO-1 performed well with respect to growth parameters, whereas Chikkaballapur Local for yield parameters at different stages of crop growth. The genotypic and phenotypic coefficients of variation were maximum for the number of branches per plant at 30 DAS, number of branches and plant spread at harvest. Heritability and genetic advance estimates were high for all the traits except for plant height, number of branches and plant spread at 30 DAS, pod length and harvest index. Seed yield was found to be positively and significantly correlated with shelling percentage, number of pods per plant, 1000-seed weight, number of seeds per pod and plant spread at harvest. Path analysis revealed that number of pods per plant, shelling percentage, harvest index, number of branches and plant height at harvest exhibited high positive direct effect on seed yield. Some of the genotypes have been identified as desirable for growth and yield attributes which can be used in the breeding programme for further improvement. 53. K. S. POORNIMA, M. CHANDREGOWDA, T. N. PUSHPA AND D. SRIKANTAPRASAD [Studies on effect of growth regulators on rooting of two rosemary types and estimation of biochemical changes associated with rooting]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 245-248 (2012). Department of Horticulture University of Horticultural Sciences, GKVK Campus, Bangalore-560 065 (Karnataka), India An experiment was conducted during the year 2008 to study the influence of growth regulators on rooting of stem cuttings of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) types viz., French type and CIMAP type. The cuttings were subjected to nine different growth regulator treatments. Among the two types of rosemary, French type registered early sprouting (17.36 days), highest number of sprouts (19.89), the maximum rooting percentage (76.17%), number of roots per cutting (14.53) at 75 days and survival rate (82.78%) and also the highest total sugar content (0.54 g) alongwith the lowest nitrogen content (0.51 g). The combination of IBA and NAA each at 3000 ppm recorded early sprouting (15.19 days), early root initiation (9.75 days), more number of sprouts (16.30), highest percentage of rooting (85.25), highest survival rate (92.75%) and also recorded lowest phenol content (0.25%) compared to control. Hence, concentration of IBA and NAA each @ 3000 ppm was found to be best for propagation of rosemary. 54. RANIA W. IBRAHIM, NASRI I. HADDAD*, MALIK HADDADIN, KAMAL K. ABU SALAH2 AND AHMED AMRI [Diversity among and within wild populations of Origanum syriacum collected from Jordan]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 249-259 (2012). Faculty of Agriculture University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan *(e-mail : n.haddad@cgiar.org) Origanum syriacum L. (common name Za’atar) is a wild growing medicinal plant in Jordan and the Middle East, while Origanum majorana L. is a native plant of Cyprus and south Turkey. In this research collecting missions were conducted in different agro-ecologies in Jordan which allowed the sampling of 14 wild populations of O. syriacum L. In addition, four cultivated O. syriacum L. accessions and two accessions of O. majorana L. were obtained from farmers and local market. The collected material was evaluated during the 2007-08 and 2008-09 growing seasons. The obtained results indicated significant differences between different populations/accessions for all the studied characters with an overall diversity value of (H¢=0.897) using Shannon Wiener diversity index. Cluster analysis clearly differentiated between O. syriacum L and O. majorana L. and also between the cultivated accessions and the wild populations. Essential oil content significantly varied between the growing seasons and the evaluated genetic material. In the second season, the essential oil per cent content among wild O. syriacum populations ranged from 1.86 to 2.60%, while for cultivated O. syriacum (1.85 to 2.13%), whereas the O. majorana accessions contained the least essential oil (1.34 and 1.41%). 55.SHAMARAJ, H. T. CHANDRANATH, A. S. PAVAN AND GIRAMALAPPA B. TUPPADA [Impact of planting dates and stage of harvesting on growth and root yield of ashwagandha (Withania sominifera Dunal.)]