Volume 12, Number 2 (August 2011)
1. PRITPAL SINGH, S. P. SAINI AND G. S. MATHARU [Effect of potassium application on yield, efficiency and economics in irrigated sub-tropical soils under rice-wheat cropping sequence : An on-farm experience]. Res. on Crops12(2): 263-268 (2011). PAU Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Ropar (Punjab), India Potassium (K) is an important macronutrient required for sustainable crop production, particularly for rice-wheat (RW) cropping system that farmers generally skip and fail in achieving economically optimal crop yield. Therefore, on-farm trials (OFTs) at 12 different farmers’ field (FF) locations under RW cropping system in Ropar and Amritsar districts (Punjab) were conducted during 2007-09 to investigate the effect of K application on crop response. Three treatments viz.. T1–30 kg K2O/ha to both rice (Oryza sativa L.) and wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), T2–Control (no K) to either crop and T3–Farmers’ practice (FP) of applying K to these crops in a cropping sequence were evaluated. Wheat yield increased significantly (P£0.05) by 4.9 and 7.8% with the application of K over T2, during first and second year at Ropar, and by 7.3 and 8.6%, respectively, at Amritsar district. Similarly, rice yield exhibited significant (P£0.05) increase by 5.2 and 7.5% at Ropar and by 4.5 and 4.6%, respectively, at Amritsar district. The production efficiency of wheat during first and second year increased from 31.2 to 32.7 kg/day/ha and from 29.3 to 31.6 kg/day/ha, respectively, at Ropar and from 29.5 to 31.6 kg/day/ha and from 30.2 to 32.8 kg/day/ha at Amritsar with K application (T1) over either control or FP (T2/T3). Results revealed that K application resulted in an augmentation in monetary returns efficiency, total output energy, energy use efficiency, energy productivity and average gross returns over T2/T3. Thus, it can be concluded that K application in RW cropping sequence is necessary to achieve economically optimal yield. 2. A. S. Patel, J. J. Patel, R. A. Patel and G. J. Patel [Grain yield and net returns of transplanted kharifrice (Oryza sativa L.) as influenced by age of seedling, organic manures and nitrogen levels]. Res. on Crops12(2): 269-272 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Anand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110 (Gujarat), India An experiment was conducted during the kharif season of the years 2006 and 2007 at Agricultural Research Station for Irrigated Crops, A. A. U., Thasra, Gujarat to evaluate productivity and economics of rice under different age of seedling A1 (10 to 12 days old seedling) and A2 (25 to 30 days old seedling), five levels of organic manures–M1 (No organic manure), M2 (FYM 10 t/ha), M3 (Vermicompost 2 t/ha), M4 (FYM 10 t/ha+Bio-fertilizer) and M5 (Vermicompost 2 t/ha+Bio-fertilizer) and two nitrogen levels N1 (75 kg N/ha) and N2 (100 kg N/ha). The grain yield was significantly the highest (5287 kg/ha) under age of seedling treatment A1 (10 to 12 days old seedling). Application of 100 kg N/ha (N2) recorded significantly the highest grain yield (5382 kg/ha) and net returns Rs. 20543/ha as well as CBR and net CBR (1 : 2 : 05 and 1 : 1.05), respectively, as compared to treatment N2 (100 kg N/ha). 3. B. G. SHEKARA, M. R. KRISHNAPPA, M. VENKATESH, M. THIMMARAYAPPA AND m. govindappa [Grain yield, nutrient use efficiency and economics of aerobic rice (Oryza sativa L.) as influenced by different levels of NPK in Cauvery Command Area]. Res. on Crops 12(2): 273-275 (2011). Zonal Agricultural Research Station, V. C. Farm, Mandya-571 405 (Karnataka), India Field experiment was conducted during kharif seasons of 2004 and 2005 at Zonal Agricultural Research Station, V. C. Farm, Mandya, Karnataka to study the different levels of NPK on growth and yield of aerobic rice in Cauvery Command area. The research results revealed that application of 125 kg N/ha recorded significantly higher grain yield (7.26 and 7.23 t/ha) and net monetary returns (Rs. 26487/ha). Among phosphorus levels, 62.5 kg P2O5/ha recorded significantly higher grain yield (7.10 and 7.14 t/ha) and net monetary returns (Rs. 25826/ha). Higher grain yield (7.26 and 7.21 t/ha) and net monetary returns (Rs. 26553/ha) were noticed with 62.5 kg K2O during the years 2004 and 2005, respectively. The nutrient use efficiency was higher with 75 kg N/ha (36.13 and 36.50 kg grain/kg NPK), 37.5 kg P2O5 (35.54 and 35.59 kg and 35.64 kg grain/kg NPK) and 50 kg K2O/ha (36.11 and 35.78 kg grain/kg NPK) which was on par with 100 kg N (36.07 and 35.97 kg grain/kg NPK ), 50 kg P2O5 (35.24 and 35.23 kg grain kg/NPK) and 37.5 kg K2O/ha (34.06 and 34.77 kg grain/kg NPK) during the years 2004 and 2005, respectively. The benefit : cost ratio was higher with 100 kg N/ha (2.51), 50 kg P2O5/ha (2.46) and 50 kg K2O/ha (2.51). 4. B. G. SHEKARA, M. VENKATESH, M. THIMMARAYAPPA AND M. GOVINDAPPA [Grain yield, nitrogen use efficiency and economics as influenced by levels and time of nitrogen application in aerobic rice (Oryza sativa) under Cauvery Command Area]. Res. on Crops12(2): 276-278 (2011). Zonal Agricultural Research Station, V. C. Farm, Mandya-571 405 (Karnataka), India Field experiment was conducted during kharif seasons of 2004 and 2005 at Zonal Agricultural Research Station, V. C. Farm, Mandya, University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore to study the effect of levels and time of nitrogen application on growth and yield of aerobic rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mean of two years’ research results revealed that application of 125 kg N/ha recorded higher grain yield (7.61 t/ha), net monetary returns (Rs. 31207/ha) and benefit : cost ratio (2.97) but was on par with 100 kg N/ha which recorded grain yield, net monetary returns and benefit : cost ratio of (7.39 t/ha, Rs. 29742/ha and 2.94, respectively). The agronomic efficiency of nitrogen was higher with application of 75 kg N/ha (45.37 kg grain/kg nitrogen). 5. R. JEYASRINIVAS AND P. RAJARATHINAM [Influence of dual cropping of green manure crops and weed management practices on the growth, yield and economics of semi-dry rice]. Res. on Crops12(2): 279-283 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore-641 003 (Tamil Nadu), India A field experiment was conducted during rabi 2004-05 (first crop) and 2005-06 (second crop) to study the influence of dual cropping of green manure crops and weed management practices on the growth, yield and economics of semi-dry rice. The experiment was laid out in split plot design with three replications. The main plot treatments consisted of in situ dual cropping of two green manure crops (daincha and cowpea) with rice and two methods of green manure incorporation (manual incorporation and chemical decomposition). Three weed control treatments viz., pendimethalin–hand weeding, hand weeding twice and unweeded control formed the sub-plot treatments. The results revealed that the dual cropping of cowpea and incorporated manually at 30 days after sowing (DAS) and pre-emergence application of pendimethalin at 1.25 kg/ha followed by one hand weeding at 45 DAS recorded the higher growth characters, yield, net returns and benefit : cost ratio of semi-dry rice cultivation. 6. R. JEYASRINIVAS AND P. RAJARATHINAM [Effect of dual cropping of green manure crops and weed management practices on the yield attributes, yield and nutrient uptake of semi-dry rice]. Res. on Crops12(2): 284-288 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore-641 003 (Tamil Nadu), India A field experiment was conducted during rabi 2004-05 (first crop) and 2005-06 (second crop) to study the effect of dual cropping of green manure crops and weed management practices on the yield attributes, yield and nutrient uptake of semi-dry rice. The experiment was laid out in split plot design with three replications. The main plot treatments consisted of in situ dual cropping of two green manure crops (daincha and cowpea) with rice and two methods of green manure incorporation (manual incorporation and chemical decomposition). Three weed control treatments viz., pendimethalin – hand weeding, hand weeding twice and unweeded control formed the sub plot treatments. The results revealed that the dual cropping of cowpea and incorporated manually at 30 days after sowing (DAS) and pre-emergence application of pendimethalin at 1.25 kg/ha followed by one hand weeding at 45 DAS recorded the higher yield attributes, yield, net returns and benefit : cost ratio of semi-dry rice cultivation. 7. R. JEYASRINIVAS AND P. RAJARATHINAM [Influence of dual cropping of green manures and weed control methods on the weed control efficiency, grain yield and weed index of semi-dry rice]. Res. on Crops12(2): 289-293 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore-641 003 (Tamil Nadu), India A field experiment was conducted during rabi 2004-05 (first crop) and 2005-06 (second crop) to study the influence of dual cropping of green manure crops and weed control methods on the weed control efficiency, grain yield and weed index of semi-dry rice. The experiment was laid out in split plot design with three replications. The main plot treatments consisted of in situ dual cropping of two green manure crops (daincha and cowpea) with rice and two methods of green manure incorporation (manual incorporation and chemical decomposition). Three weed control treatments viz., pendimethalin–hand weeding, hand weeding twice and unweeded control formed the sub-plot treatments. The results revealed that the dual cropping of cowpea with rice under manual incorporation at 30 days after sowing (DAS) and pre-emergence application of pendimethalin at 1.25 kg/ha followed by one hand weeding at 45 DAS recorded the lower weed population, higher weed smothering and weed control efficiency and higher grain yield of semi-dry rice. 8. M. Motamedi* and R. Farhoudi [Effect of salinity stress on seed germination and antioxidant activity of wheat (Triticum aestivum) genotypes]. Res. on Crops12(2): 294-299 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shoushtar Branch, Shoushtar, Iran*(e-mail : rfarhoudi@gmail.com) The response of four cultivars of wheat (cultivars Tajan, Marvdasht, Kavir and Tabas, SPCRI, Karaj, Iran) to NaCl salinity at germination and early seedling growth stage was recorded. Salinity treatments measuring 4, 8, 12 and 16 dS/m were achieved by adding NaCl in demonized water. All experiments were carried out under a dual factorial (cultivar × salinity level) completely randomized design at four replications. Results showed that salt stress decreased seedling length and seedling fresh weight but increased seedling MDA and carbohydrate and peroxidase (POD) activity. Among the cultivars under investigation cultivar Marvdasht appeared to be more sensitive at germination stage. Cultivars Tabas and Kavir seemed to be salt tolerant wheat cultivars since they showed the highest seedling fresh weight, highest POD activity and the lowest MDA concentration at 12 dS/m level compared to Marvdasht cultivar. 9. MOHAMMAD REZA DADNIA* [Physiological and agro-morphological traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) as affected by Bacillus coagulance strains under different rates of nitrogen]. Res. on Crops12(2): 300-303 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shahr-e-Qods Branch, Tehran, Iran The production of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) with high protein content over different environments requires the correct management practices. The objectives of this study were to evaluate the effects of Bacillus coagulance strains and N management on grain protein and grain yield. Seeds were inoculated during pre-planting with B. coagulance strains to replace from 30 to 100% nitrogen. Nitrogen stress reduced grain yield and kernel weight. Reduction in nitrogen could decrease average grain protein content from 108.5 g/kg in 90 kg N/ha to 124.6 g/kg in 120 kg N/ha. Grain yield was affected by B. coagulance strains. Increase in kernel weight and grains/spike were observed under high N fertilization. High N fertilization would increase the number of kernels, which was resulted by B. coagulance. Among the B. coagulance strains, HM and 14-5, had greater effect on grain yield and grain protein. In poor regions where nutrient stress is common, B. coagulance strains are more likely to improve grain yield production. 10. MOHAMMAD REZA DADNIA* AND PAYAM MOAVENI [Effect of different strains of Bacillus megaterium on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) yield under different rates of nitrogen]. Res. on Crops12(2): 304-307 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shahr-e-Qods Branch, Tehran, Iran *(e-mail : rezadadnia@yahoo.com) Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grain yield is improvement by the combination of main nutrients and water. Experiment was conducted in 2010 in Karaj Research Field to determine the effects of Bacillus megaterium strains on yield in relation to nitrogen rates at sowing time. The experiment was a randomized complete block design (RCBD) with a split plot arrangement and four replicates. Treatments consisted of N rates (90 and 120 kg N/ha) in main plots and B. megaterium strains (Russian 3, 24-2, SP, 22-2 and Chinese 9) in sub-plots. Low N rate significantly increased tillers/m2, yield and yield components affected by strains in comparison with control treatments. Increase of N (120 kg N/ha) rate significantly increased spikes/m2 and 1000-seed weight due to strain treatments. The effects of Russian 3 and SP influenced the relative contribution of the main spike and primary tillers to grain yield improvement. B. megaterium strains such as Russian 3 and SP appear to have the largest effect on tiller numbers without negative influence on yield. 11. Rozbeh Farhoudi* [Effect of seed size on salt tolerance at germination and seedling growth stages of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 308-311 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shoushtar Branch, Shoushtar, Iran The effects of seed size and salt stress on seed germination and seedling growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) were evaluated. The experimental design was two factors factorial (2 × 5) arranged in a completely randomized design with four replications. The first factor was seed size (small= 2 mm and large=3 mm) and the second factor was salt stress (0, 4, 8, 12 and 16 dS/m). Salt stress decreased shoot and root length but increased mean germination time in both large and small seeds. However, at 12 and 16 dS/m in small seeds, seed germinated faster and shoot length and seedling fresh weights were higher compared to large seeds. Small seeds could be preferred for use in saline soils to achieve better stand establishment. 12. SAEID HEIDARI, KHOSRO AZIZI*, ALIREZA DARAEI MOFRAD AND ABDOLREZA AHMADI [Study of quantitative and qualitative traits of triticale (X. triticosecale Wittmack) and rough pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) in sole and mixed cropping in dry farming conditions of Iran]. Res. on Crops12(2): 312-319 (2011). Department of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, Lorestan University, Khorramabad, Iran *(e-mail : azizi_kh44@yahoo.com) In order to study the effect of mixed and sole cropping triticale (X. triticosecale Wittmack) with rough pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) on their qualitative and quantitative traits, this experiment in cropping year 2008-09 was conducted with five levels of seed contribution of triticale : rough pea (100 : 0, 0 : 100, 20 : 80, 40 : 60 and 60 : 40) (in dry land conditions of khorramabad in Iran) in the form of randomized complete block design (RCBD) with four replications at the research farm of College of Agriculture, Lorestan University. Results showed that proportion of complementary components had significant effect on hay (leaf and stem). The highest leaf dry weight was related to sole cropping of triticale and rough pea (349.8 and 612.3 kg/ha), respectively. Also, stem dry weight by these two treatments (1751 and 715.1 kg/ha). The maximum of biological yield in triticale and rough pea obtained from sole cropping of triticale and combination 40 : 60 was equal to 6492 and 2919 kg/ha, respectively. The results in study treatments showed that under efficacy of different seed combinations, changed dry matter (DM) and its quality, the highest total hay yield (3101 kg/ha) was related to combination 60 : 40. Thus, this treatment was higher than other treatments in quality and total LER (TLER). Therefore, this combination was found the most suitable for forage produce and exploitation of resources. 13. Mohammadreza Delfieh*, Moosa Meskarbashi, Bahram Andarzian, Roozbeh Farhoudi and Saeid Saeidipour [Evaluation of CERES-Maize model for simulating the growth and development of maize cultivar SC-604 under climatic conditions of south-western Iran]. Res. on Crops12(2): 320-325 (2011). Department of Agronomy & Plant Breeding, Shahid Chamran University, Ahvaz, Iran *(e-mail : mdelfieh@scu.ac.ir) Considering the ever increasing importance of computer models to help for better understanding of agricultural systems and improving agronomic and administrative decisions, this research was designed and carried out. In this research, the CERES-maize model was calibrated and validated for the SC-604 maize cultivar. The requred data were from an experiment which had been carried out in 1990 at experimental farm of Agronomy and Plant Breeding Department of Agricultural College in Shahid Chamran University. After acquiring the genetic coefficients, the results of model evaluation with statistical indices, RMSE and MAE, showed that the model was capable to exactly predict the growth parameters, and phenological stages and so these indices for anthesis date, physiological maturity date, yield and dry matter was lower than 10% of observed data means. 14. Mohammadreza Delfieh*, Moosa Meskarbashi, Bahram Andarzian and Roozbeh Farhoudi [Simulating the effects of planting date and nitrogen fertilizer on yield and phenological stages of maize cultivar SC-604 under climatic conditions of south-western Iran using CERES-Maize model]. Res. on Crops12(2): 326-335 (2011). Department of Agronomy & Plant Breeding, Shahid Chamran University, Ahvaz, Iran Considering the importance of planting date and nitrogen fertilizer to identify the proper sowing date and achieving the highest yield through a wider range of treatments, a simulation experiment was carried out with CERES-Maize model. The genetic coefficients needed for running this model had been already obtained from another research which had been conducted by author to calibrate and validate the CERES-Maize model. In the present experiment, nine planting date treatments from May 20 to August 11 with 10-day intervals, and nine nitrogen fertilizer treatments from 0 to 400 kg/ha with 50 kg/ha intervals were applied. The results of simulation showed that whenever we used the later planting dates, due to shorter photoperiods, floral initiation began sooner. From the 4th planting date and after, a relative reduction was obvious for both anthesis and beginning of grain filling dates. Also from the 1st planting date to the last, an increment of the physiological maturity date happened, which was supposed to be because of the greater time that plant had for grain filling, considering the more appropriate environmental temperature and solar radiation. Investigation of the simulated grain yield showed that as we used the later planting dates, in addition to produce higher yields, the fertilizer acceptance of plant became better. Finally, considering all results and indices, it could be concluded that the planting date of August 11 with 250 kg/ha nitrogen, will produce the best result for grain yield. 15. Mehrdad Esfandiary, Ali Soleymani*, Mohamad Hesam Shahrajabian and Homauon Darkhal [Effect of planting methods on grain yield and leaf orientation at different stages of corn cultivars]. Res. on Crops12(2): 336-340 (2011). Department of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, Khorasgan (Esfahan) Branch, Islamic Azad University, Esfahan, Iran Recent studies showed that maize leaf orientation at the horizontal side could cover all empty canopies’ spaces to appropriate solar radiation absorption. Hill planting method is the agronomical practice in maize production that with competition in plants hill, significant reduction in grain yield was seen. In order to evaluate the effect of planting methods and cultivars on grain yield and leaf orientation of maize, an experiment was conducted in 2010, at Research Farm, Faculty of Agriculture, Islamic Azad University, Khorasgan Branch (Esfahan), Iran. A factorial layout within randomized complete block design with three replications was used. Cultivars were ZP 633, ZP 677 and SC 704, and planting patterns were included single and hill planting. Each experimental plot had 8 m length. Seed plantation was done on June 21. The results showed that at single planting method, leaf orientation of two cultivars, namely, SC 704 and ZP 677 was in the form of distich. The ZP 633 form was randomized. Hill planting had no significant influence on ZP 633, but leaf orientation of SC 704 and ZP 677 in hill planting and single planting was randomized and distich, respectively. Grain yield of SC 704 and ZP 677 at single planting method with distich leaf orientation was more than ZP 633 with randomized leaf orientation. Hill planting caused significant increase in planting height and significant decrease in cultivar,s grain yield. On the basis of the results, SC 704 and ZP 677 in hill and single planting method had obtained the highest grain yield. 16. Tooraj Mir mahmoodi*, Kazem Ghassemi-Golezani, Davood Habibi, Farzad Paknezhad and Mohammad-Reza Ardekani [Effect of hydro-priming duration on seedling vigour and field establishment of maize (Zea mays L.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 341-345 (2011). Department of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, Mahabad Branch, Islamic Azad University, Mahabad, Iran *(e-mail : toraj73@yahoo.com) Laboratory tests and two field experiments were conducted in RCB design in 2008 and 2009, to evaluate the effects of hydro-priming duration on seedling vigour and field establishment of maize (Zea mays cv. SC 301). Seeds were divided into five sub-samples, one of which was kept as control (non-primed) and four other samples were soaked in distilled water for 6, 12, 18 and 24 h and then dried back to about 30% moisture content. All hydro-priming durations significantly improved mean germination rate, seed vigour index as well as shoot, root and seedling dry weights and reduced electrical conductivity of seed leachates, compared with unprimed seeds. This has resulted in better stand establishment of seedlings from primed seeds. The highest improvement was achieved by 18 h priming duration. Seedlings from hydro-primed seeds also emerged earlier than those from unprimed seeds. It was concluded that hydro-priming duration for 18 h is a simple and low cost technique for improving seedling vigour and field establishment of maize. 17. Ahmad Reza Golparvar* and marzieh karimi [Effects of drought stress on seed yield and yield components of sweet corn (Zea mays L.) cultivars]. Res. on Crops12(2): 346-351 (2011). Department of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, Khorasgan (Isfahan) Branch, Islamic Azad University, P. O. Box. 81595-158, Isfahan, Iran *(e-mail : dragolparvar@gmail.com) This experiment was achieved to survey the effects of drought stress on seed yield and its components in three sweet corn cultivars. The experiment was performed by using the split plot design in the layout randomized completely block design with three replications in Arid and Dry land Regions Research Station, Kashan in 2009. In this research, the irrigation intervals including four, six, eight and ten days were established as the main factor levels and arranged in the main plots. On the other hand, the sweet corn cultivars including Chase, Shaker and Iranian cultivars were considered as the sub- factor levels and randomly arranged in the sub-plots. Four and ten days irrigation intervals showed the highest and the lowest seed yield, respectively. The seed yield loss was due to decrease in number of seed rows/ear and number of seeds/row. Mean comparison among the cultivars revealed that Shaker had the highest seed and biological yield. As well as, comparison of the mean of interaction effects of cultivars and irrigation intervals indicated maximum seed yield in Shaker (16375.5 kg/ha) under non-drought stress condition (four days irrigation) and minimum seed yield in Chase cultivar (1193.3 kg/ha) under severe stress condition (10 days irrigation). In non-stress as well as severe stress condition, maximum seed yield and harvest index were obtained from Shaker cultivar. Therefore, Shaker was suggested as the most drought tolerant cultivar to drought. This cultivar also indicated high yield potential to propose in non-stress conditions. 18. MOHAMMAD REZA DADNIA* and Payam moaveni [Response of corn (Zea mays L.) production in response to PGPRs under different rates of phosphorus]. Res. on Crops12(2): 352-355 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shahr-e-Qods Branch, Tehran, Iran*(e-mail : rezadadnia@yahoo.com) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPRs) may be significant on yield levels and efficient for crop production. Field experiment was conducted in Karaj Research Field in 2010 with corn cultivars (Zea mays L. var. SC 704 and SC 700) and combination of PGPRs (Pseudomonas putida, Azospirillum lipoferum and Azotobacter chrococcum) and different phosphorus fertilizer rates. In our research, a significant difference was observed in PGPR+P treatments. The mean yield was 4.7 and 4.1% higher with PGPR+20% P (60 kg triple super phosphate/ha) than adequate phosphorus fertilizer (300 kg triple super phosphate/ha without PGPRs) applied in SC 704 and SC 700 cultivars, respectively. Overall application of all PGPR+P (60 to 240 kg TSP/ha) treatments increased mean grain yield. The results indicated that P supply was related to PGPRs and it was the way for reduction of chemical fertilizers application. 