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 260-263 (2012). Department of Agronomy College of Agriculture, Raichur (Karnataka), India Studies on planting dates and stage of harvesting in ashwagandha were conducted at the Agricultural College Farm, Raichur on medium deep black soil during kharif season of 2007-08 to know the optimum date of planting and stage of harvesting. The results showed that planting on II Fortnight (F. N.) of July recorded the highest plant height (29.97 cm), number of leaves (33.76), leaf area (30.64 dm2/plant) and leaf area index (15.12), and were on par with I F. N. of August. Planting on II F. N. of July recorded the highest dry matter production (37.58 g/plant) and its distribution in leaves (8.21 g/plant), stem (11.60 g/plant) and reproductive parts (16.46 g/plant). Among stages of harvesting, the crop harvested at 100% flowering stage recorded the highest number of leaves (30.85), leaf area (30.08 dm2/plant), leaf area index (13.64), dry matter accumulation in leaves (9.51 g/plant) and also these were on par with 50% flowering stage. However, the crop harvested at maturity stage recorded significantly higher plant height (31.64 cm), dry matter production (37.33 g/plant) and its distribution in stem (12.52 g/plant) and reproductive parts (20.48 g/plant) and also these were on par with berry ripening stage. Planting on II F. N. of July produced maximum fresh (1737 kg/ha) and dry (819 kg/ha) root yield of ashwagandha closely followed by I F. N. of August planting (1706 and 810 kg/ha). Among different stages of harvesting, maximum fresh (1714 kg/ha) and dry root yield (873 kg/ha) was observed when the crop was harvested at maturity stage which was on par with berry ripening stage (1695 and 823 kg/ha, respectively). 56. A. P. MALLIKARJUNA GOWDA, C. S. RAVI, M. NARAYANASWAMY AND B. RAJU [Assessment of genetic variability in Terminalia chebula using RAPD markers]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 264-267 (2012). PG & Hi Tech Horticultural Research Centre University of Horticultural Sciences (Bagalkot), GKVK Campus, Bangalore-560 065 (Karnataka), India Eighty-three bands ranging from 300 bp to 3 kb, consistent, unambiguous and repeatable, produced from selected primers were used for estimating the genetic diversity and relatedness among the Terminalia chebula trees from five provenances of Karnataka. Out of 83 bands, 62 were polymorphic and 21 were monomorphic. The dendrogram was constructed by Ward’s method of clustering using minimum variance algorithum (Ward, 1963). The five provenances of T. chebula were clustered into two groups at a distance of 44 units on dendrogram with Shimoga and Arasikere spanning the extremes with all other provenances distributed in between them. RAPD analysis revealed that the genetic diversity of five provenances was medium with Shimoga and Channapattana being 47% dissimilar, while BR hills and Arasikere differed only by 28%. 57. D. V. SUBHASHINI* [Bacillus circulans–novel bio-inoculant for FCV tobacco]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 268-272 (2012). Central Tobacco Research Institute, Rajahmundry-533 105 (Andhra Pradesh), India *(e-mail : dv_subhashini@rediffmail.com) Both nursery and field experiments were conducted with Bacillus circulans during 2008-09. Effect of seed bacterization with carrier based (1% w/w) inoculum of B. circulans was tested in tobacco nursery and recovered highest number of healthy and vigorous transplantable seedlings. Inoculation with B. circulans alongwith the recommended dose of fertilizer in the irrigated tobacco enhanced the population of B. circulans in the rhizosphere and chlorophyll content in the leaf, yield of green leaf, cured leaf, grade index, apart from quality in all positions compared to un inoculated treatment and proved to be a promising biofertilizer for northern light soil tobacco. Biological activities are enhanced by microbial interactions in the rhizosphere of tobacco plants. The PGPR, B. circulans could influence the plant growth directly through the production of phytohormones and indirectly through the production of biocontrol agents against soil-borne phytopathogens. 58. MALLIKARJUN G. AWATI, G. F. D’SOUZA, N. S. RENUKASWAMY, C. G. ANAND, D. VENKATARAMANAN AND JAYARAMA [Variation in physiological parameters of coffee cultivars under different soil moisture regimes]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 273-278 (2012). Division of Plant Physiology Central Coffee Research Institute Coffee Research Station-577 117, Chikmagalur District (Karnataka), India Assessment on physiological parameters was carried out using two arabica (Sln. 9 and Sln. 3) and one robusta (Sln. 1R) coffee cultivars under different soil moisture regimes i. e., before stress, at stress and after alleviation of stress under field conditions for two seasons. The results indicated that considerable reduction in net photosynthesis (Pn), transpiration rate (E), stomatal conductance (gs), sub-stomatal CO2 concentration (Ci), carboxylation efficiency (CE) (Pn/Ci), relative water content (RWC), physiological water use efficiency (pWUE) (Pn/E) and higher stomatal resistance (rs) was observed during soil moisture stress in all the cultivars. The less reduction of physiological parameters in Sln. 9 at stress might be associated with an increase in the epicuticular wax content (ECW) and relative water content (RWC). The