19. MOHAMMAD REZA DADNIA* [Effect of nitrogen levels and PGPRs on yield of corn (Zea mays L.) cultivars]. Res. on Crops12(2): 356-359 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shahr-e-Qods Branch, Tehran, Iran*(e-mail : rezadadnia@yahoo.com) N can be replaced by Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPRs) in corn. Our objective was to assess the relationship between the PGPRs (Pseudomonas putida, Azospirillum lipoferum and Azotobacter chrococcum), and different N rates on yield and yield components in grain corn cultivars (Zea mays L. var. SC 704 and SC700). Seven N treatments were used in this study which were mixed by PGPRs conducted in Karaj Research Field in 2010. In this study, we combine different nitrogen fertilizer rates with PGPRs. N rates were based on 20, 40, 60 and 80% of plant needed with PGPRs, 100% N and control treatments without PGPRs. 20 to 80% of N applied with PGPRs increased grain yield about 4.3 to 25.3% in SC 704 and 3.5 to 22.5% in SC 700 in comparison with 100% of N applied without PGPRs. This response was affected by N management showing that yield production would make the difficult challenges to reduction of nitrogen rate and agricultural practices. 20. MOHAMMAD REZA DADNIA* [Effect of different strains of Bacillus subtilis on growth and grain yield of corn (Zea mays L.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 360-363 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shahr-e-Qods Branch, Tehran, Iran This study evaluated the effects of Bacillus subtilis strains on maize [Zea mays (L.) var. SC 704] in respect to nitrogen application, and their relationship with yield, harvest index (HI), plant height and yield components. Experiment was conducted with five strains of B. subtilis (Russian 2, 25-1, American 7, Chinese 5, 26-1) and control treatments (un-inoculated with Bacillus) in sub-plots and nitrogen fertilizer [75% (340 kg urea/ha) and 100% (340 kg urea/ha)] were in main plots. The total yield was increased about 32% by Russian 2 than control treatments at 75 and 100% of N applied, which represents a relative of N supply with thesestrains. 25-1, 26-1 and Chinese 5 strains had no significant differences on investigated traits. High harvest index and low values of nitrogen were associated with high plant height with Bacillus strains was advantageous for yield production. 21. MOHAMMAD REZA DADNIA* [Effect of Azospirillum strains on regulation of chemical markers activity in corn (Zea mays L.) under water deficit condition]. Res. on Crops12(2): 364-367 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shahr-e-Qods Branch, Tehran, Iran*(e-mail : rezadadnia@yahoo.com) The Azospirillum strains effects that would present direct (nutrient supply) and indirect (reduction water deficit effects) in agricultural systems. We evaluated the relative of Azospirillum on two chemical markers such as Dityrosine (Di-TY) and Dihydroxy-guanozine (8-oH-dg) to control water deficit effects in corn (Zea mays L. var SC 704). We found significant differences among the different Azospirillum strains (A. lipoferum, A. brasilense and A. irakiens) to reduction markers activity. The optimum yield was produced in water deficit situation at inoculated treatments. Seed inoculation with Azospirillum in drought stress condition decreased content of oxidative damage by biomarkers (Dityrosine and Dihydroxy-guanozine). It indicated the positive effect of strains in reduction of drought stress effects. A. lipoferum, A. brasilense and A. irakiens significantly increased grain yield about 16.3, 12.9 and 8.2% and decreased markers activity about 11.1, 7.6 and 5.8% than un-inoculated (control) treatments at 12% soil moisture, respectively. It seems that inoculated plants scavenge produced free radicals under water deficit stress.These results suggest that Azospirillum strains notably influenced the markers activity at environmental stresses. 22. P. ASHOKA, MUDALAGIRIYAPPA and N. H. SUNITHA [Effect of different nutrient management practices on yield, economics and nutrient uptake of baby corn (Zea mays L.)*]. Res. on Crops12(2): 368-371 (2011). Department of Agronomy, College of Agriculture, Raichur-584 101 (Karnataka), India A field experiment was conducted during kharif 2005 to evaluate the effect of different nutrient management practices on yield and nutrient uptake of baby corn. The results indicated that higher yield on baby corn (64.43 q/ha), net return (Rs. 68, 702/ha), B : C ratio (3.85) and uptake of nutrients viz., nitrogen (183.10 kg/ha), phosphorus (71.41 kg/ha), potassium (1693.84 kg/ha), zinc (413.8 g/ha) and iron (3023.2 g/ha) were recorded. Application of RDF+25 kg ZnSO4+10 kg FeSO4+35 kg vermicompost over RDF alone and all other treatments except RDF alongwith micro nutrients was combination of FYM. While significantly lower yield of baby corn (43.28 q/ha), net return (Rs. 34,563/ha) and uptake of nutrients viz., nitrogen (134.04 kg/ha), phosphorus (33.76 kg/ha), potassium (115.77 kg/ha), zinc (311.5 g/ha) and iron (1946.3 g/ha) were recorded with application of only RDF. Application of RDF alongwith micro nutrients and organics resulted in increase in yield of crop acceptance. 23. Li Pu Han, Xiuling Wang, Xingqiang Guo, Manjunatha S. Rao, Yosef Steinberger, Xu Cheng and Guang Hui Xie* [Effects of plant growth regulators on growth, yield and lodging of sweet sorghum]. Res. on Crops12(2): 372-382 (2011). Biomass Engineering Center, College of Resources and Environmental Sciences China Agricultural University, 100193 Beijing, P. R. China *(e-mail : xiegh@cau.edu.cn) Sweet sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] has been widely regarded as a potential feedstock for producing bio-fuel. Lodging is a limiting factor due to its height, particularly in susceptible varieties and hybrids. An experiment was performed in order to study the influence of plant growth regulators (PGRs) on lodging and yield of sweet sorghum lodging-susceptible variety Yuantian 1. The experiment was carried out in a randomized block design. Treatments of ethephon (ETH 90, 180 and 360 g/ha), uniconazole (S-3307 22.5, 45 and 90 g/ha), chlormequat chloride (CCC 225, 450 and 900 g/ha), 2, 3, 5-triiodobenzoic acid (TIBA 45, 90 and 180 g/ha) and a control (water) were used in this study. The results indicate that ETH, among the four PGRs, had significant dwarfing effects on the stalk length, resulting from a significantly shorter stalk length increment before 14 days after treatment (DAT). A reduction in internode length was observed at the orders between 6th and 15th (not significant for 8th, 9th and 10th) from the base. The ETH treatments significantly reduced lodging rate of sweet sorghum plants with an increase in ETH dose. It is in agreement the ETH treatments exhibited significantly higher stem bending strength compared that in the control. There was no significant difference in between the ETH treatment and the control. The ETH treatment exhibited lower grain yield (not significant), stem and biomass yield (significant) than the control. However, the leaf blades at the 3rd and 4th orders from the top were significantly shorter after treated with ETH. The leaf orientation value (LOV) of the two leaves was significantly higher than the control. The improvement in leaf blade length and LOV after the ETH treatments opened a new possibility for increasing yields through increasing plant density. This study contributes to the knowledge and importance of PGR usage, especially ETH hormone in lodging enhancement. 24. Mohamad Mehdi Shahri, Ali Soleymani*, Mohamad Hesam Shahrajabian and Hossein Yazdpour [Effect of plant densities and sulphur fertilizer on seed and oil yields of canola]. Res. on Crops12(2): 383-387 (2011). Department of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, Khorasgan (Esfahan) Branch, Islamic Azad University, Esfahan, Iran*(e-mail : a_Soleymani@khuisf.ac.ir) In many regions in the world, sulphur deficiency has been recognized as a limiting factor for canola seed production. To investigate the effect of sulphur fertilizer and plant density of new cultivars of canola on length of growth phase of canola under climatic condition of Gorgan region and its suburb, an experiment was conducted in 2004-05 in form of split split plot design with in randomized complete block design with three replications. The main plots consisted of level of sulphur fertilizer (0, 125 and 150 kg/ha). Sub-plots were composed of three plant densities (60, 80 and 100 plants/m2), and sub sub-plots included three kinds of canola, namely, RGS 003, Hyola 401 and Hyola 420. Application of sulphur fertilizer and plant density had no significant influence on any of the experimental traits, but cultivar had significant effect on all traits except of 2 and 4 leaves stages. Hyola 401 had the most number for flowering, and the cultivar RGS 003 showed the most number of days for six leaves, extension of stem and the beginning of flowering. Hyola 401 also had the most seed yield, 1000-seed weight and oil yield which had the significant difference with other cultivars. So, under similar condition with this study, application of 250 kg S/ha and using Hyola 401 and the plant density of 60 plants per m2 seemed appropriate. 25. Hossein Zahedi* and Hamid Reza Tohidi Moghadam [Effect of drought stress on antioxidant enzymes activities with zeolite and selenium application in canola cultivars]. Res. on Crops12(2): 388-392 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamshahr Branch, Islamic Azad University, Islamshahr, Iran In order to study the effects of drought stress on antioxidant enzymes activities with zeolite and selenium application in canola cultivars, an experiment was conducted in two growing seasons in 2006 and 2007. Site study was conducted at Seed and Plant Improvement Institute, Karaj, Iran. The experimental design was a randomized complete block arrangement in factorial split plot with three replications. Irrigation factor was chosen at two levels, including complete irrigation and irrigation holding at stem elongation stage. Zeolite was used at two levels, non-application and 10 t/ha. Also selenium was sprayed at three concentrations that are 0, 15 and 30 g/l from sodium selenate. These treatments were randomized in main plots, while three canola cultivars (Zarfam, Sarigol and Okapi) were randomized in sub-plots. The results showed that main effect of treatments was significant on antioxidant enzymes activities and drought stress increased them. Soil zeolite application was significant on enzyme activities and decreased it. Also selenium foliar applications had significant effect on enzyme activities and led to increase in activities. The cultivars had significant difference each other in aspect of antioxidant enzymes activities as Okapi had the highest enzyme activities. In general, zeolite and selenium application increased water stress resistance via improving water availability and alleviating destroyer effect of drought stress. 26. HAMID REZA TOHIDI MOGHADAM*, HOSSEIN ZAHEDI, FARSHAD GHOOSHCHI and SHAHRAM LAK [Effect of super absorbent application on destructive oxidative stress in canola (Brassica napus L.) cultivars under water stress conditions]. Res. on Crops12(2): 393-401 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Varamin-Pishva Branch, Islamic Azad University, Varamin, Iran*(e-mail : hamid_tohidi2008@yahoo.com) Drought stress significantly limits canola (Brassica napus L.) growth and crop productivity. Hence, efficient management of soil moisture and study metabolic changes which occur in response to drought is important for agricultural production of this crop. For a better understanding of drought tolerance mechanisms and improving soil water content management strategies, an experiment was laid out in a randomized complete block design with factorial split arrangement with three replications. Irrigation strategy and super absorbent application were allotted to main plots. Irrigation strategy had two levels : 80% of evaporation as control (I1) and drought stress started from flowering stage (I2). Application of super absorbent had two levels : Non-application of super absorbent as control (S1) and application of super absorbent with 7% concentration. Cultivars (Rgs 003 (V1), Sarigol (V2), Option 500 (V3),Hyola 401 (V4), Hyola 330 (V5) and Hyola 420 (V6) were allotted to sub-plots. Plants under water deficit stress and application of super absorbent showed a significant increase and decrease, respectively, in malon dialdehyde, dityrosine and hydroxy deguanosine contents in leaves compared with control plants. In this context, plants with higher levels of antioxidants showed higher resistance to these stress conditions and higher yield and dry matter allocation to grain filling process i. e. harvest index. Our results suggest that drought stress leads to production of oxygen radicals, which results in increased lipid, protein and nucleic acids peroxidation and oxidative stress in the plant. In conclusion of present study, application of super absorbent polymer could reserve different amounts of water in itself and so increases the soil ability of water storing and preserving and at last in water deficiency, produce plant water need and approve its growth under postanthesis water deficiency. 27. K. N. PAWAR [Influence of water stress treatment on seed quality of groundnut genotypes]. Res. on Crops12(2): 402-404 (2011). Department of Crop Physiology, University of Agricultural Sciences, Bijapur (Karnataka), India Experiment was conducted at Department of Crop Physiology, UAS, Bijapur during 2007-08 to study the effect of water stress treatments on seed germination, seedling growth and vigour index of some groundnut genotypes. The experiment consisted of four genotypes viz., ICG-1930, KRG-228, ICGS-11 and S-206 and was laid out in completely randomized block design with factorial concept. The water stress levels -1, -3, -5, -7, -10 and -12 bar were prepared using PEG 6000 distilled water was used as control. The seed germination, seedling growth and vigour index decreased significantly with increasing intensity of stress irrespective of cultivars tested. However, ICGS-11 and ICG-1930 followed by ICGS-11 showed higher seed quality parameters indicating drought tolerance. 28. B. D. Patel*, H. P. Khedkar, R. B. Patel and B. T. Sheta [Bioefficacy of some selective post-emergence herbicides in kharifsoybean]. Res. on Crops12(2): 405-408 (2011). DWSR Anand Center, B. A. College of AgricultureAnand Agricultural University, Anand-388 110 (Gujarat), India*(e-mail : bdpatel62@yahoo.com) A field experiment was carried out at the College Agronomy Farm, B. A. College of Agriculture, Anand Agricultural University, Anand, Gujarat duringkharif season of the year 2008. Post-emergence application of herbicide imazethapyar @ 75 g/hafb hand weeding at 30 DAS, fenoxaprop-p-ethyl @ 75 g/hafb hand weeding at 30 DAS, quizalofop ethyl @ 75 g/ha fb hand weeding at 30 DAS effectively controlled the monocot, dicot and sedges weeds at 30 and 60 DAS. Interculturing fb hand weeding at 20 and 40 DAS had higher WCE. Plant height, number of branches/plant, pods/plant, seed (2251 kg/ha) and straw yield (3756 kg/ha), protein and oil content remained at par with hand weeding at 20 and 40 DAS as compared to weedy check. 29. MOHAMMAD REZA DADNIA* [Response of soybean (Glycine max L.) to Bacillus strains and nitrogen fertilization]. Res. on Crops12(2): 409-412 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shahr-e-Qods Branch, Tehran, Iran*(e-mail : rezadadnia@yahoo.com) In soybean yield (Glycine max L.), N uptake during seed-filling period can be increased by Bacillus strains in association with Rhizobium. Three Bacillus strains (subtilis, megaterium and coagulance) were compared with Bradyrhizobium japonicum (BJ) effects on soybean. The experiment was conducted in Karaj Research Field during 2010. In urea placed at 20 cm below the soil surface before planting and Bacillus strains split-applied with seed before planting with 50 and 100 kg urea/ha as starter. The yield at 200 kg urea/ha (starter : 50 and 100 kg/ha) was 3740 kg/ha, but the mean yield of BJ applied treatments was 4114 kg/ha (upto 10%). In BJ treatments at 50 kg urea/ha, N uptake was 347 kg/ha, but it was 12% greater than the mean of the 200 kg urea/ha treatments. Nitrogen uptake with combined BJ by B. subtilis (BS), B. megaterium (BM) and B. coagulance (BC) treatments was 434, 397 and 375 kg/ha at 50 kg urea/ha as starter, respectively. Yield maximization (12.5 to 16.5%) for BJ × Bacillus strains induced high nitrogen fixation when soybean plants acquired N from urea applied before planting. 30. MOHAMMAD REZA DADNIA* [Effect of different formulations of Rhizobium japonicum on yield and yield attributes of soybean (Glycine max L.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 413-416 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shahr-e-Qods Branch, Tehran, Iran*(e-mail : rezadadnia@yahoo.com) One of the ways to achieve available biological nitrogen is the use of Rhizobiums for root symbiosis in legumes. Rhizobium needs a carbon source for nitrogenase enzyme protection. However, different Rhizobium japonicum formulations can be effective on N2 fixation. Here, we applied powder and liquid formulation of Rhizobium to demonstrate that is essential for effective N2 fixation. This is independent for root development due to their known regulation of glutamate synthesis, that is the main parameter on nitrogen fixation in soybean yield production. In our study, liquid formulation had high yield, seeds/pod and had a higher root development than other treatments. In addition, the powder formulation had a positive effect for soybean yield as compared to 250 kg urea/ha. Control plants regulated their development by low nitrogen as starter. This makes it a critical point for regulation of symbiosis. 31. MOHAMMAD REZA DADNIA* [Studies on Bradyrhizobium japonicum interactions with Pseudomonas putida, Azospirillum lipoferum and Azotobacter chrococcum in soybean (Glycine max L.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 417-420 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shahr-e-Qods Branch, Tehran, Iran*(e-mail : rezadadnia@yahoo.com) Nitrogen plays an essential role in the life of legumes and root nodules. Symbiosis occurs in root cells, as shown nodules. In soybean, symbiosis can activate by Bradyrhizobium japonicum, in response to a moderate decrease of nitrogen. This response can induce with Pseudomonas, Azospirillum and Azotobacter. Here, we showed bacterial interactions effects on symbiosis. Management factors included (i) Bradyrhizobium japonicum (BJ), BJ × Pseudomonas putida (BJ × PP), BJ × Azopirillum lipoferum (BJ × AL), BJ × Azotobacter chrococcum (BJ × AC) and applied 200 kg urea/ha without inoculation (control) and (ii) inorganic fertilizer (urea) at 50 and 100 kg/ha as starter. Consideration of main effects, BJ × PP gave the highest yield response (27.45%) in comparison with 200 kg urea/ha suggesting that inorganic fertilizer provided growth factors in addition to nutrient contents. BJ, BJ × AL and BJ × AC increased yield about 19.55, 24.12 and 21.88% in comparison with 200 kg urea/ha. We hypothesize that symbiosis reactive by bacterial strains was a practice to achieve high yield and nutrients management. 32. MOHAMMAD REZA DADNIA* [Effects of bacterial strains on pod formation, yield, protein and oil content in soybean (Glycine max L.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 421-424 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shahr-e-Qods Branch, Tehran, Iran*(e-mail : rezadadnia@yahoo.com) Rhizobium can enter into root nodule for symbiosis and nitrogen-fixing in leguminous plants. Here we describe the effects of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and interactionof B. japonicum with Bacillus subtilis, B. megaterium, B. coagulance (Mix strain1), and Azotobacter chrococcum, Pseudomonas putida, Azospirillum lipoferum (Mix strain 2) on yield, respectively. Our objective was to evaluate yield and seed quality relationships to strains during the seed-filling period, as average protein and oil content in soybean seed. Field experiment was conducted at two urea rates (50 and 100 kg/ha) as main plots to examine the effects of mix strains 1 and 2 and 200 kg urea/ha as sub-plots on pod formation, soybean yield, seed protein and oil concentration. In mix strains 1 and 2 treatments, seed weight increased about 12.5 to 16.1%, respectively, when compared with B. japonicum. In 200 kg urea/ha treatments average yield was 10.3, 18.5 and 22.6% lower than B. japonicum, mix strains 1 and 2 treatments, respectively. Different urea treatments with mix strains effects on seed growth and pods/plant caused high seed protein and low oil concentration. The effects of mix strain 2 on seed quality were 8-9 g/kg lower oil concentration and 10-11 g/kg higher protein concentration than mix strain 1. No result was observed in high oil concentration relative to 200 kg urea/ha. 33. AJAY KUMAR MEDHI AND A. ROY [Effect of foliar application of growth regulators on growth physiology, quality and yield in greengram [Vigna radiata (L.)Wilczek] var. PDM-54]. Res. on Crops12(2): 425-428 (2011). Regional Agricultural Research Station, Assam Agricultural University, Titabar-785 630 (Assam), India A field experiment was conducted to study the effect of greengram to foliar application of growth regulators (IAA 25 ppm, NAA 50 ppm, cycocel 250 ppm, ascorbic acid 25 ppm, ethrel 250 ppm and GA3 30 ppm) on growth physiology, yield attributes, yield and quality parameters of seed during foliar application of different growth regulators significantly influenced the plant growth and yield attributing characters. Leaf area index, leaf chlorophyll and N, P, K content of leaf were significantly increased due to application of growth regulators. NAA 50 ppm recorded the highest yield (14.66 q/ha) followed by cycocel 250 ppm (14.39) which was due to highest number of pods (53.06/plant ), number of seeds per pod (11.32/pod) and 1000-seed weight (35.54 g). The yield increment was 44.0% and 41.3% increase over control. Nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium contents of seed after harvest were significantly increased by growth regulators, highest being observed in NAA 50 ppm. Application of growth regulators significantly improved quality parameters of seed viz., total soluble sugar, starch, protein and free amino acid content. NAA 50 ppm recorded total soluble sugar (59.68 mg/g), starch (429.43 mg/g), protein (304.80 mg/g) and free amino acid (18.33 mg/g) dry weight of seed. 34. S. S. DEKHANE, H. R. KHAFI, A. D. RAJ, R. M. PARMAR AND M. A. SHEKH [Effect of biofertilizer and fertility levels on growth and yield of cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.]]. Res. on Crops12(2): 429-431 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh-362 001 (Gujarat), India A field experiment was conducted during kharif 2008 at Instructional Farm, Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh (Gujarat) on clayey soil to study the effect of bio-fertilizer and fertility levels on growth and yield of cowpea. Sixteen treatments comprising all possible combinations of four levels of biofertilizers viz., without inoculation, with PSB (Phosphate solubilizing bacteria) inoculation, with liquid PSB inoculation and with Rhizobium inoculation and four levels of chemical fertilizers viz., 0, 50, 75 and 100% RDF (Recommended dose of fertilizer) were tried in factorial randomized block design with four replications. The results of the experiment indicated that application of 100% RDF and seeds inoculated with Rhizobium significantly increased the growth parameters viz., plant height, number of branches per plant as well as yield attributes like number of pods per plant, grain yield per plant, stover yield per plant and test weight. Significantly highest grain (1441 kg/ha) and stover (1716 kg/ha) yields were also recorded by seed inoculation with Rhizobium. The highest grain (1439 kg/ha) and stover (1678 kg/ha) yields were reported with 100 % RDF but found statistically at par with 75% RDF. 35. A. S. CHAVAN, H. R. KHAFI, A. D. RAJ, R. M. PARMAR AND M. A. SHEKH [Effect of potassium and zinc on growth and yield of cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.]]. Res. on Crops12(2): 432-434 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh-362 001 (Gujarat), India A field experiment was conducted during kharif 2008 at Instructional Farm, Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh (Gujarat) on clayey soil to study the effect of potassium and zinc on growth and yield of cowpea. Twelve treatments comprising all possible combinations of four levels of potassium viz., control, 20, 40 and 60 kg/ha and three levels of zinc viz., control, 20 and 40 kg/ha were tried in factorial randomized block design with four replications. The growth and yield attributes as well as grain (1587 kg/ha) and stover (2047 kg/ha) yields were significantly increased by application of 60 kg K2O/ha over 40 kg K2O/ha, 20 kg K2O/ha and no potassium application. Application of zinc (ZnSO4) to the cowpea at 40 kg zinc/ha recorded remarkably higher plant height, yield attributes, grain (1553 kg/ha) and stover (2010 kg/ha) yields as compared to lower levels of zinc treatments. The higher net realization of Rs. 21725/ha with BCR (3.43) and Rs. 20545/ha with 3.18 BCR accrued under the application of 60 kg K2O/ha and 40 kg zinc/ha, respectively. Application of 60 kg K2O/ha along with 40 kg zinc/ha recorded the highest net realization of Rs. 24344/ha with BCR 3.54. 36. Rozbeh Farhoudi* and Maryam makezadeh Tafti [Improvement in germination and seedling growth of Caper (Capparis spinosa L.