pWUE was maintained high in Sln. 9 under different soil moisture regimes. Significant (P>0.01) positive correlations between Pn and E, rs with E and Ci were observed at before stress in all the cultivars. The rs showed highly significant negative relationship with Pn and E under water stress. The Ci had significant positive correlation with Pn and E in arabica cultivars at stress, whereas such a relationship could not be observed in robusta coffee. The significance of the relationship of physiological parameters for drought tolerance in coffee is discussed. Thus, high Pn/Ci, rs, pWUE, ECW and less reduction in Pn and maintenance of RWC with low E and gs during moisture stress period might be the contributing factors for drought tolerance in Sln. 9 arabica cultivar. 59. P. SRINIVASULU REDDY, B. V. NAIDU, B. KASI REDDY AND CH. SATYANARAYANA RAJU [Combination effects of organic manures and chemical fertilizers on growth and certain physiological traits in mulberry]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 279-283 (2012). Regional Sericultural Research Station, P. B. No. 50, Anantapur (Andhra Pradesh), India A field trial was undertaken to study the combination effects of organic manures, biofertilizers and chemical fertilizers on mulberry variety under irrigated conditions. The experiment comprised nine treatments viz., T0 (Control)–Recommended dose of chemical fertilizers (RDCF)+Recommended dose of farm yard manure, T11<–Recommended dose of chemical fertilizers (RDCF), T>2–RDFYM+Azotobacter biofertilizer (AB)+Vesicular arbuscular mychorrizae (VAM)+Green manure (GM)+Vermicompost (VC), T3–RDCF+RDFYM+VAM+AB, T4–50% RDCF+RDFYM+VAM+AB, T5–RDCF+RDFYM+VAM+AB+VC, T6–50% RDCF+RDFYM+VAM+AB+VC, T7–RDCF+RDFYM+VAM+AB+VC+GM and T8–50% RDCF+RDFYM+VAM+AB+VC+GM. Pronounced growth and physiological traits observed in T2, T7 and T8 indicated that a mixture of organic manure could give the effects of chemical fertilizers. The results also indicated that 50% chemical fertilizers could be saved when different organic manures with biofertilizers are combined and used. 60. P. SRINIVASULU REDDY, B. SRINATH, S. KISHORE, B. V. NAIDU AND CH. SATYANARAYANA RAJU [Knowledge and adoption levels on organic farming in mulberry cultivation with the farmers in Chittoor district of Andhra Pradesh]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 284-288 (2012). Regional Sericultural Research Station, P. B. No. 50, Anantapur (Andhra Pradesh), India The study was conducted with the objective to appraise the knowledge and extent of adoption pattern of recommended organic manures in Chittoor district of Andhra Pradesh to find out the relationship between the socio-economic factors with knowledge and adoption levels and to identify the constraints/reasons and suggesting measures for increasing the adoption levels of farmers. The results are based on an interview conducted among 125 farmers in Chittoor district of Andhra Pradesh. The findings revealed that cent per cent (100%) farmers had good knowledge, but only 67.5-72.5% farmers had fully adopted the technologies like farm yard manure (FYM) and tank silt application due to availability, cheaper in rates and also due to certain programme implemented by Government of Andhra Pradesh. 70 -100% of farmers had nil knowledge and non-adopted the practices like seri residue composting, biofertilizers, VAM and PSB. Knowledge and adoption on/in preparation and use of panchagavya is very negligible (1.5%). The lack of credit facilities (75%), lack of technical guidance (74%), non-availability of organic fertilizers in time (67%), etc. were the main constraints/reasons for partial/non-adoption of the above practices. The variables such as education, extension contact, social participation, cattle population and cocoon yield were positive and significantly associated, whereas age, family size and experience of respondents had shown negative relationship with knowledge and adoption levels. 61. KUNAL PRATAP SINGH AND SURJEET SINGH [Effect of different substrates on yield parameters of paddy straw mushroom under natural conditions]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 289-292 (2012). Department of Plant Pathology CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar-125 004 (Haryana), India The effect of different substrates on yield, yield parameters and morphological characters of Volvariella volvacea was studied under natural conditions in the months of March-April, 2010 and 2011. The cultivation of paddy straw mushroom was done on paddy straw (PS), wheat straw (WS), brassica straw (BS) and wheat straw+brassica straw. It was found that wheat straw was more suited as substrate for the cultivation of V. volvacea than paddy straw in terms of biological efficiency/yield. The spawn run was completed in paddy straw (8.24 days) earlier than brassica straw (9.66 days) and wheat straw (10.13 days). Eventually, the days taken for pin head formation were more for wheat straw substrate (17.78 days) and significantly higher from paddy straw (10.34 days). The maximum number of fruit bodies per 100 kg was recorded from wheat straw substrate. The maximum and minimum stipe length and pileus diameter were reported in wheat straw and brassica straw, respectively. 