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 435-439 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shoushtar Branch, Shoushtar, Iran*(e-mail : rfarhoudi@gmail.com) In order to survey the effects of dormancy-breaking treatments on germination in Caper (Capparis spinosa L.), a completely randomized design was implemented at four replications. Treatments were : gibberellic acid soaking (500 and 1000 ppm), leaching, KNO3 soaking (3%), acid scarification (20 min), GA3 soaking (500 or 1000 ppm)+leaching, GA3 soaking (500 or 1000 ppm)+acid scarification and KNO3+leaching. Results showed significant differences (P<0.01) between dormancy-breaking techniques. The highest germination rate and the lowest mean germination time belonged to 100 ppm GA3+leaching and 500 ppm GA3+leaching treatments, respectively. 37. Rozbeh Farhoudi* and Maryam makezadeh Tafti [Improvement in germination and seedling growth of Astracantha adescendens]. Res. on Crops12(2): 440-444 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Islamic Azad University, Shoushtar Branch, Shoushtar Iran*(e-mail : rfarhoudi@gmail.com) In order to survey the effects of dormancy-breaking treatments on germination in Astracantha adescendens, a completely randomized design was implemented at four replications. Treatments were : hot water scarification with 70° and 90°C for 10 and 15 min, sulfuric acid scarification (15, 30 and 45 min), seed stratification for 2,4 and 8 weeks, scarification (with hot water or acid) + seed stratification (4 week). Results showed significant differences among seed dormancy breaking methods (P<0.01). The highest germination rate and the lowest mean germination time were obtained with 90°C water for 15 min+4 week stratification (83%) and 90°C water for 10 min+4 week stratification (81%) treatments. Seedlings were, however, injured during 45 min acid scarification procedure. 38. R. S. KALIRAMANA* AND B. S. PANNU [Effect of wetting and drying cycles on potassium fixation with chloride, sulphate, carbonate and nitrate anions in Haryana soils]. Res. on Crops12(2): 445-452 (2011). Department of Soil Science, CCS Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar-125 004 (Haryana), India*(e-mail : raghubir29@rediff.com) The studies were carried out to study the effect of wetting and drying cycles on potassium fixation with anion i. e. chloride, carbonate, sulphate, nitrate on potassium fixation in soils of Haryana. The most of the soils were light in texture and ranged from sandy to clay loam. The soils were alkaline in reaction. The amount of K fixed increased with the increasing days of wetting and drying cycles at different levels K from 20 to 1000 µg/ml in soil upto a depth of 25 cm. The highest amount of fixed K was observed after seven days followed by 14 and 28 days as compared to the wet fixed K. It appeared that a period of 7 to 28 days of wetting and drying cycles was sufficient for transfer of K ions from the non-exchangeable K pool to the available K pool. The amount of K fixed was observed maximum in the Palwal soil and minimum in Chautala soil with different levels of K. 39. K. G. Anitha and M. Thangaraju [Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus to influence leaf n and enhance cane yield by increased colonization under reduced N fertilization in sugarcane]. Res. on Crops12(2): 453-461 (2011). Centre for Advanced Studies in Agricultural Microbiology, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore-641 003 (Tamil Nadu), India Field experiment conducted at Coimbatore, India has come out with the following results that in sugarcane the application of Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus at 50% N fertilizer level has increased the cane yield by 4.53% than 100% N level. Higher counts of G. diazotrophicus were observed in shoot, root and leaf samples of sugarcane under 50% N+G. diazotrophicus treatment when comparing to 50% N and or 50% N+Azospirillum. Moreover, this treatment is having more positive correlation with leaf N content (r2= 0.75). Leaf Ncontent and G. diazotrophicus counts in leaf are positively correlated. Because of this leaf N was maximum in those treatments that had maximum G. diazotrophicus load i. e. at 5th month population of G. diazotrophicus was more in 50% N +G. diazotrophicus treatment (3.1 x 106) and so as the leaf N level (26.5 mg/g dry weight of leaf). Low level of N alongwith G. diazotrophicus application has favoured the increased colonization. Many studies have shown that the isolation or enumeration of G. diazotrophicus is not possible in highly N fertilized sugarcane but in this study even under 100% N levels (275 kg N/ ha) colony count was ranging between 102 to 103 CFU/g of leaf/root/shoot of sugarcane. Though the whole sugarcane crop is colonized by G. diazotrophicus, correlation of leaf N with G. diazotrophicus counts in leaf, shoot and root was linear and positive but the G. diazotrophicus count in root had higher degree of correlation (r2=0.84) followed by count in shoot (r2=0.79). 40. A. I. PATEL [Effect of 2,4-D on callusing and morphogenesis of sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrid)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 462-464 (2011). Regional Sugarcane Research Station, Navsari Agricultural University, Navsari-396 450 (Gujarat), India Tender leaf material of two prominent sugarcane cultivars viz., Co 99004 and CoN 05071 were cultured on MS medium augmented with various levels of 2,4-D (2, 4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid) for callusing and 6-BAP (6-benzyl amino purine) and NAA (Naphthalene acetic acid) for morphogenesis. Among different levels and combinations the 3 to 5 mg/l 2,4-D included in MS medium produced maximum dry, soft, compact and whitish callus within 18-30 days in both the cultivars. Whereas the 3 mg/l BAP and NAA, 4 mg/l BAP and NAA induced 81-100% morphogenesis or organogenesis within 27-35 days after culturing of both the varieties. The average number of shoots after organogenesis also varied with different levels of auxin like BAP and NAA. The combination 3 and 4 mg/l BAP and NAA produced maximum number of shoots upto 10.8 to 12.5 in Co 99004 and 11.9 to 13.5 in CoN 05071. Whereas maximum length of shoot ranged upto 4.8 to 7.5 and 4.8 to 6.8, respectively. 41. A. I. PATEL [In vitro regeneration using shoot tip culture in commercial cultivar CoN 05072 of Saccharum spp. hybrid]. Res. on Crops12(2): 465-470 (2011). Regional Sugarcane Research Station, Navsari Agricultural University, Navsari-396 450 (Gujarat), India A protocol for direct shoot regeneration without intervening callus phase was developed by using shoot tip culture on MS (Murashige and Skoog) medium for sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrid) variety CoN 05072. The study revealed that aseptically inoculated shoot tip of sugarcane in BAP (Benzylamine purine) @ 2.00 mg/l established the shoot induction and shoot multiplication was also observed at the same concentration. At 2.00 mg/l of BAP (82.00%), the shoots were weak, tiny and non-separable, whereas at 1.0 mg/l of BAP (25.84%) rate of multiplication was low (6.46) but resulted in desirable quality, well grown, easily separable and healthy plantlets. The root induction was observed NAA (Napthalene acetic acid) @ 2 mg/l (90.00%) and complete plantlets were hardened and transferred to greenhouse for establishment with survival rate of 80%. 42. G. Shabani*, M. R. Chaichi, M. R. Ardakani, J. K. Friedel, K. Khavazi and H. R. Eshghizadeh [Effect of chemical and biological soil amendments on production and soil seed bank of annual medic (Medicago scutellata cv. Robinson)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 471-478 (2011). Agriculture Research Center, Karaj Branch, Islamic Azad University, Karaj, Iran*(e-mail : bb1379@yahoo.com) In order to study the effect of different fertilizing systems consisting of control (no fertilizer), chemical, biological and its combination fertilizer on forage yield and conservation of soil seed bank of annual medic (Medicago scutellata cv. Robinson), an experiment was conducted based on a complete randomized block design with three replications in two locations under dry farming conditions in Kermanshah province, Iran, in 2009. The results showed that the highest amount of cumulative biomass of 4185 kg/ha was produced in urea fertilizer+phosphorus solubilizing bacteria+mycorrhiza treatment, and the lowest amount (3183 kg/ha) was observed in nitrogen fixing bacteria+mycorrhiza treatment, respectively. The number of pods in soil seed bank was significantly influenced by different fertilizing systems. The highest number of 314.6 pods per square metre was found in nitrogen fixing bacteria+phosphorus solubilizing bacteria treatment and the lowest of 139.8 pods per square metre in control treatment, respectively. Also the highest yield of pods (1147.2 kg/ha) was obtained in nitrogen fixing bacteria+phosphorus solubilizing bacteria application, while the lowest pod yield of 446 kg/ha was found in control treatment. 43. Esmaeil Nabizadeh* and Hussein Heydari Sharif Abad [Nitrogen fixation and nodulation in annual medic (Medicago rigidula) as influenced by inoculation with foreign and inside root symbiotic bacteria]. Res. on Crops12(2): 479-481 (2011). Faculty of Agriculture and Natural Resources, Mahabad Branch, Islamic Azad University, Mahabad, Iran*(e-mail : nabizadeh.esmaeil@gmail.com) Annual species of Medicago are important pasture legumes in western parts of Iran. Their productions are affected by suitable soil Rhizobium meliloti strains and environmental conditions. The principal objective of this study was to find out a suitable Rhizobium meliloti strain(s) for Medicago rigidula. The study was conducted in the greenhouse in 2007 to determine nodulation and nitrogen fixation of M. rigidula inoculated with five R. meliloti strains (Domestic from Mahabad, M3, M15, M29 and WSM540). Symbiotic effectiveness was measured by nodule number and nitrogen fixation by subtracting seed N from total plant N in minus-nitrate treatment at the end of the experiment. The R. meliloti strain “Domestic (Local) from Mahabad” was found to be more effective than the M3, M15, M29 and WSM540 in terms of nodulation, dry matter production and N2 fixation. This may be due to cold resistance of this Rhizobium strain. While nodule number is a very important consideration of symbiotic effectiveness it should be combined with total dry matter and total nitrogen in the evaluation of strains. R. meliloti strain “Domestic of Mahabad” is recommended for inoculation of M. rigidula in western parts of Iran. 44. RECEP ÇAKIR* [Effect of water stress during different developmental stages on some growth indices of flue-cured Virginia tobacco]. Res. on Crops12(2): 482-488 (2011). Lapseki Vocational College, Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University, Lapseki/Çanakkale, Turkey *(e-mail : crec56b@yahoo.com) Paper discusses the results of the evaluations done on the basis of the data obtained from the 3-years field study on the effects of different irrigation regimes and water stress imposed at different growth stages on plant growth of flue-cured tobacco plant (Nicotiana tabacum L.). A randomised complete block design with three replications was applied in the field. Experiments were conducted on the fields of Soil and Water Resources Research Institute in Kýrklareli, Turkey. Three known stages of the plant were considered and a total of 14 irrigation treatments were applied in the experiments with K-326 Virginia tobacco cultivar. All the experimental treatments were irrigated at the same time as the control irrigated at each growth stage with water amount enough to replenish the water deficit in 0-90 cm soil layer, and three levels of water amount reductions (0, 40 and 60%) were done at each development stage. Results of the 3-years study showed that water stress imposed at earlier growth stages was influential mainly on plant growth, leaf formation and on the physiologically based parameters as net assimilation rate (NAR), leaf area index (LAI), absolute growth rate (AGR) and relative growth rate (RGR). 45. D. Adilakshmi* and P. Raghava Reddy [heterosis and inbreeding depression for grain quality traits in rice (Oryza sativa L.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 489-492 (2011). Rice Research Institute and Regional Agricultural Research Station, Maruteru-534 122, West Godavari District (Andhra Pradesh), India Investigation was taken up to study the nature and magnitude of heterosis and inbreeding depression in crosses, namely, Samba mahsuri/Polasa prabha and Samba mahsuri/Nellore mahsuri for quality characters and yield in rice. The estimates of heterosis in the cross Samba mahsuri/Polasa prabha for all the traits were positive and significant except for gelatinization temperature and iron content. The estimates of heterobeltiosis for traits, namely, milling per cent, head rice recovery, length : breadth ratio, elongation ratio and grain yield in the cross Samba mahsuri/Polasa prabha, whereas hulling (%), milling (%), head rice recovery, volume expansion ratio, amylose content and yield per plant in Samba mahsuri/Nellore mahsuri were positive and significant. These crosses could be utilized in heterosis breeding for development of high yielding hybrids. Hulling (%), milling (%) length : breadth ratio, amylose content and yield per plant exhibited significant inbreeding depression. Both the hybrids recorded higher values in F2 generation for volume expansion ratio and iron content which indicated the role of fixable gene effects. In such crosses, pedigree method of selection may be adopted for improvement of these quality traits. 46. R. A. GAMI*, C. J. TANK, R. M. CHAUHAN, S. S. PATEL AND S. V. BURUNGALE [Heterosis for grain yield and quality traits in durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) under late sown condition]. Res. on Crops12(2): 493-495 (2011). Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, S. D. Agricultural University,Sardarkrushinagar-385 506 (Gujarat), India*(e-mail : ramangami@gmail.com) Twenty-eight cross combinations were developed by 8 x 8 diallel analysis during rabi2007-08 and evaluated 28 F1’s and eight parents during rabi2008-09 under late sown condition. Seven crosses out of 28 crosses manifested significant positive heterobeltiosis for grain yield per plant. The range of heterobeltiosis for grain yield was wide (22.30 to 82.54%). The hybrid GW-02-51 x VDW-99-176 (82.54%) expressed the highest heterobeltiosis. The cross combination GW-1139 x GW-1240 expressed highest level of heterosis over better parent (10.78%) for grain protein. 47. R. A. GAMI*, C. J. TANK, R. M. CHAUHAN, S. S. PATEL AND D. M. THAKOR [Heterosis for grain yield and quality components in durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 496-498 (2011). Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, S. D. Agricultural University, Sardarkrushinagar-385 506 (Gujarat), India(e-mail : ramangami@gmail.com) Heterosis studied was carried out by 8 x 8 diallel analysis (excluding reciprocals). Out of 28 crosses, 12 crosses manifested significant and positive heterobeltiosis for grain yield per plant. The range of heterobeltiosis for grain yield was wide (16.98 to 82.44%). The hybrid GW 1239 x GW 1240 (82.44%) expressed the highest heterobeltiosis. The hybrid GW 1139 x GW 1240 expressed highest level of heterosis over better parent (12.29%) for grain protein and cross GW-02-51 x GW 1139 expressed highest heterosis over better parent (1.91%). 48. R. A. GAMI*, C. J. TANK, R. M. CHAUHAN, S. V. BURUNGALE AND D. M. THAKOR [Genetic analysis for grain yield and quality parameters in durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) under late sown condition]. Res. on Crops12(2): 499-501 (2011). Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, S. D. Agricultural University,Sardarkrushinagar-385 506 (Gujarat), India Combining ability analysis was carried out in 8 x 8 parental diallel progenies for grain yield and its component traits in durum wheat. General combining ability and specific combining ability variances were highly significant for all the characters suggesting importance of both additive as well as non-additive type of gene action in the inheritance of characters. The magnitude of the non-additive genetic variance was higher than additive variance for all the characters except plant height and length of main spike. The parent BAWAJI was good general combiner for all the characters except plant height. For grain yield per plant, the crosses GW-02-51 x VDW-99-176, GW 1239 x GW 1189 and GW-02-51 x RD-1009 recorded the highest sca effects. The cross GW-1139 x GW-1240 expressed highest sca effects for grain protein and hectoliter weight. 49. R. A. GAMI*, C. J. TANK, S. S. PATEL, R. M. CHAUHAN AND H. N. PATEL [Combining ability analysis for grain yield and quality component traits in durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 502-504 (2011). Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, S. D. Agricultural University, Sardarkrushinagar-385 506 (Gujarat), India*(e-mail : ramangami@gmail.com) Combining ability analysis was carried out in 8 x 8 diallel parental lines of durum wheat for grain yield and its component traits (excluding reciprocals). Both additive and non-additive type of gene action played an important role for the inheritance of characters. The parent BAWAJI was good general combiner for grain yield per plant, 1000-grain weight, length of main spike, grains per spike, harvest index and grain protein. For grain yield per plant, the crosses GW-1139 x GW-1240 and GW-1239 x GW-1240 recorded the highest sca effects and they involved poor x good and good x good gca parents. The cross VDW-99-176 x GW-1139 expressed highest sca effects for grain protein and cross GW-02-51 x BAWAJI for hectoliter weight. 50. G. H. PAWAR, D. G. KANWADE, K. D. BHOITE AND R. B. GHORADE [Heterosis and combining ability for yield and its component traits in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 505-508 (2011). Agriculture Research Station, Jail Road, Buldhana-443 001 (Maharashtra), India Combining ability analysis for yield and yield contributing component traits in sorghum was carried out during 2006-07 in diallel fashion excluding reciprocals. The general combining ability (gca) and specific combining ability (sca) variances were significant for all the traits except panicle girth, indicating the importance of both additive and non-additive genetic components. However, preponderance of additive gene action was observed for days to 50% flowering, plant height, number of primaries per panicle, panicle length and fodder yield, whereas non-additive gene action was of greater importance for number of leaves per plant, number of secondaries per panicle, panicle weight and grain yield per plant. AKR-426-2 x ICS-70B and AKMS-30B were superior over the parents based on per se performance and gca effects. The cross combination AKR-426-2 x ICS-70B followed by AKR-426-2 x AKMS-30B and AKR-436 x ICS-70B was the best specific combiner for grain yield. 51. D. P. GOHIL AND J. D. PATEL [Genetic variability studies in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under conserved soil moisture condition]. Res. on Crops12(2): 509-511 (2011). Agricultural Research Station, Anand Agricultural University, Arnej-382 230 (Gujarat), India Twenty-two genotypes of chickpea were evaluated for genotypic and phenotypic variability, heritability and genetic advance in 10 quantitative characters. Genotypic coefficient of variation was highest for effective branches per plant followed by biological yield per plant, 100-seed weight, harvest index and seed yield per plant. High heritability values coupled with high to moderate GCV value were exhibited by 100-seed weight, effective branches per plant, harvest index, days to 50% flowering and days to maturity. Thus, phenotypic selection would be effective for genetic improvement in these traits. 52. H. G. SHEKHAT, J. H. VACHHANI, L. L. JIVANI AND V. H. KACHHADIA [Gene action in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 512-516 (2011). Main Oilseeds Research Station, Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh-362 001 (Gujarat), India Gene action for yield and its attributing traits was studied in the F1’s and F2’s of a 10 x 10 half diallel in sesame. The analysis of genetic components revealed that both additive (D) and non-additive (H) type of gene actions were involved in the inheritance of most of the traits studied with preponderance of non-additive gene actions for all the characters in both the F1 and F2 generations. It was also supported by estimates of s2g/s2s ratios. Further, dominance ratio (H1/D)1/2 indicated the presence of over dominance for all the traits in both the generations except days to maturity, which was partial and complete dominance in F1 and F2 generations, respectively. Asymmetrical distribution of positive and negative genes and unequal frequency of dominant and recessive genes in the parents were observed for most of the traits. The estimates of narrow sense heritability were low in most of the traits. It was high for days to maturity in both the generations and moderate for number of effective branches per plant and number of seeds per capsule in F2 generation. 53. Rajesab, Satish, R. G. Muniraj, C. Chikadevaiah and Anulaxmi Nayak [Studies on character association and path coefficient analysis in grain amaranth (Amaranthus spp. L.)]. Res. on Crops12(2): 517-520 (2011). Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, University of Agricultural Sciences, GKVK, Bangalore (Karnataka), India One hundred genotypes of three different species of grain amaranth (Amaranthus spp. L.) were evaluated in 10 x 10 simple lattice design with two replications during kharif 2006 at Main Agricultural Research Station, Hebbal, Bangalore to assess the character association and path coefficient analysis. Mean sum of squares revealed highly significant differences among genotypes for all the 13 characters studied. Seed yield per plant showed a highly significant positive correlation with plant height, panicle fresh weight, number of spikelets per panicle, dry weight of panicle and harvest index both at genotypic and phenotypic levels. In the present study generally the genotypic correlation coefficients were higher than their respective phenotypic correlation coefficients. Path coefficient analysis was carried out both at genotypic and phenotypic levels taking seed yield as a dependent character and the characters which were significantly correlated with seed yield were viz., plant height, fresh weight of panicle, number of spikelets per panicle, dry weight of panicle and harvest index as independent characters. In the present study, all the characters exhibited highly significant and positive correlation with seed yield. From the above discussion, it can be concluded that due emphasis should be given to the characters viz., fresh weight of panicle and harvest index while making selection. 54. G. SEEJA AND K. SREEKUMAR [Association and contribution of different biometrical characters and red rot disease score on cane yield in sugarcane]. Res. on Crops12(2): 521-523 (2011). Department of Plant Breeding and Genetics, College of Agriculture, Vellayani, Thiruvananthapuram (Kerala), India An experiment was conducted to determine direct and indirect effects of important biometrical characters and red rot disease incidence on cane yield among certain inter-varietal crosses of sugarcane. Crosses were evolved from different combinations of three varieties, namely, Co 740, Co 775 and Co Tl 85119 as parents. Analysis of variance revealed significant genotypic differences for all the characters under study except for SMT Brix. Path coefficient analysis revealed that single cane weight recorded high direct and positive effect on cane yield, whereas red rot disease score recorded high direct and negative effect on cane yield. Hence, in the selection of superior sugarcane clones due emphasis should be given on single cane weight and red rot disease resistance to improve cane yield. The present study revealed that sugarcane yield improvement was possible through the careful selection of superior clones with high single cane weight, SMT Brix and red rot resistance. Since residual effect is 52%, other traits which are not included in the present study should also be considered for making sugarcane improvement more successful. 55. SAT PAL SAINI AND PRITPAL SINGH [Micro-nutrient concentration in different vegetative parts of grape (Vitis vinifera) vines varying in age]. Res. on Crops12(2): 524-528 (2011). PAU Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Ropar-140 001 (Punjab), India The study was conducted to investigate micro-nutrient (Zn, Cu, Fe and Mn) concentration in different vegetative (leaves and petiole) parts collected from 15 grape vines (Vitis vinifera) yards varying in age from 2 to 20 years, so as to know their micro-nutrient concentration. Average micro-nutrient concentration was comparatively higher in leaves than petioles, regardless of vine age. The concentration of total Zn and Mn in leaves and petiole decreased remarkably, in contrast to remarkable increase in total leaf and petiole Fe and Cu concentration with increase in vine age from less than 5 years to vines with age between 5 to 10 years. The relationship between leaf and petiole micro-nutrient concentration revealed significantly linear distribution of micro-nutrients in different vegetative parts of grape vines, emphasizing that micro-nutrient absorption in grape vines exhibited similar pattern. Among the four micro-nutrients analyzed, leaf : petiole Fe concentration was highest than other three micro-nutrients. 