62. A. S. SIDHU, B. S. SIDHU AND J. S. BRAR [Effect of different quality of irrigation water on wheat yield and soil properties]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 293-295 (2012). PAU Regional Research Station, Bathinda-151 001 (Punjab), India A field study was carried out to find out the effect of quality of irrigation water on the yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and soil properties in fields irrigated with different water quality i. e. sewage water, sewage water+canal water and canal water alone at Regional Research Station, Bathinda. The wheat yield improved in fields irrigated with sewage water as compared to canal water alone irrigated fields. The soil pH and electrical conductivity of the soils did not differ significantly but organic carbon content was higher in fields irrigated with sewage water than canal water alone. The fields irrigated with sewage water contained maximum content of Zn, Cu, Mn and Fe as compared to canal water alone and content was 2.18, 0.91, 9.81 and 11.29 mg/kg, respectively. The depth-wise distribution of these micronutrients in soils showed a decrease in Zn, Fe and Cu content with the increase in depth. 63. J. SURESH, R. SAIKUMAR, A. GEETHA AND P. SAIDAIAH [Correlation between performance of S1 and half sib families in maize composites]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 296-297 (2012). Agricultural Research Station (Maize), Rajendranagar, Hyderabad-500 030 (A. P.), India Phenotypic correlations were studied between S1 and inter population half sib progenies in two random mating populations, namely, Harsha and Ashwini. The correlations were significant in both the composites for ear height and days to 50% silk. In case of grain yield, the correlations were not significant revealing that S1 selection had very limited value for this trait. 64. G. P. PAINKRA, D. C. SALAM AND R. K. MISHRA [Role of front line demonstrations on yield enhancement of different crops in Surguja district of Chhattisgarh]. Crop Res. 43 (1, 2 & 3) : 298-300 (2012). I. G. K. V. Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Ambikapur, Surguja-497 001 (C. G.), India The frontline demonstrations were conducted at IGKV KVK, Ambikapur, Surguja within operational area at the adopted villages, namely, Lamgaon, Kundikala, Silsila, Jamdei, Labji, Kanchanpur and Mondesa of blocks–Lundra, Surajpur and Ambikapur, respectively. These demonstrations were conducted other than oilseeds and pulses i. e. maize, rice, wheat, and horticultural crops viz., tomato, chilli and elephant foot yam. Under the oilseed crops, toria and niger and pulses crops–arhar and gram were demonstrated during 2007-08 to enhance the productivity of different crops. Some technologies were demonstrated viz., varietal, timely sowing, integrated nutrient management, production technology, integrated pest and disease management and line sowing. In cereal crops under the recommended practice (RP), the averege yield ranged from 34.33-43.73 q/ha, horticultural crops 164.6-480.2 q/ha, oilseed crop 3.95-8.35 q/ha and pulse crops 12.20-16.12 q/ha, respectively. Whereas the farmers’ practice (FP) worked out significantly lower yield i. e. in cereals 13.45-21.20 q/ha, horticultural crops 101.5-310.2 q/ha, oilseed crops 2.18-5.40 q/ha and pulse crops 5.80-13.90 q/ha. The economics and benefit : cost ratio in recommended practice worked out significantly higher ranges in cereals 2.58-3.52 (RP),1.90-2.20 (FP), horticulture crops 3.06-8.25 (RP), 1.70-5.43 (FP), oilseed crop 1.60-2.14 (RP), 1.41-1.75 (FP) and pulse crop 2.64-2.90 (RP), 2.00-2.33 (FP), respectively.
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
********



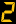
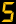
 Users Today : 9
Users Today : 9 Users Yesterday : 109
Users Yesterday : 109 Users Last 7 days : 589
Users Last 7 days : 589 Users Last 30 days : 2679
Users Last 30 days : 2679 Users This Month : 1741
Users This Month : 1741 Users This Year : 1741
Users This Year : 1741 Total Users : 11125
Total Users : 11125 Views Today : 9
Views Today : 9 Views Yesterday : 129
Views Yesterday : 129 Views Last 7 days : 908
Views Last 7 days : 908 Views Last 30 days : 3516
Views Last 30 days : 3516 Views This Month : 2286
Views This Month : 2286 Views This Year : 2286
Views This Year : 2286 Total views : 37276
Total views : 37276 Who's Online : 0
Who's Online : 0