56. R. N. Wankhade, S. P. Dhanawate and S. B. Gajbhiye [Value addition of dry land fruits in Vidarbha, Maharashtra]. Res. on Crops12(2): 529-531 (2011). Department of Agricultural Economics & Statistics, Dr. Panjabrao Deshmukh Krishi Vidyapeeth, Akola (M. S.), India The present study was undertaken in Vidarbha region. As ber is an important dry land fruit in Vidarbha region, it plays important role in value addition. Therefore, ber fruit was selected for study. Two processing units of ber were selected i. e. Vardha Agro-processing Industry and Akash Gruh Udyog. Results of the present study concluded that average capital investment in ber processing industries was Rs. 2063500, whereas the annual fixed cost for ber processing industries was Rs. 231725. The cost incurred per quintal production of Borkut was Rs. 1862.89 and input : output ratio of Borkut was 1.87. Borkut had the value addition over purchase of dried ber of Rs. 1637.02/q. The actual quantity handled by the unit was higher than required to maintain the processing unit. The break-even point of Ber Processing Unit was 141.55 q. 57. Hojjat Turajizadeh*, Mohammad Reza Naderi, Ahmad Reza Golparvar and Ali Soleimani [Effect of planting pattern and phosphorus on growth and yield of potato grown in Freidan region (Esfahan) of Iran]. Res. on Crops 12(2): 532-538 (2011). Department of Agronomy and Plant Breeding, Khorasgan (Isfahan) Branch, Islamic Azad University, P. O. Box. 81595-158, Isfahan, Iran *(e-mail : hojatturaji@yahoo.com) In order to evaluate the planting pattern and phosphorus rate on potato growth characteristics and yield, this study was conducted in 2009-10 in an agricultural research farm, located in Freidan, in the province of Isfahan, Iran. The study was conducted in the form of strip plot design in the layout randomized complete block design with four replications. The horizontal factor included four different planting patterns of single row, double rows, zigzag, and triple rows with respective planting densities of 5.3, 6.6, 6.6 and 8 per m2. The vertical factor included four different levels of phosphorus, including control, 10, 20 and 30% increase in consumption above the recommended level. By reducing the row spacing and increasing density in the triple-row planting pattern together with 10% increase in the amount of phosphorus, stem height, total shoot weight, leaf area index, number of tubers and tuber yield/m2 increased significantly. Therefore, the triple-row planting pattern treatment with 10% phosphorus increased 53 t/ha, created the highest level of tuber yielding. According to the results, the single-row planting pattern together with 10% phosphorus increase produced 35 larger-size tubers per square metre and would therefore be appropriate for domestic consumption and the triple-row planting pattern together with 10% phosphorus increase produced 54 smaller-size tubers per square metre and would be appropriate in tuber production for seeding purposes in terms similar to those of this research. 58. M. S. Kahlon, c. b. singh and N. K. Sekhon [Response of onion to irrigation and potassium application]. Res. on Crops12(2): 539-544 (2011). Department of Soils, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana-141 004 (Punjab), India The effects of three irrigation levels (IW/PAN-E i. e. 1.0,1.5 and 2.0) and four levels of potassium (0, 25, 50 and 75 kg/ha) on onion production were studied during rabi season of 2008-09 in an experiment carried out on a loamy sand soil of experimental research area of Department of Soils, PAU, Ludhiana. Frequently applied irrigation i. e. IW/PAN-E of 2.0 resulted in significant increase of onion yield as compared to other two treatments. Onion yield increased from 21.1 t/ha at IW/PAN-E 1.0 to 25.5 t/ha at IW/PAN-E 2.0. The applied irrigation levels had significant effects on the size i. e. diameter of onion bulbs. The positive effect of applied K was noted on the yield of onion at all irrigation levels. Increase in K level increased the onion yield from 21.2 t/ha without K application to 25.8 t/ha at 75 kg K2O/ha. Correlation studies revealed that bulb yield was positively correlated with bulb diameter. Total soluble solid (TSS) contents did not show any significant correlation with K level, but it increased with increase in irrigation level. Observed data showed that the highest bulb yield and diameter were recorded with 75 kg K2O /ha and IW/PAN-E = 2.0. 59. Rajya Lakshmi and Vijaya Padma [Evaluation of onion varieties in high altitude and tribal zone of Andhra Pradesh]. Res. on Crops12(2): 545-547 (2011). Agricultural Research Station, Seethampeta-532 443, Srikakulam (A. P.), India Performance of 11 cultivars of onion was studied in rabi season over three years. The pooled analysis revealed that B-780 followed by Phule Samarth recorded significantly higher yield (24.14 and 23.86 t/ha, respectively) compared to other cultivars due to the production of significantly larger size bulbs with more length, diameter and weight. It was found that kharif varieties if grown in rabi season could also confer good bulb yield. Though B-780, Agri Found Dark Red and Arka Kalyan are recommended for rainy season, the yields conferred that they could be grown in rabi season also under tribal zone of Andhra Pradesh. 60. Rajya Lakshmi and Vijaya Padma [Correlation and path analysis studies in chilli in high altitude and tribal zone of Srikakulam district of Andhra Pradesh]. Res. on Crops12(2): 548-550 (2011). Agricultural Research Station, Seethampeta-532 443, Srikakulam (A. P.), India The yield performance was studied in seven varieties of chilli for 2006 and 2007 at Agricultural Research Station, Seethampeta during rabi season. The genotypic and phenotypic correlations and path coefficient analysis were studied for seven characters viz., plant height, plant spread, number of branches, number of pods per plant, 100-pod weight, pod length and pod yield. The genotypic correlation was more than the phenotypic correlation for all the traits. Pod yield was positively correlated with 100-pod weight and pod length. The genotypic and phenotypic path coefficients revealed that 100-pod weight, number of pods per plant and pod length had high positive direct effect on pod yield. Hence, selection made on the basis of pod weight and length would be rewarding. 61. D. B. Patel* AND R. H. Patel [Influence of drip irrigation, mulch and N-fertigation on biometric yield of okra [Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench]]. Res. on Crops12(2): 551-555 (2011). Centre of Excellence for Soil and Water Management Technology, Regional Research Station, Anand Agricultural University, Anand -388 110 (Gujarat), India* (e-mail : dbpatel55@yahoo.in) A field experiment was undertaken at Centre of Excellence for Soil and Water Management Technology, R. R. S., Anand Agricultural University, Anand during summer seasons of 2004 and 2005 to study the effect of drip irrigation, mulch and N-fertigation on biometric yield of okra [Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench]. The treatments comprising four levels of irrigation [drip irrigation at 0.4, 0.6 and 0.8 pan evaporation fraction (PEF) and surface irrigation at 1.0 IW/CPE ratio], three levels of mulch (no mulch, black polyethylene mulch and organic mulch) and two levels of nitrogen (70 and 100% recommended dose) were tested in split plot design with four replications. The results of pooled data for two years indicated that growth attributes viz., plant height, leaf area index (LAI), dry matter accumulation per plant, crop growth rate (CGR) and total chlorophyll content recorded at 90 days of crop and root length at harvest were significantly increased under drip irrigation at 0.8 PEF as compared to surface irrigation. Significantly the highest pod yield (207.96 q/ha) was recorded under drip irrigation at 0.8 PEF and was higher by 46.25% with 30.48 kg/ha-mm water use efficiency (WUE). Among mulching, black polyethylene mulch recorded significantly the highest plant height (110.71 cm), LAI (1.453), dry matter accumulation (68.94 g/plant), CGR, (5.551 g/day/m2 ) and total chlorophyll content (10.75 mg/g) and it was followed by organic mulch, while the lowest values were observed under no mulch treatment. Black polyethylene mulch increased pod yield by 29.65% over no mulch. N-fertigation @ 100 % recommended dose was found significantly superior to 70% recommended dose and recorded higher values of all the growth parameters and registered higher pod yield of okra (169.72 q/ha). Maximum values of CGR and pod yield were recorded under drip irrigation at 0.8 PEF in conjuction with 100% recommended dose of nitrogen with 18% water saving compared to surface irrigation with 100% recommended dose of nitrogen. 62. J. H. VACHHANI, H. G. SHEKHAT, V. H. KACHHADIA, L. L. JIVANI AND P. R. PADHAR [Heterosis and inbreeding depression in okra [Abelmoschusesculentus (L.) Moench]]. Res. on Crops12(2): 556-560 (2011). Main Oilseeds Research Station, Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh-362 001 (Gujarat), India Forty-five hybrids of okra derived from 10 x 10 diallel crosses excluding reciprocals were studied in F1 and F2 generations for heterosis and inbreeding depression for fruit yield and yield components. The analysis of variance revealed significant differences among parents, F1’s and F2’s for most of the characters indicating considerable amount of genetic variability present in the material studied. High magnitude of heterotic effect was detected for fruit yield per plant, number of fruits per plant, 10-fruits weight and internodal length. The cross combination AOL-99-24 x Ajeet-121 expressed the highest heterobeltiosis alongwith high magnitude of inbreeding depression for fruit yield per plant, which will be suitable for exploitation of hybrid vigour for commercial purpose. Another three crosses viz., JOL-1 x HRB-55, JOL-1 x VRO-6 and GO-2 x HRB-107- 4 exhibited high heterobeltiosis with high inbreeding depression for fruit yield per plant. So, these crosses could also be utilized to exploit hybrid vigour and also to bring an improvement through hybridization programme. 63. V. H. KACHHADIA, J. H. VACHHANI, L. L. JIVANI, R. B. MADARIA AND C. J. DANGARIA [Combining ability for fruit yield and its components over environments in okra [Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench]]. Res. on Crops12(2): 561-567 (2011). Department of Agricultural Botany, Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh-362 001 (Gujarat), India The combining ability studies were conducted using line x tester (10 lines and 4 testers) mating method over three environments for nine characters in okra. The pooled analysis of variance for combining ability revealed the preponderance of non-additive gene action in the expression of yield and all the yield contributing characters except fruit girth, which was governed by the additive gene action. The lines i. e. GO-2 and JOL-06-S-5, while the tester viz., HRB-55 were found as good general combiners for fruit yield per plant and possessed concentration of favourable genes as indicated by significant and positive gca effects for fruit yield and other contributing traits viz., number of nodes per plant, number of branches per plant and fruit length. The parents JOL-06-S-4, JOL-06-S-5, JOL-06-S-6 and Parbhani Kranti were identified as good general combiners for early flowering. Among the hybrids, JOL-06-S-5 x HRB-55, JOL-06-S-8 x JOL-06-S-1 and GO-2 x Parbhani Kranti had high sca effects for fruit yield per plant and other related traits, were also accompanied with high per se performance; hence, per se performance of the hybrids would be a good indicator for predicting sca effects. These hybrids could be exploited through heterosis breeding as these are expected to give desirable trangressive segregants in the succeeding segregating generation. 64. V. H. KACHHADIA, J. H. VACHHANI, L. L. JIVANI, H. G. SHEKHAT AND C. J. DANGARIA [Heterosis for fruit yield and yield components over environments in okra [Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench]]. Res. on Crops12(2): 568-573 (2011). Department of Agricultural Botany, Junagadh Agricultural University, Junagadh-362 001 (Gujarat), India Heterosis for fruit yield and its component traits over three environments was studied in okra through line x tester mating method involving 10 lines (females) and four testers (males), over better parent and standard check (GO-2). The magnitudes of heterosis varied from cross to cross over the environments for all the characters studied. The analysis of variance revealed that significant differences for all the characters among the parents and hybrids studied indicating an appreciable amount of heterosis were observed among the genotypes. Maximum heterosis over better parent of 66.87% was observed for number of branches per plant in the hybrid Pant Bhindi x HRB-55, whereas the highest standard heterosis was depicted by the hybrid JOL-06-S-5 x HRB-55 of 78.43% for fruit yield per plant. The pronounced heterotic effects were observed for fruit yield per plant and number of branches per plant, moderate for plant height, number of fruits per plant and number of nodes per plant, whereas low for fruit length, fruit girth, days to 50% flowering and internodal length. The three crosses viz., JOL-06-5 x HRB-55 (47.05 and 78.43%), JOL-06-3 x Pusa Sawani (37.89 and 36.08%) and GO-2 x Parbhani Kranti (24.34 and 63.04%) manifested significant and desirable heterobeltiosis and standard heterosis, respectively, for fruit yield per plant resulting from significant and positive heterosis by number of fruits per plant, which could be further exploited in okra breeding. 65. S. Anuja and L. Jayalakshmi [Effect of foliar application of organic nutrients and inorganic fertilizers on growth and yield of palak [Beta vulgaris (L.) var. bengalensis]]. Res. on Crops12(2): 574-577 (2011). Department of Horticulture, Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar-608 002 (T. N.), India The experiment was carried out at the Orchard Field Unit, Department of Horticulture, Faculty of Agriculture, Annamalai University during January-March, 2010. Foliar organic nutrients viz., panchagavya (3 and 4%), vermiwash (1 : 3 and 1 : 5 dilution ratio), humic acid (0.1 and 0.2%), water spray (control) and two levels of fertilizers (basal) 100% and 75% recommended dose of fertilizers were tried in this study. Application of panchagavya 4+100% NPK (T3) favourably increased the plant height, leaf area and total leaf yield in all the four clipping stages of palak. 66. SELIME ÖLMEZ BAYHAN* AND MEHMET RIFAT ULUSOY [Population development and parasitism rate of Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera : Braconidae) in Balcali (Adana), Turkey]. Res. on Crops12(2): 578-587 (2011). Department of Plant Protection, Dicle University, Diyarbakir, Turkey*(e-mail : solmez@dicle.edu.tr) In this study, the population development and parasitisim rate of Diaretiella rapae parasitising Brevicoryne brassicae was evaluated on cabbage (Yalova 1), cauliflower (Early Snawball), broccoli (Marathon) and radish (Antep radish) in the experimental fields without any pesticides application in the research field of the Plant Protection Department, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Cukurova, between 2001 and 2004 in Turkey. During the monitored, naturally occurring aphids and mummies were counted. The population of B. brassicae and its parasitoid generally increased in December to January and March to April. 67. SONER SOYLU* AND SIBEL DERVIS [Determination of prevalence and incidence of fungal disease agents of pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants growing in Amik plain of Turkey]. Res. on Crops12(2): 588-592 (2011). Department of Plant Protection,Mustafa Kemal University, Agriculture Faculty, 31034 Antakya, Hatay, Turkey *(e-mail : soylu@mku.edu.tr or ssoylu69@gmail.com) During spring 2008 growing season, quantitative disease surveys were conducted to identify the fungal disease agents causing root-foot rot and foliar diseases of pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants growing in different fields in Amik Plain of Hatay province of Turkey. Disease surveys were conducted at three major plant growing stages such as post-emergence (seedling stage), flowering and fruiting-harvesting stages. The disease survey was conducted in randomly selected pea fields in major pea-growing locations. The results of fungal isolations from diseased pea roots taken at regular intervals over the entire growth period have indicated that the most frequently encountered and widespread soil-borne fungal disease agents were Fusarium oxysporum, Rhizoctonia solani, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Thielaviopsis basicola and Pythium spp. causing foot, root and collar rots which were found at the seedling stages of pea plants growing especially in fields which have shallow groundwater problems. Observation in several pea fields showed that Ascochyta blight caused by Mycosphaerella pinodes, leaf and pod spot caused by Ascochyta pisi, and Alternaria leaf and stem spot caused by Alternaria alternata were the most frequently observed (55.0, 67.0 and 47.0% of the fields inspected, respectively) foliar fungal disease agents at both the flowering and fruiting stages. Phoma medicaginis var. pinodella was also observed and isolated from necrotic pods. Incidence and severity of the A. pisi were especially higher on local population of plant variety which produces small pods (spring type). Originates of pea cultivars seeds sown in the region were unknown by the local growers. Powdery mildew (Erysiphe pisi) and downy mildew (Peronospora viciae) were observed on local varieties with minor importance. 68. M. Mokarram, S. Askari Marnani, A. A. Moezi and S. Hamzeh* [Land suitability evaluation using ordered weight averaging with fuzzy quantifier in Shavoor plain, Iran]. Res. on Crops12(2): 593-599 (2011). Department of Irrigation and Drainage, Faculty of Water Science EngineeringShahid Chamran University of Ahvaz, Ahwaz, Postal Code 61357-43311, Iran*(e-mail : saeidhamzeh@gmail.com) Land suitability is a process of assessment of land performance when used for specified purposes. It provides information on the constraints and opportunities for the use of the land and therefore guides decisions on optimal utilization of land resources. The aim in integrating Multi-criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) with Geographical Information Systems (GIS) is to provide more flexible and more accurate decisions to the decision makers in order to evaluate the effective factors. This paper presents a ordered weighted averaging (OWA) approach for land suitability. OWA is a multi-criteria evaluation procedure (or combination operator). The nature of the OWA procedure depends on some parameters, which can be specified by means of fuzzy (linguistic) quantifiers. By changing the parameters, OWA can generate a wide range of decision strategies or scenarios. The quantifier-guided OWA procedure is illustrated using land-use suitability analysis in a region of Shavoor plain, Khuzestan province, Iran. This method showed fuzzy-quantifier-based OWA approach is capable of capturing qualitative information the decision maker or analyst may have regarding his/her perceived relationship between the different evaluation criteria. It is in this effort one can see the benefit of the fuzzy quantifier approach to GIS-based multi-criteria analysis. This is especially true in situations involving a large number of criterion maps. 69. MAHDI DELGHANDI*, MAJEED BEHZAD, SAEED BROOMANDNASAB AND MEHRI SAEEDINIA [Study on effects of temperature changes on emitters outflow of drip irrigation]. Res. on Crops12(2): 600-606 (2011). Department of Irrigation & Drainage, Shahid Chamran University, Ahwaz, Iran *(e-mail : delghandi@gmail.com) The uniformity of emitter flow rate depends on many factors such as water temperature. Temperature variations influence water properties, especially viscosity, which may make significant changes in emitter outflow. The laboratory studies and field surveys are expensive and time-consuming. Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a helpful tool to study flow behaviour in water channels. Thus, in present study the effect of temperature on the discharge of three samples of a kind of tape emitter were tested under six pressures of 2, 4, 6.1, 9.2, 12.25 and 16.33 mH2O and each pressure in six temperatures of 5, 15, 20, 25, 35, 45 and 55°C were simulated by CFD. Verification of results showed that results obtained from simulation were in good consistency with laboratory results. Also results indicated that emitter discharges were insensitive to temperature variations and the computational fluid dynamics can be a very appropriate tool to study the hydraulic performance of emitters in less time and at a lower cost. 70. Okan Esturk*, Mehmet Arslan, Yurtsever Soysal, Ilhan Uremis and Zehra Ayhan [Drying of sage (Salvia officinalis L.) inflorescences by intermittent and continuous microwave-convective air combination]. Res. on Crops12(2): 607-615 (2011). Department of Food Engineering, Mustafa Kemal University, Tayfur Sokmen Campus, Antakya, Hatay -31034, Turkey *(e-mail : okanesturk@gmail.com; oesturk@mku.edu.tr) The effect of microwave-convective air (M-CA) drying (continuous and intermittent) and convective air (CA) drying of sage (Salvia officinalis L.) inflorescences on drying kinetics and essential oil content was studied. For M-CA drying, four pulse ratio levels (PR1, PR2, PR3 and PR4) at 25°C drying air temperature were used. The average drying rates were 0.211, 0.105, 0.067 and 0.053 kg H2O/kg DM/min for PR1, PR2, PR3 and PR4, respectively. The experimental data were fitted to nine different moisture ratio (MR) models to describe the drying kinetics under various drying conditions. Page model was found satisfactory to describe the drying curves of sage inflorescences. The total quantity of essential oils of sage inflorescences decreased considerably during M-CA drying, whereas the loss of essential oils was limited during CA drying. Compared to shade drying, two essential oil components, sabinene and p-cymene, were lost during CA drying. On the other hand, in addition to these two, a-pinene, campene, b-pinene, limonene, g-terpinene, camphor, bornyl acetate, a-copaene, g-cadinene, d-cadinene and caryophyllene oxide were disappeared during M-CA drying. M-CA drying may not be proper technique for drying of sage inflorescences when essential oil content is important. 71. V. S. Mynavathi, N. K. Prabhakaran and C. Chinnusamy [Nutrient uptake by maize as influenced by the use of manually operated weeders]. Res. on Crops12(2): 616-617 (2011). Department of Agronomy, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore-641 003 (T. N.), India A field investigation was carried out at Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore during kharif season of 2006 to study the nutrient uptake by the use of manually operated weeders. Four manually operated weeders were tested and compared with manual and chemical weed control. The significantly higher yield was obtained with pre-emergence application of atrazine 0.5 kg/ha on 3 DAS followed by a hand weeding on 45 DAS and it was on par withhand weeding twice. Among the weeders tested, wheel hoe weeding twice recorded higher grain yield. Significantly higher nutrient uptake of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium was recorded with pre-emergence application of atrazine 0.5 kg/ha on 3 DAS followed by a hand weeding on 45 DAS. 72. DHANANJAYA SINGH*, P. C. RAM AND VISHNU DAYAL RAJPUT [Influence of pre-soaking of seeds with ascorbic acid and gibberellins on antioxidant enzymes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under salinity]. Res. on Crops12(2): 618-620 (2011). Department of Crop Physiology, N. D. University of Agricuture & Technology, Kumarganj, Faizabad-224 229 (U. P.), India*(e-mail : dsingh_06@yahoo.co.in) The effect of salinity on antioxidant metabolites and antioxidant enzymes activity was studied in two wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes HD 2285 (salt susceptible) and KRL 19 (salt tolerant) grown for 10 days under the influence of 10 dS/m salinity. Seeds were pre-soaked with 50 ppm ascorbic acid and 50 ppm gibberellic acid for 4 h followed by germination in 10 dS/m of sodium chloride. Contents of proline, ascorbic acid and activities of catalase and superoxide dismutase were examined in the seedlings at the end of experiment. Salinity increased the proline content, catalase and superoxide dismutase activity and decreased the ascorbic acid content. Deleterious effect of salinity was counteracted by ascorbic acid and gibberellic acid.
For full text, please contact to Editor-in-chief at :info@cropresearch.org
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
*(e-mail : rezadadnia@yahoo.com)Abstract
Abstract
*(e-mail : rfarhoudi@gmail.com)Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
*(e-mail : mdelfieh@scu.ac.ir)Abstract
*(e-mail : a_soleymani@khuisf.ac.ir)Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
*(e-mail : rezadadnia@yahoo.com)Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
*(e-mail : hzahedi2006@gmail.com)Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
*(e-adilakshmi87,@gmail.com)Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
*(e-mail : ramangami@gmail.com)Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract
Abstract



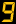
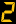
 Users Today : 17
Users Today : 17 Users Yesterday : 22
Users Yesterday : 22 Users Last 7 days : 191
Users Last 7 days : 191 Users Last 30 days : 191
Users Last 30 days : 191 Users This Month : 191
Users This Month : 191 Users This Year : 191
Users This Year : 191 Total Users : 192
Total Users : 192 Views Today : 23
Views Today : 23 Views Yesterday : 41
Views Yesterday : 41 Views Last 7 days : 454
Views Last 7 days : 454 Views Last 30 days : 454
Views Last 30 days : 454 Views This Month : 454
Views This Month : 454 Views This Year : 454
Views This Year : 454 Total views : 21800
Total views : 21800 Who's Online : 0
Who's Online : 0